A patent is a form of intellectual property that provides legal coverage to the owner’s invention against the act of violation. In view of the Indian Patents Act, a patent is issued on a product or process for a prescribed timeline of 20 years. Henceforth, the patent validity in our country is not more than 20 years from the date of filing.
Nature of Patent Registration and Expiration
Patent registration is non-renewal in nature and it expires as soon as the aforesaid timeline is crossed. Once the patent gets expired, the invention would no longer rejoice the legal protection against the act of duplication/violation. This means non-patented invention becomes accessible to public domains.
However, there is an exception; Under Section 53, rule 80 of the Indian Patents Act, the patent holders are liable to pay an annual fee as a part of renewal cost to safeguard the validity of the patent. By doing so, the patent will continue to serve its purpose till the date of expiration.
Is there is Any Scope to Extend the Patent Validity?
The concept of the extending of patent validity does not work in a real-world scenario expect in drug industries. The pharmaceutical companies leverage various strategies (official and non-official) to extend the patent validity for a particular drug. Since patenting is the only way to remain abreast of the competitors and reap consistent revenue, the drug industries utilize every possible strategy at their disposal to extend the patent validity.
Generalized Techniques that Drug Manufacturer Utilize to Safeguard or Extent the Patent Validity
Official methods are used by the drug industries for extending the term of a patent beyond 20 years.
Data Exclusivity
Exclusivity refers to a timeline when a branded drug/medicine is safeguarded from the genericDrug competition. Data Exclusivity(also known as the exclusivity of registration data) is a timeline of non-disclosure and non-reliance that is granted to the new drugs or the test data. It is for a specified period of time when the authorities do not permit the test date of the owner to be used to register the generic version.
Orphan Drug Exclusivity
Orphan drug exclusivity (ODE) granted to a drug that aims to treat diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 in the United States. The patent validity in this arrangement increased up to 7 years.
Pediatric Exclusivity
Under the Pediatric exclusivity, the authority grants an additional timeline of 6 years to a drug containing the active moiety, when a sponsor submitted pediatric studies on the active moiety against a written request from FDA.
New Chemical Exclusivity
New chemical Exclusivity provides a drug with an additional 5-year timeline that contains no active moiety approved by FDA section 505 (b).
Unofficial Method for the Extension of Patent Validity
Polymorphism
Polymorphism in a drug reflects its ability to posses’ more than two crystallization forms. Pharmaceutical companies leverage Polymorphism to increase the solubility of the drug. But it is also being used to change the crystallization forms of the drug without compromising the basic structure, so that drug companies can file an application for a new patent for the same.
OTC switching
OTC switching enables the drug producers to extend the lifecycle of an off-patent drug. Since OTC switching works on a concept of self-medication, it allows the drug producer to avail long-term sale even in the absence of patent registration.
Chiral switches
Chiral switche is the process of developing a drug on the basis of single enantiomers- a single molecular arrangement. Chiral switches impart distinctiveness in the drug, and it is prominently used by the drug industry to increase the patent validity.
Conversion to NDDS
Novel Drug Delivery System (NDDS) is an advanced drug delivery system that improves the therapeutic efficiency of the drug as well as its potent. Novel Drug Delivery System provides the infusion of the therapeutic element in the existing drug so that it can sustain longer in the market. The majority of the methods listed above talks about modification of drug which seems to impart countless benefits to the drug producers in United States.
What does Patent Protection Mean in General?
It protects an invention from legal disputes that might arise later on account of manufacturing, utilization, and trading of an invention without the consent of the patentee. As mentioned above, patent validity is still capped at 20 years in most of the countries including India.
A patent is Imperative- Get it As soon as Possible
The inventor must act swiftly in case of filing the patent application for their invention. It’s because once an invention is exposed to the public domain, it dissolves its right to avail the patent ever.
However, there is an availability of a grace period of 365 days after issue under certain scenarios listed under Chapter VI of the Act (Sec 29-34), Patents Act 1970. Delay in the patent application could be costly affairs for the inventor both in terms of time and money. What is the Procedure in India for Filing a Patent Application?
