Overview on Payment Gateway License
As we are aware of the fact that the popularity of online shopping in India has increased immensely due to the benefits of ease and flexibility offered by this platform. The term Payment Gateway denotes a financial service that is provided by way of an e-commerce application service provider. However, to start a Payment Gateway service in India, one needs to obtain Payment Gateway License from the Reserve Bank of India.
Apart from shopping, this digital platform facilitates the payment of bills and recharges. Over the period of time, the same has taken an online route as well. Further, it shall be noted that whenever a person purchases one or the other thing online or even pay a bill, he/ she clicks on the option ‘Pay Now’, and is redirected to a new page. The page to which that person is redirected is known as the Payment Gateway Website, this is used for making the payment of goods and services purchased.
Concept of Payment Gateway
The term Payment Gateway means an intermediary, which works between the website that facilitates communication concerning transaction and the banks. That means it generates information from the respective buyer bank and supplies the same transaction information to the receiving bank, after that it notes the feedback as to whether the said transaction has been duly approved or declined.
License for Starting Payment Gateway Business in India
Based on the provisions of section 4 of the Payment and Settlement System Act 2007, no individual except the Reserve Bank of India can either operate or start a payment mechanism. Further, if an individual or a business entity want to commence the same, then, in that case, they need to file an application for authorization to the Apex Bank. The same must be based on the provisions of section 5 of the PSS Act 2007.
Laws Governing Payment Gateway License in India
The main reason behind the enactment of the Payment and Settlement System Act, 2007 (PSS Act) was to regulate and supervise the payments system and mechanisms operating in India by the Reserve Bank of India. The same shall be the primary regulatory authority for the purposes and all the incidental matters that fall under the ambit of this Act.
Further, there are two regulations that have been passed under this Act by the Reserve Bank of India, namely:
Board for Regulation & Supervision of Payment & Settlements System Regulations 2008
This particular regulation mainly deals with the constitution & composition of the Board for Regulation & Supervision of the Payment and Settlement System and a Committee of the RBI’s Central Board of Directors.
Payment & Settlements System Regulations 2008
The same deals with all the matters, such as the application for authorization of starting payment system, issuing such authorization, instructions concerning to payments, standards to be maintained in the payment system, timely submission of relevant Documents and financial information, etc.
Benefits of Obtaining Payment Gateway License
The benefits of obtaining Payment Gateway License are as follows:

PCI – DSS Wallet
The PCI – DSS Wallet compliance provides security to the users of the application by securing their personal data in the portal or gateway for recurring payments.
For example, an individual who is a regular customer on the Amazon Application can save his/ her bank account details on it or on its official website, and the gateway safeguards the same from every sort of cyber security threat.
White Label Wallet
It shall be noted that some of the payment gateways permit customers to make digital transactions from the mobile wallet applications. It is the latest trend, as it allows the users to carry all their operations and transactions from one place.
Further, one can easily transfer the amount from the bank account to his/ her mobile wallet application, and can then use the same for making payments on other mobile applications or websites.
Fraud Screening Tools
Some of the payment gateways gives their customer the benefit of FST (Fraud Screening Tools) for the purpose of reducing the risk of losing personal data.
The term Fraud Screening Tools comprises of the CCV (Card Code Value), AVS (Address Verification Service), and CVV (Card Verification Value).
Further, it shall be noted that the primary objective of these tools is to confirm that there is no fraudulent transaction going on.
Also, another significant benefit of a payment gateway is that it permits transactions and dealings from multiple users that, too at the same time. This itself makes the same feasible for a customer to buy or sell goods & services whenever he or she wants.
Book a Free Consultation
Get response within 24 hours
How Does a Payment Gateway Operate in India?
Once a customer has placed his/ her order from an online website, then, there are a series of operations that are carried out by the Payment Gateway which are explained as follows:

Encryption
In the first step, the browser used by the user encrypts the information that has to be sent to the respective vendor’s server. After that, the payment gateway then transmits the transaction data to the specified payment processor.
Request for Authorisation
Once the data is successfully received by the payment processor, it then transmits the same to the respective card association.
Further, the Bank that has issued the payment card checks the transaction at this point and then denies or agrees it, accordingly.
Filing of the Order
If the respective bank agrees to the transaction made, then, the authorization concerning to the customer and the merchant is further forwarded to the main processor of the Payment Gateway.
Once the response from the main processor is duly received, the same is further transmitted to the portal for the processing of the payment.
In this way the information and data is interpreted and the payment is made. The entire procedure of making payment takes around a time of a few seconds.
Additional Facilities Offered by Payment Gateways
Besides providing the facility of quick payments, the additional facilities offered by Payment Gateways are as follows:
Major Components of Payment Gateway
The major components of a Payment Gateway are as follows:
Merchant Agreement
The term Merchant Agreement denotes a contract between the business and the respective payment service provider. Further, each of the party that is engaged in the online transactions is directed by the prescribed roles, responsibilities and the rules that have been specified under this agreement, in relation to the acceptance of payment, authorisation, processing & settlement.
Secured Electronic Transaction
The Secured Electronic Transactions (SET) are provided by the main payment providers of the electronic transactions, such as Visa and MasterCard.
