Overview of GST Advisory Services
On 1st July 2017, Government of India has introduced the concept of Goods and Services Tax (GST). It is implemented on all business activities performed in India. GST is the largest indirect tax reform in India since independence. GST is a PAN-India single unified tax imposed on Goods and as well as services, levied only on ‘value added’ to goods and services at each stage in the economic supply chain. GST has not only changed the tax pattern in India but is expected to impact hugely on each facet of business operations conducted in the country such as supply chain optimization, pricing of products and services, IT, accounting and tax compliance systems. GST will have its effect on tax structure, tax incidence, tax computation, tax payment, compliance, credit utilization, and reporting, moving towards a complete overhaul of the current indirect tax system.
Corpbiz has been intimately involved in providing GST Advisory Services. We work with business units and help them out in drafting policies that will have a positive impact on their operations. We provide a host of GST advisory services such as covering the impact of GST on the business of clients, examining different market scenarios of business models, legislative business level implementation assistance, transition management and undertaking key compliance.
Broad Impact Assessment
Benefits of GST Registration
Book a Free Consultation
Get response within 24 hours
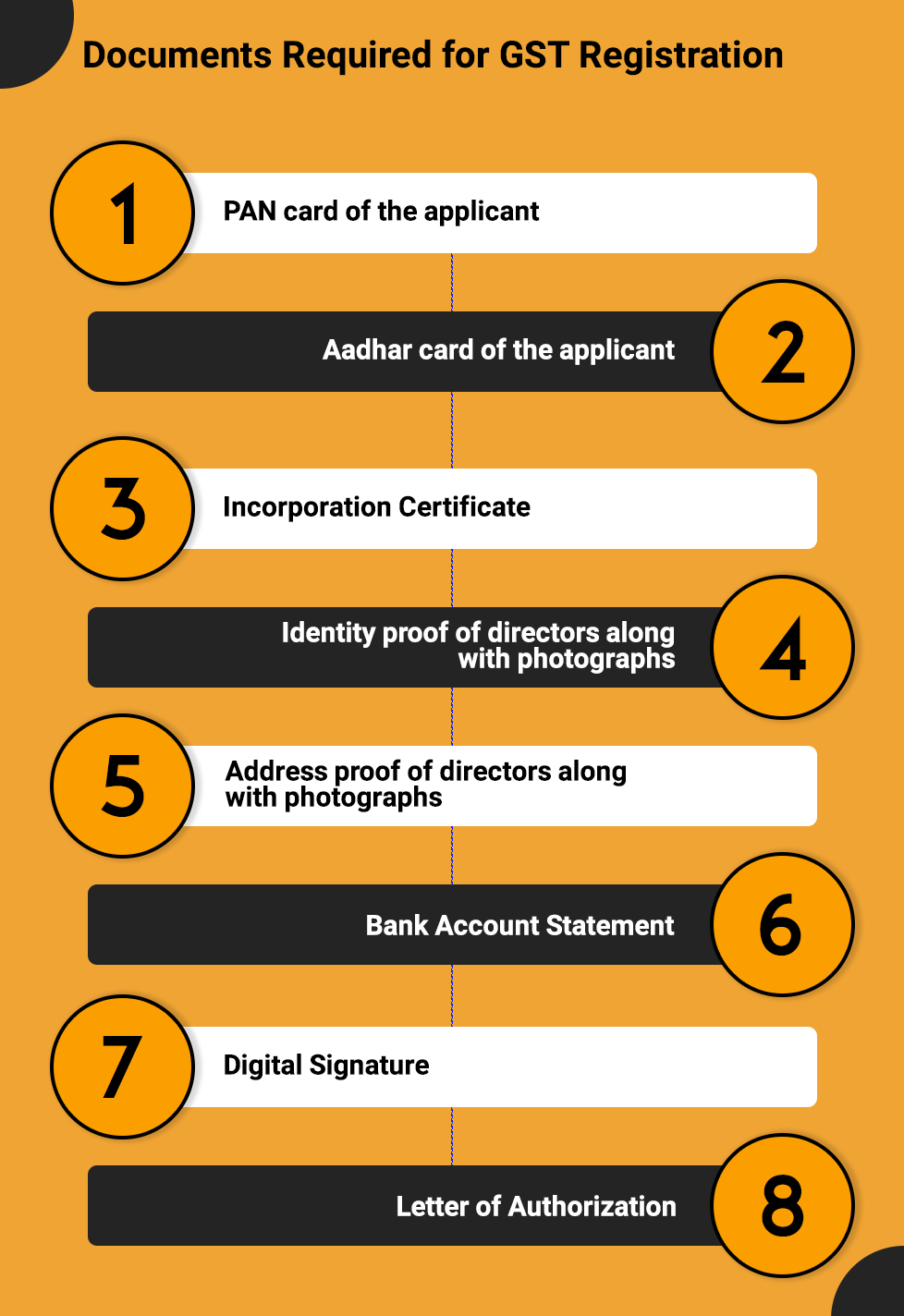
Eligibility for GST Registration
Section 22 to Section 30 of the CGST Act, 2017 deals with the process of registration by the every supplier of goods and services. Note on registration under GST with effect from 1st April 2019.