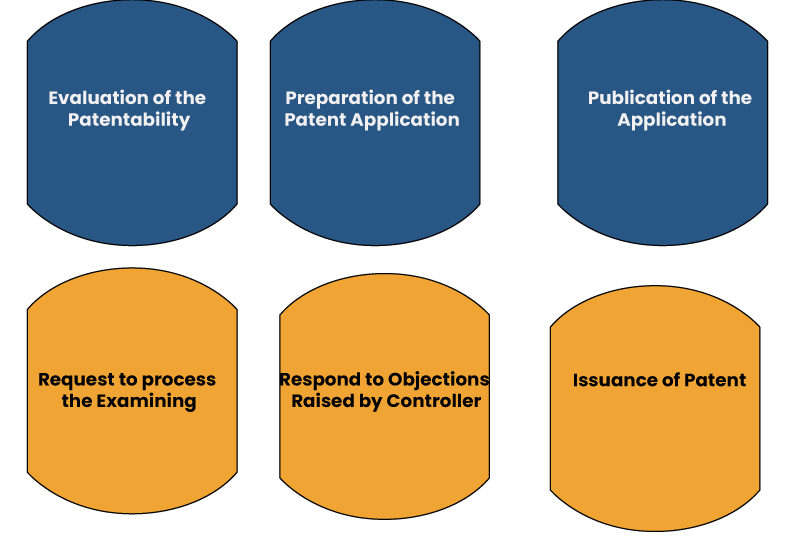

The patent validity commences with an application filed along with a provisional specification such as the title, description, & claims- that exhibits the notion of the invention. The patent registration procedure encloses the given instructions.
Evaluation of the Patentability
The first step is to determine whether the invention is patentable or not. Here, the prior art search would assist you to determine the patentability of the invention. You can reach out for free online patent databases to conduct a prior art search. You can avail of legal services from a professional firm to evaluate it better.
Under the influence of legal advice and report of databases, you would be able to determine whether to draft an application or not. There might be a possibility that someone else has already patented a similar invention that you were looking for. So, the report of databases could come handy when it comes to saving money and time.
The following list shows the patentability criteria for an invention:
- Novelty – It should be new and original.
- Inventive Step – It should have an inventive step with the ability to create new things.
- Industrial application – It should have the capability of Industrial application.
- Enabling – It should not come under the provisions of sections 3 and 4 of the Indian Patents Act 1970[1].
Preparation of the Patent Application
Make sure to enlist every possible detail about the invention without holding anything back. Here you need to enclose the details regarding the invention, mode of operation, functionality aspects, technical information, lab records, and claims. It would be conducive for those who have spent plenty of time during the research and development phase.
Drafting a patent application is tedious and a critical process. The filing date adheres to utmost importance in the patent market. You can get one additional year of the patent in case if the application is to the point.
If you are drafting the application by yourself, then you must have a good understanding of patent laws. In general, the public is not accustomed to the legal and applicable laws. So we recommend you to take the advice from a competent legal advisor like CorpBiz for preparing the patent application.
Publication of the Application
The patent application becomes publicly accessible after 18 months of first filing. However, if you do not wish to wait for long, you can request early publication after paying the prescribed fees. By doing so, you can expect the patent application to publish within a month.
Request to Process the Examining
The patent examiner from the patent office commences the process of examining the application as soon as he/she receives the request for the same. They will analyze the invention on the grounds of Patentability, Originality, Industrial application, Non-obviousness, and others.
There will be the first substantive examination report that is supposed to be submitted to the controller. The steps taken prior to the grant of patent are termed as “patent prosecution”.
Respond to Objections Raised by Controller
The majority of applicants encounter multiple objections raised by the controller from the patent office after a brief examination of the report. You must respond to these objections as soon as possible to overcome unnecessary delays.
However, during such a scenario, the applicant may encounter some technical issues that only an expert can resolve. Hence, it would be helpful to hire a professional service to serve such a purpose.
Issuance of Patent
If the invention effortlessly met the patentability requirements, the application will accept for the issuance of the patent. The grant of the patent would be notified in the Patent journal of the patent office to invite the objection raised by the public.
Such activity is known as ‘pre‐grant opposition’. In case the opposition succeeds in filing an objection, the patent may still be issued but with limited claims. On the contrary, if the patent bypasses all the objections with ease, the authority will grant the patent along with a certificate. Finally, the authority will publish the patent in the gazette of the patent office.
Conclusion
That’s how patents safeguard the businesses and enable them to remain abreast of the rest of the competitors. Hope, this article has rendered you sufficient information regarding the patent validity and other attributes. Make sure to take help from an expert of CorpBiz in case if you find it difficult to cope up with the requirements for obtaining the patent.
Read our article:A Note on the Patent Protection for Drug Industry in India