Further, the customers that are protected through SET, as the same allows the merchants to cross check the payment information, that, too, without actually seeing it. Also, the information and details mentioned on the card is straightaway received by the card issuer for the purpose of verification.
Basic Requirements of Payment Gateway License
The basic requirements of Payment Gateway License in India:
Capital Requirements of Payment Gateway License
The capital requirements of Payment Gateway License in India are as follows:
Documents Needed for Payment Gateway License in India
The Documents needed for obtaining Payment Gateway License in India are as follows:
Registration Procedure for Obtaining Payment Gateway License in India
The steps involved in the Registration Procedure for obtaining Payment Gateway License in India are as follows:
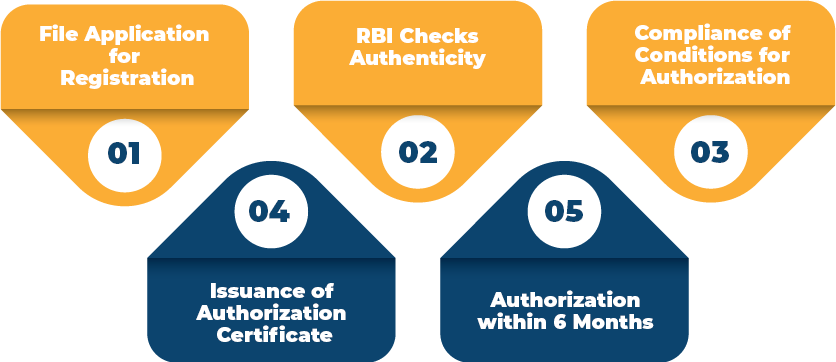
File Application for Registration
In the first step, the applicant needs to file an application for authorisation in the prescribed Form A. The same is done based on the provisions of section 5(1) of the PSS Act.
Further, the said application will be made to the “Chief General Manager” of the “Department of Payment & Settlement Systems” at the Central Offices of the Reserve Bank of India at Mumbai, or at other offices of the RBI, as may be prescribed by it from time to time.
RBI Checks Authenticity
Based on the provisions of section 6 of the Payment and Settlement System Act 2007, obtaining RBI’s approval for the issuance of the authorisation is discretionary.
Further, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has the authority to hold such type of inquiries as it may consider required for the purpose of satisfying itself regarding the authenticity of the details and information that have been furnished by the applicant and for verifying the credentials of the involved participants.
Compliance of Conditions for Authorization
The Reserve Bank of India will take the conditions as follows into the account prior to issuing the authorization:
a) The necessity for the proposal payment mechanism or the services that have been declared to be undertaken by it;
b) All the technical standards that have been decided for the payment mechanism or the structure of the decided payment system;
c) The terms and conditions, inclusive of the security procedure, for the operation of the proposed payment system;
d) The method in which the assignment is done in the provided payment system;
e) The manner or the way for getting of payment instructions that will affect the payment conditions under the payment system;
f) The overall management’s financial status, experience, and the integrity of the applicant;
g) The terms & conditions that govern and regulate the relationship of the customers with the respective payment providers;
h) The credit & monetary policies;
i) Time frame for authorization;
Issuance of Authorization Certificate
If the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is satisfied that all the requirements laid down in section 7(1) are duly fulfilled, it may issue the Authorization Certificate in Form ‘B’ for commencing and carrying on a payment system to the applicant. Further, the authorization will take effect from the date as mentioned by the RBI and as per the conditions that have been imposed by the RBI.
Authorization within 6 Months
Based on the provision of section 4 of the Payment and Settlement System Act 2007, the Reserve Bank of India is needed to process the application filed for authorization at the earliest, with a maximum time frame of six months, starting from the date on which the said application for the authorization has been filed.
IT Requirements for Obtaining Payment Gateway License in India
The different IT Requirements for obtaining Payment Gateway License in India are as follows:
Frequently Asked Questions
Payment Gateways are intermediary elements in between the banks and the websites promoting the delivery of Transaction reports.
The sensitive information needs to be protected from any fraud and misrepresentations such as Debit/Credit Card Numbers, internet banking ids, and passwords, etc. For this reason, governing security standards to be followed by anyone get access to card information such as payment gateways by the card associations along with various rules and regulations.
Any business can take the form of sole-proprietorship, partnership, or the structure of a company; however, the business of payment gateways is suited if formed as a private limited company in India.
Parties starting from Rs 30,000 (setup costs are very high), Like HDFC, ICICI, and Axis having low Transaction Discount Rate (TDR) with lower transaction fees.
Third-Party Providers such as EBS, CCAvenue, Payzippy, PayU, Direct Pay, which charges setup and annual fee; however, some even don’t charge that.
PCI DSS contained rules and regulations and has launched on September 7, 2006. It intends to optimize the security of credit, debit, and cash card transactions and protect cardholders from facing any scams.
SET allows merchants to verify their customers’ payment information protecting the customer without actually seeing it.
Merchant Agreement is a contract between the payment and business service provider.
A separate Website Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions Policy must also be completed to comply with IT regulations up for the company's lawyer's portal.
RBI may issue the Authorization Certificate in Form ‘B’ for commencing and carrying on a payment system to the applicant only if RBI is satisfied that all the requirements laid down in Section 7(1) gets fulfilled.


