GST Rates
Rates under GST will depend upon the type of goods and services. Currently, the slab rates are 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. The rate for gold is 3% and 0.25% for rough stones.
GST Advisory Services- Our Role
Evaluating the fiscal impact of GST on business and product pricing, through evaluation of key parameters include:
Advise on realigning the operations to ensure tax efficiency:
Advise on implications under the anti-profiteering provisions under the GST laws:
Ensuring steps for smooth GST Transition:
IT Functional Advisory
Customised GST Trainings
Frequently Asked Questions
All businesses that successfully register under GST are assigned a unique Goods and Services Tax Identification Number also known as GSTIN.
If a business operates from more than one state, then a separate GST registration is required for each state. For instance, If a sweet vendor sells in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, he has to apply for separate GST registration in Karnataka and TN respectively. A business with multiple business verticals in a state may obtain a separate registration for each business vertical.
According to section 24 of the CGST Act, any person making interstate supplies must obtain registration irrespective of the Rs 20 lakh threshold limit for GST registration. If an unregistered person is willing to make an inter-state purchase, the seller must be registered under GST.
Yes, you can register two different businesses with different trade names under single GSTIN. You must remember to mention all the trade names while applying for the GST registration.
The three types of GST in India are; Central Goods and Service Tax (CGST), State Goods and Services Tax (SGST), Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST), and Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST).
Supplies that attract nil rate of tax (0% tax) are cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables, milk, natural honey, salt, and more. Along with this, petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas, and aviation turbine fuel are also exempted from GST.
As a sole proprietor, all incomes will be clubbed together for Income Tax purposes and for determining the turnover limits under GST. However, if two firms are operated under different trade names i.e. A Marbles and A General Stores, you would need to apply for separate GST numbers.
Businesses whose turnover is less than INR 1.5 Crore can opt for Composition Scheme. While there is an exemption for the North Eastern states. If their turnover exceeds INR 75 Lakh, then they can opt for Composition Scheme.
Composition Scheme is not applicable to following:
The legal name is a name that is registered at the time of incorporation of a company or business. The legal name is generally the name of the company on the PAN. On the other hand, the trade name is the name that is used in normal business practices or common parlance.
Petrol and diesel will not come under the purview of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in the immediate future as neither the Central government nor any of the states is in favour on fears of heavy revenue loss, a top source said today.
Exemption from registration has been provided to such suppliers who are making only those supplies on which recipient is liable to discharge GST under RCM.
Not liable to tax means supplies which is not leviable to tax under the CGST/SGST/IGST Act. Please refer to definition under Section 2(78) of the CGST Act.
There will be only one registration per State for all activities. But, you have the option to be registered as a separate business vertical.
A simple formula arises: GST Amount = (Original Cost*GST Rate Percentage) / 100. Net Price = Original Cost + GST Amount.
As the name itself says Maximum Retail Price (MRP) is the maximum price the seller can charge from the buyer. MRP is inclusive of all taxes including GST. It must be noted that retailers cannot charge GST over and above the MRP. GST is already included in the MRP printed on the product.


























