Get Free Expert Consultation
1 Lakh+ Global Brands That Trust Us!











Talk to an Expert

Online
Expertise in Payments Banks License
(4.8)
Enquiry Form
Among Asia Top 100
Consulting Firm

Get Consultation
Lowest Fees
100,000 + Clients.

Overview of Payment Bank License
In the recent era, the concept of Payment Bank has received both remarkable and reachable hooks in its banking circle business. The term Payment Bank denotes a newly introduced RBI model, which had accelerated transactions, such as a regular bank, except for issuing credit cards and lending. However, to start an online Payment Bank in India, a company or an NBFC needs to acquire Payment Bank License from the RBI.
Further, the main reason due to which the concept of Payment Bank has got much significance is the said model has the capability to give extensions to the Government’s Financial Targets. Also, it shall be noted that the concept of Demonetization had completely recast the Indian Economic System. As a result, people now rely more on digital payment portals and paperless transactions, which has ultimately given a significant boost to the E-wallets or Mobile Wallets that were earlier outcasted.
Laws Governing RBI License for Payment Banks
To open a Payment Bank in India, it is mandatory for the applicant company to obtain a Payment Bank License from RBI. Also, it’s essential for payment banks to follow the laws governing RBI license for payment banks.
The concept of a specialised bank model was introduced by the Reserve Bank of India in the year 2013. The same was termed as Payments Bank. It shall be noted that similar to the services offered by other Banks, a Payment Bank provides a range of financial services, except for offering credit cards and facilitating loans.
Further, based on the provisions of section 22 of the Banking Regulations Act 1949, the Reserve Bank of Bank will issue the Payment Bank License to the applicant company. The said license allows the applicant to carry out banking activities. The term banking activities have the same meaning as specified under the provisions of section 5 (b) and 6 (1) (a) to (o) of the Banking Regulation Act.
Regulatory Structure of Payment Bank License
The regulatory structure of Payment Bank License are as follows:

