The BJP-led NDA government introduced the Make in India Scheme during their first tenure that triggered exponential growth in the country’s economy. The scheme aims to foster skill development, attract FDI, build manufacturing infrastructure, and use ways to ensure 100% utilization of talents nationwide. Make in India put stress on 25 sectors which include aviation, automobiles, chemicals, etc. In this write-up, you will come across an extensive overview of this scheme, its benefits, downsides, and different sectors of Make in India.
What are the Objectives of Make in India Scheme?
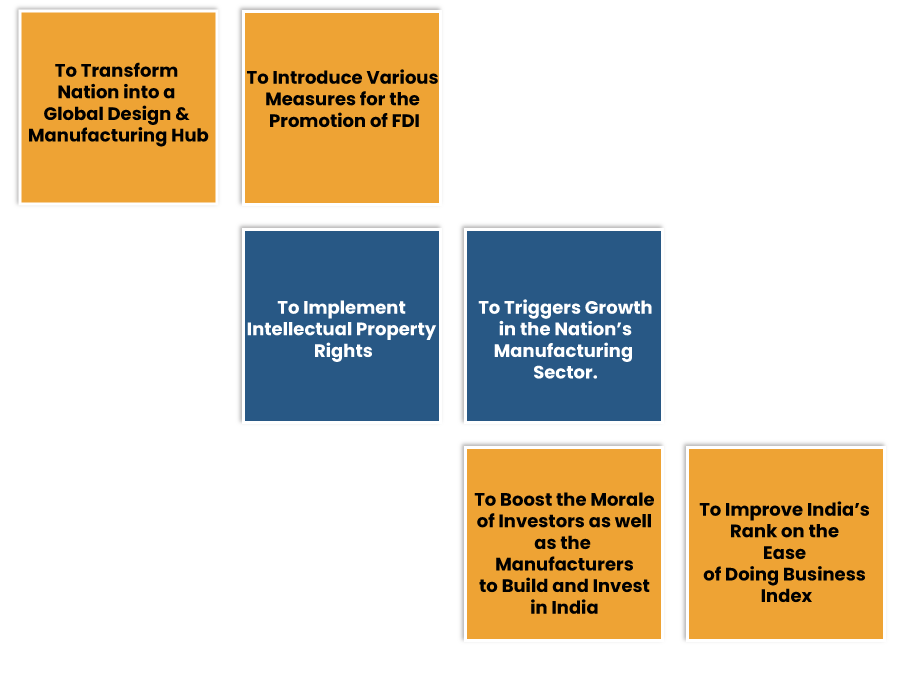

The ultimate objective of Make in India scheme is to stimulate the growth of the country’s manufacturing sector, create jobs, and simplify the ease of doing business. Make in India initiative regarded ‘ease of doing business as the most vital development component that fosters entrepreneurship.
Apart from this, numerous other factors influence the development of the manufacturing sector, such as infrastructure, the belief of people, & many more. Make in India scheme aims to alter the bonding between the Government & industries by incorporating a standard shift in how the Indian Government interacts with industries.
Advantageous Outcomes Expected from Different Sectors via Make in India Scheme
Presently, India has a large workforce to meet the requirement of overseas investors. A skilled workforce is readily available in India due to the presence of a high unemployment rate. All these factors have transformed India into the best outsourcing destination in the world. Countless measures focusing on the ease of doing business in our nation have been introduced under the Make in India program.
GOI has introduced several initiatives to simplify the licensing rules at the state level to align them with best practices that are pursued globally. This initiative of GOI fosters skill development, attracting investment, promoting innovations, and, most importantly, providing job opportunities to the nation’s unemployed youth.
Some of the Accomplishments under the Make in India scheme
There are primarily two sectors in which the Make in India scheme has been successfully propounded for, which are as follows:-
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
The Indian Government changed the Foreign Direct Investment policy in 2014 to stimulate growth in the FDI inflow. The Government raised the overseas investment limit from 26% to 49% in the insurance sector. After the launch of the Make in India scheme, the Indian Government ensured the liberalization of FDI in some vital sectors, including Pharmaceuticals, Telecommunications, Space, Agriculture, Pensions and Medical Devices, etc.
