Gaining insights on the difference between VAT and GST would help the household consumers, and the businesses get familiar with the seamlessness that the GST tax regime offers. On July 1, 2017, the implementation of goods and service tax took place, and it came with a different philosophy, i.e., one nation, one tax.
Various forms of Central and State indirect taxes like service tax, VAT, and excise duty got levied on all the steps of product value addition, thereby creating a cascading effect. However, the advent of goods and service tax in the field of the taxation system has subsumed indirect taxes like service tax, VAT, octroi, and excise duty in India.
Goods and service tax have brought uniformity all over India through a single unified tax, making sure that the unrestricted flow of tax credit will prevail. The purpose of the introduction of the GST regime is the fact that it would bring down inflation in the economic system. Gear up to learn about the difference between VAT and GST, along with their implications.
Difference between VAT and GST
The difference between VAT and GST is stated in the points given below-
- The VAT gets charged at the sale point. On the other hand, GST gets levied at the goods and services supply point.
- VAT is a system that is a summary based, while GST is a tax system that is transaction-based.
- VAT is a direct tax levied on the value addition on manufacturing as well as production stages of goods and services, whereas GST is a singular tax levied on the sale along with the consumption of goods and services.
- In the VAT system, the responsibility of revenue collection lies in the hands of the seller, while in the case of the GST system, the responsibility of revenue collection lies in the hands of consumers.
- In the case of the VAT system, there is no applicability of Input Tax Credit. On the other side, there is the applicability of Input Tax Credit under GST.
Besides this, we are covering the difference between VAT and GST through example along with answer to the question that shows an edge of GST over VAT.
Example-Based Concept about the Difference between VAT and GST
Let’s suppose that a consultant extends different types of support to his customers.
Under VAT Regime
- The consultant charged a 15% professional tax on the service being provided of Rs 60,000. Thus, his output tax was 60,000*15%= Rs 9,000.
- After that, in case he went on purchasing supplies related to the office for 25,000 INR goes on paying 5% as VAT. The resultant figure was- 1250 INR (25000*5%)
- In this case, he had to make the payment of Rs. 9,000 output service tax. Furthermore, no deduction would get availed of 1250 INR paid on stationery.
- The total tax outflow for the consultant will be Rs. 10,250.
Under GST Regime
- The consultant charged an 18% professional tax on the service being rendered of Rs 60,000.
- Therefore, the output tax was 60,000 INR * 18%= Rs. 10,800.
- After that, in case he went on purchasing supplies related to the office for 25,000 INR goes on paying 5% as GST. The resultant figure was- 1250 INR (25000*5%)
- In this case, he had to make the payment of Rs. 9,550(Rs. 10800- Rs 1250). It has happened because, under GST, there is a provision regarding the deduction of tax paid on supplies from the output tax on services provided.
Read our article:Concept of Input Service Distributor under GST
What do you understand by Cascading Effect?
In simple words, a cascading tax is nothing but a tax on top of a tax. Cascading effect of tax gets produced where a tax gets charged on the tax levied on a product on all the steps of the sale. It has been considered as one of the key distortions in the taxation system of India[1]. The tax gets imposed on a value encompassing tax paid by the previous buyer. For this reason, it makes the end consumer go on paying tax on already paid tax. GST applied brake on the cascading tax effect and also restricted its compounding effect.
VAT and Its Drawbacks
VAT is an indirect value-added tax levied on various stages of production, as well as the distribution of goods. The introduction of value-added tax into the taxation system of India took place on 1 April 2005. It was the replacement of sales tax in the form of a taxation concept.
It came into existence with the mission to turn India into a single integrated market. After its implementation, it became a major revenue-generating source for all the States of India and UTs with two exceptions, i.e., Lakshadweep, and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands. VAT has got the recognition as a consumption tax since it is borne by the end consumer.
The main drawbacks associated with value-added tax are-
- Different VAT laws in all the states
- Cascading tax effect
- Claiming for Input Tax Credit on services under value-added tax was not a possibility
- The difference in VAT rates in different states made the taxation process complex
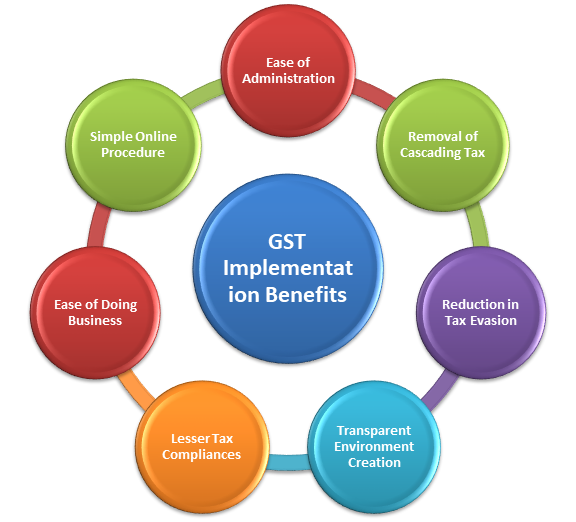
Benefits of GST Implementation
Goods and service tax has brought revolutionary changes in the tax system of India. It’s a unified, single, destination-based taxation system that is bringing unification in the whole nation in terms of ways through which collection to tax takes place in India. In the coming years, GST will stimulate the growth of the Indian economy. It has simplified the processes and measures concerning the indirect tax system. It’s not wrong to say that GST implementation is like a reform in the taxation process of India.
The benefits of GST implementation are-

Conclusion
An in-depth understanding of the difference between VAT and GST, along with the GST implementation benefits, is vital for businesses as well as consumers in India. The concept of GST is much beyond the confines of VAT as it comprises all the things which fell under the range of indirect taxes. It is serving a friendlier indirect tax regime in India. To gather additional information on the difference between VAT and GST or to get any help regarding GST registration, you can consult our experts at Corpbiz.
Read our article: AAR: Applicability of GST & its Registration for Charitable Medical Stores & Security Service