Objectives of Payment Bank in India
The main objective behind the introduction of Payment Bank in India was to amplify the reach and ambit of the payment facilities to the small businesses and income groups. Further, the Reserve Bank of India, by way of the model of Payment Bank, wanted to increase the penetration of finances into the remote areas. The first-ever Payment Bank that got established in India is the Bharti Airtel.
Further, a comprehensive list of the Payment Banks that are operating in India are as follows:
Key Benefits of the Payment Bank License in India
The key benefits of the Payment Bank License in India are as follows:
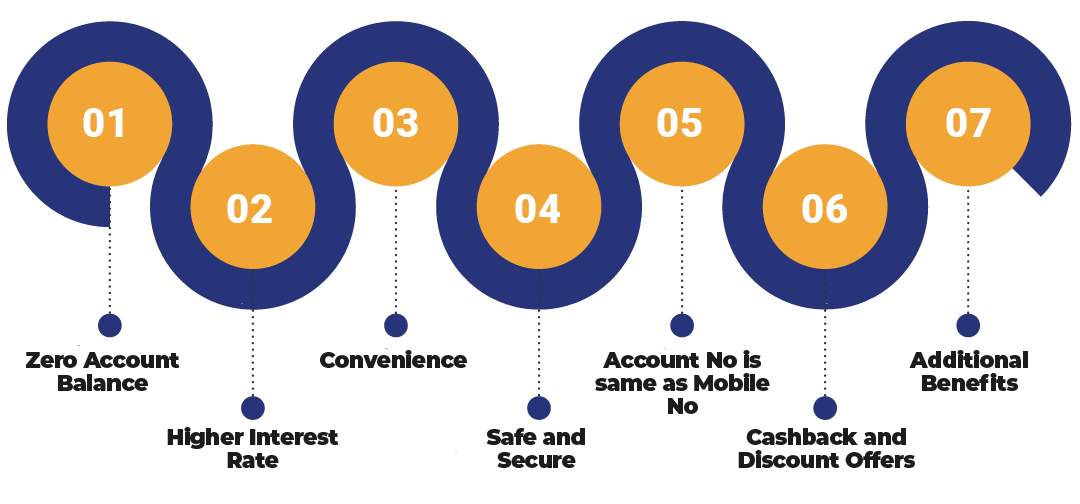
Zero Account Balance
One of the major benefits of a payment bank is that it is not mandatory and obligatory for the account holder to maintain a certain amount as the minimum required amount. That means one can have zero account balance as well.
Higher Interest Rate
The cost-saving benefit, due to operational efficiency, is further passed to the customer through higher interest.
Convenience
Another significant benefit of a Payment Bank is that due to its wide distribution network, the telecom services providers and mobile wallet are able to convert its retail outlets to separate banking points.
Safe and Secure
Due to 4 factor authentication, the concept of a payment bank is one of the secured models of online transaction introduced by the Reserve Bank of India.
Account No is same as Mobile No
Normally, this is not that significant feature, but it does increase the level of ease for the holders, who are an especially small business trader, merchants, etc., as there is no need for them to remember any other number as account number for carrying out transactions.
Cashback and Discount Offers
Similar to any other mobile wallet, a payment bank provides various discount and cashback offers to the holder.
Additional Benefits
A Payment Bank offers various benefits to its account holders other than the cashback and discount offers.
Book a Free Consultation
Get response within 1 hour
Characteristics of a Payment Bank License in India
The basic characteristics of a payment bank license in India are as follows-
Offers Deposit up to Rs 2 lakh
A payment bank with a payment bank license is eligible to accept deposits up to Rs 2 lakh. All the customers need to comply with the specified limit, and nobody is allowed to exceed the said limit at any point in time. Further, it shall be noted that an individual can opt to deposit an amount, either completely or partially.
The Reserve Bank of India has stated that the limit to protect and safeguard customer’s interest and in regards to the relatively new nature of such banks.
Facility of Virtual Debit Card
Another peculiar characteristic of the payment bank having a payment bank license is that it provides the facility of both physical and virtual debit cards. Further, the debit cards render an edge to the customers to utilise all ATMs (Automated Teller Machines) in both the domestic boundaries and abroad. The facility of virtual debit cards does not demand any kind of extra charges on cash withdrawals. Moreover, the physical debit cards are supplemented by an annual fee only.
Smooth Transactions through Online Portal
Unlike the old and traditional banks, the concept of payment banks streamlines the procedure of making and receiving money through digital platforms. Also, it duly facilitates online fund transfer services, such as NIFT, IMPS and many more to the customers.
Feasible Way of Making Payment
Irrespective of where one resides or situate, he/ she can easily have the access of services to payment banks, as the same runs digitally. A payment bank with a payment bank license eliminates the requirement of visiting a physical bank for the purpose of depositing or withdrawing cash.
Further, it shall be noted that anybody can start his/ her payments bank business online, that, too, without having any physical outlet. The only thing required is the Payment Bank License.
Who are all Qualified to Obtain Payment Bank License in India?
The ones who are qualified to obtain Payment Bank License in India are as follows:
Capital Requirements to Get Payment Bank License in India
Given below are the capital requirements to get payment bank license in India-
Details to be Furnished with RBI for Payment Bank License
The details to be furnished with the Reserve Bank of India for acquiring a payment bank license are mentioned below-
Details from Individual Partner to Get Payment Bank License
The details required from the Individual Partner to get a payment bank license are as follows:
Details from Entity Promoting the Bank
The details required from the Entity Promoting the Bank are as follows:
Common Details from Entities for Bank & Individual Partner
Activities Permitted by Obtaining Payment Bank License in India
The activities permitted by obtaining a payment bank license in India are as follows:
Process of Obtaining Payment Bank License
The steps involved in the process for obtaining Payment Bank License are as follows:
Timeline for Securing RBI License for Payment Banks
The time it takes to acquire a RBI license for payment banks in India is 25 to 30 working days. The timeline may get extended due to regulatory delay.
To avoid delay in the process of getting a payment bank license in India, speak to business consultants at Corpbiz.
Why Trust Corpbiz for Getting a Payment Bank License?