Ease of Doing Business
In the recent past, India secured a significant position in the World Bank’s annual report related to the Ease of Doing business, ‘Doing Business 2020’. The sharp rise in the ranking can be credited to reforms deployed in the different sectors of Make in India.
Read our article:What is the Procedure for Start-up Registration India?
Positive Execution in Different Sectors under Make in India Scheme
Soon after the launch the Make in India scheme, the below-mentioned sectors have reaped string of achievements cited below.
Basic Metals and Cement
- The growth of FDI in the mining sector is quite substantial. According to government data, FDI grew 4.43 times from $293 million (2011-14) to $1297 million (2014-18)
- Government-commissioned country’s largest blast furnace viz Kalyani blast furnace at SAIL, Burnpur.
- The Government has made efforts to rejuvenate the Rourkela steel plant as per the latest standard to improve the plant from 2 million tonnes/annum to 4.5 million tones/annum.
Aviation Sector
- FDI witnessed six times growth between the periods of 2011-17. In 2011, total FDI was accounted for $93 million; meanwhile, in 2017, this figure increased up to $ 519 million, exhibiting the six times growth.
- Passengers carried by local airlines raised by 29% from 148 million between 2012-14 to 191 million in (2014-16).
- Government renders green light to 6 Greenfield Airports.
- Around 160 airports are being scrutinized & operationalized.
- 16 Common User Domestic Cargo Terminals (CUDCT) have been brought to life.
- The Government introduced the GPS-Aided Geo Augmented Navigation system.
Tourism
- The tourism ministry introduced the Swadesh Darshan Scheme for integrated development of theme-oriented tourist circuits in the nation in 2014-15. The scheme objectively helps in positioning tourism as the primary source of employment and economic growth.
- Another scheme rolled out by the Ministry of Tourism is PRASAD. The ultimate goal of this scheme is to trigger the development of religious tourism.
Biotechnology
- Indian Government introduced the first Rotavirus vaccine named ‘Rotavac.’ The Government launched the virtual center across five IITs to ensure the development of advanced technologies in biofuels.
- Indian Government has decided to lay the foundation of Asia’s largest MedTech Zone (AMTZ) in Andhra Pradesh.
- This MedTech Zone will accommodate 200 independent manufacturing units.
MSME
The Indian Government rolled out a new scheme viz Prime minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP). The Government sanctioned INR 139.58 crore for the cluster to create jobs for artisans across 72 clusters. A new portal is known as Samadhaan’ was introduced to render information on the payment pending with Central Ministries.
Challenges of Make in India scheme
The bureaucratic mindset of the Indian Government has always created hassles for overseas investors to establish industries in India. Apart from this, other factors such as lack of proper infrastructure, corruption, compromised labor laws restrain investors from investing in the country. However, the existing Government[1] via the Make in India scheme is striving its best to mitigate these issues and develop the nation as an outsourcing destination.
Our country is yet to secure a good ranking in the ‘ease of doing business index’. And this situation is likely to remain stagnant in upcoming years if the Government doesn’t take the required measures to promote international funding.
Conclusion
Make in India initiative is all about the integrated development of the country where different sectors is anticipated to contribute significantly towards the country’s GDP. The scheme intends to build manufacturing infrastructure, improve skill development, and promote outsourcing capabilities.
With these objectives in hand, the Government is eyeing to attract investors worldwide and create job opportunities for the nation’s youth. There are 25 sectors of Make in India scheme that seeks promotion to address the demand of overseas investors. For the most part, it seems to be a groundbreaking initiative of the Government that has immense growth potential for the country. However, there is a need to amend labor laws, control corruption, and undermine bureaucracy from the nation to make India a viable alternative for foreign investment.
Read our article:Growth and Quality of FDI: Are all FDI Equal?