Getting a payment bank license can be a time-consuming and complex thing. Thus, getting expert suggestions from Corpbiz will help you secure the license without any hassle. Given below are the reasons why entrepreneurs trust us to obtain a payment bank license-
FAQs on RBI License for Payment Banks
Under section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, the Reserve Bank of India issues the Payment Bank License to the applicants.
According to the RBI guidelines, the minimum required paid-up equity capital for opening a payment bank and receiving a Payment Bank License is Rs. 100 Cr.
Existing PPI, Professionals/Individuals, NBFCs (Non-Banking Financial Company), Supermarket chains, Corporate Business Correspondents, Companies, Mobile Telephone Companies, Real-Estate sector Co-operatives, and Public Sector units can get the Payment Bank License.
There are many Documents and Information that need to be furnished for getting the Payment License Application. To know in detail, kindly refer to the above context for better understanding.
- Detailed Information about the persons/entities,
- A subscriber to 5 % or more of the paid-up equity capital (shareholding arrangement) of the proposed payment bank,
- Show foreign equity participation,
- Details of the sources of capital of the proposed investors and proposed bank
A project report must show the viability of the proposed and bank business potential, the business plan, any other financial services planned to be offered, etc. as per the RBI guidelines, and any other information that is reflected as relevant.
The Foreign Direct Investments policy for private banks must be the guiding policy for foreign shareholding.
Those are:- Reserve Bank of India, 1934; The Companies Act, 2013; Banking Regulation Act, 1949, Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, Payment and Settlement System Act, 2007; Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961, and Other Statutes and Directives, Prudential Regulations and other Guidelines issued by RBI that may apply from time to time.
No. NRIs are not permitted to make any deposit in the Payment Banks
Yes, a Payments Bank must embark on its own CFT (Combating Financial Terrorism) exercise and KYC (Know Your Customer)/AML (Anti Money Laundering) as any other bank.
Yes. Under the payment system approval by the Reserve Bank of India, a Payment Bank can operate as a channel of accepting 'remittances' from banks, such as RTGS/IMPS/NEFT.
Yes. A Payment Bank needs to agree to take RBI (Reserve Bank of India) Compliances on Web-Banking, Technology Risk Management, Cyber Laws, Data Security, and Electronic Banking.
The payment bank license application shall be addressed to the "Chief General Manager" of the Department of Banking Regulation, RBI.
An EAC (External Advisory Committee), consisting of distinguished professionals like Chartered Accountants, Finance Professionals, Bankers, etc. shall assess the applications. They may call for Information and have deliberations and negotiations with applicants as may be deemed fit by it.
All the applicants for the payments bank's license will be obligatory to furnish their project reports and business plans with their applications. The business plan for the application should address how the bank aims to achieve the purposes of setting up payment banks in India.
Yes. It is advisable that an attorney with "Banking experience" must be appointed to overwhelm many of the potential pitfalls that creep around within the Payment Bank License, and to understand the requirement in detail.
Yes. You should. The payment banks are predictable enough to be a game-changer and transform the current banking system. It will fetch the banking on a broader scale in India and delivers a hugely profitable business.
Authors
Written by Aarya Pokharel. Last updated on Nov 11 2025, 09:56 PM
Aarya Pokharel brings 3 years of solid experience in legal research and compliance. Her expertise spans tax filing, secretarial compliances, and advisory services, with a strong focus on delivering precise legal research and strategic advisory support.
Why Choose Corpbiz for Your Payments Banks License
We make technical compliance certifications effortless and convenient.

100,000+
Clients Worldwide

Top 3% of Industry
Professionals

100% Satisfaction
Guaranteed
Get started?
We also help you market your products through an online marketplace.

Fill up Application Form

Make Online Payment

Executive will Process Application

Get Confirmation Mail
Testimonials
Updated testimonials from our customers
Mr. Vinay Arora
MD, India
Really thankful to Corpbiz. Our experience with its expert was tremendous. Strong professional approach towards clients. My Company Registration was filed in a very less time, thanks to Corpbiz experts.
Ms Seema Singh
CFO - Online food Delivery App
We would recommend Corpbiz incorporation services to any founder without a second doubt. The process was beyond efficient and shows Corpbiz founder's commitment and vision to truly help entrepreneurs and early stage startups to get them incorporated with ease.
Priti Singh
MD, India
I was searching for a company for assistance in the incorporation services. Then one of my friend tell me about Corpbiz and definitely the Corpbiz team is really efficient and has an experienced staff to guide us through the entire process of Company Incorporation.
Lavanya Singh, Startup Founder, Greater Noida
Verified User
Setting up our Bio Medical Waste Recycling Plant was a huge project. Mukul managed the entire compliance framework seamlessly from start to finish.

