The patentability of an idea is one of the controversial topics faced during the grant of patents. There is a slight difference between an idea and an invention because every invention is first an idea that later matures and then get idea patentable. It seems there is no substantial way to protect an idea under intellectual property rights.
Copyright protects the literary and artistic works, but not any innovations, however, a patent registration protects novel and unique inventions. Even though the idea patentable is the first step towards an invention and is of significant importance, there has been no monetary value attached to it, as per law.
What is Patent according to Law?
The patent is a kind of intellectual property that grants certain legal rights to the owner of such IP against unauthorized selling, using, making, or sharing any of his work or invention for a limited period of time.
A patent is a license granted to an inventor giving him exclusive rights over an invention, be it a process or product, for the certain period of time. Such the invention should be a new method of doing something or providing a solution to an already existing problem. The patent is granted for the period of 20 years, and after that, an invention is made available in the public domain.
Non- Disclosure Agreement for securing patent
Inventors prefer to have non-disclosure or confidential agreement in the initial stage of their invention development in order to protect their idea. However, such an agreement does not bind any other person or organization except the one signing the agreement. So, not being a party to an agreement or the third party if discloses or uses the idea cannot be sued upon by an inventor.
The idea patentable can be protected within the Patent laws, and the idea must not be ambiguous and vague. However, a mere idea cannot be protected, but when the idea is concrete with enough specificity. One has the strategy to describe it, and it’s functioning, making it an asset valuable enough to be protected, then that idea can be protected.
Types of Patent
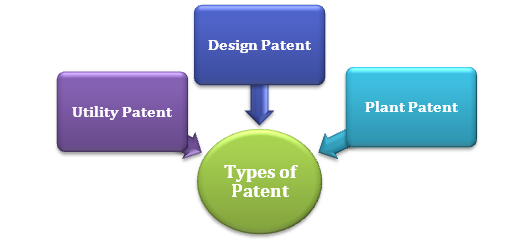

Utility Patent
It is the most common patent, and it covers all new inventions and significant modification and improved process or product, having some utility. A utility patent is referred to as ‘patent for an invention.’ The patent protects the inventor’s rights over his invention by preventing any third party from using, selling, or making the invention in question, without proper authorization.
Design Patent
An exclusive right providing legal protection to a useful product’s ornamental design is granted under the design patent. Design a printer, shape of spoons, etc. are some examples that can be granted design patents.
Plant Patent
This plant patent is the patent granted on plants. New plants produced through asexual modes of reproduction like cutting, vegetative propagation, etc. are eligible for granted plant patents. However, in India, plant patents are not granted.
Inventions that Cannot Be Patented in India
Even after fulfilling all the patent requirements, some inventions cannot be granted as a patent in India for some specific reasons. Under section 3 and section 4 of the Indian Patent Act, 1970, it is specifically mentioned that certain types of inventions have been excluded from being granted as a patent, irrespective of their fulfilling the requirement of patent conditions.
Some of such inventions are discussed below:


An Invention Contrary To Natural Law
The invention that violates the public’s morality at large and disturbs public order cannot be patented. For example, an invention that eases gambling, theft, cyber-crimes[1], or any criminal offense cannot be patented. The same as an invention used for commercial exploitation is excluded from being granted as a patent. Any invention that causes or is likely to harm humans, animals, plants, or the environment is not patented. Only those micro-organisms with genetic modification can be patented, specifically, do not fall under Section 3 (b) only can be granted patent.
Mere discovery
A mere discovery of a living creature or any non-living substance found in the natural environment or simply discovering a scientific principle must not be patented. The thing which has not been created or invented, but it has already been existed in the environment from immemorial, time. But the fact that such thing was found or recognised late, or use of such substance was earlier not known, does not provide a ground to call it an invention and the same cannot be patented.
Discovery of the New Property of a known substance
A patent is granted on a new invention and not on an already existing creation. A mere finding of a new feature of an already existing creation does not amount to it qualifying for a patent. This is because the creation already existed, of which a new feature was discovered. Hence, nothing new has been said to be created or invented. Similarly, various forms of a known substance cannot be granted as a patent. However, it is merely a discovery result in information on new products or includes at least one new reactant.
Arrangement or Re-Arrangement of a Known Substance
If two substances or devices or techniques are known and work independently as separate units when arranged or rearranged for the functioning, such an arrangement must not be patented.
For example, a torch, in a case attached on a mug or television, must not be patented. However, if an arrangement in question results in completely different use of the combined product, it is eligible for the patent Registration.
Agriculture and horticulture
The technique for cultivation and agriculture cannot be patented. For instance, a new type of soil, or a new technique to cultivate any crops or any food grains cannot be granted a patent.
Medical processes
The medical, curative, surgical, or therapeutic process or treatment of humans or a similar process or treatment for animals, which has been made to cure them or prevent them from disease or to increase their economic value, must not be patented. It is noted that processes, in this case, are not considered an invention and are not entitled to be patented. For instance, the process of heart surgery or kidney transplant is not patentable.
Plants and animals
Apart from micro-organisms, the other species, seeds, and essential sexual and asexual modes and reproduction and propagation methods are must not be patentable.
Mathematical Methods and Computer Programs
Any mathematical process, algorithms, a business method or a computer program, cannot be patented. A computer program can be given copyright as a ‘literary or artistic work, but the same cannot be patented.
Literary and Artistic Work
The types of literary, musical, artistic, or other aesthetic creation, including cinematography and television production, comes within the ambit of the Copyrights Act and get excluded from the scope of being patented. Method of solving a puzzle and, likewise, a process or rule of playing a game or a mental act cannot be patented.
Topography & traditional knowledge
Presentations, be it audio or visual, must not be patented. The topography of any circuit must not be granted as patent. Any traditional knowledge or accrual of traditionally known components is also not patentable unless it is modified to become the new process or product that is unique and non-obvious.
Invention out of Atomic Energy
The Section 4 of the Patent Act specifically excludes all the inventions coming within the meaning of Section 20 (1) of Atomic Energy Act, 1962. If the atomic activities are allowed to be patented then it can be misused and the same can affect the public’s safety or people at large.
Characteristics of Patentable Inventions
Successfully filing a patent requires meeting a handful of eligibility standards, including:
When an invention is useful
This means that an idea attempting to patent has to have some use. Further, this means it has a practical application or a specific process of fixing, creating, or using something. The best way is to pass the usefulness test is to explain what your created item can do.
When an invention is explainable
A heavy component of a patent application process shows what a product does, how it was created and how it works. Many patent applications also required diagrams and schematics to help the further show and explain your patent. If it cannot fully explain how an invention works or should be used, then it takes time to do additional research to meet the requirement.
An invention has to be Legal
Any product that is a design and attempts to have patented must be for legally backed up. The inventions that break laws or support illegal activity cannot be patented. Also, attempting to patent an item that breaks the law might not be wise.
An invention has to be significantly different from previous versions
In many cases, people are granted patents for items that already exist, with the caveat that they have significant changes. In the Patent and Trademark Office’s eyes, these improvements essentially create a new product to increase the use of a current item, and solve a problem that an already existing product has or creates.
Can an idea be patented?
Section 10 of the Patent Act provides some essential specifications that must be provided in the patent application. One such specification is the ‘preamble’. In the case of a provisional application, the preamble starts with “the following specification describes the invention”. The preamble of a complete application reads as “the following specification particularly describes the invention and how it is to be performed”.
It is said that for an invention to be patented, it is essential that it has its practicability. Considering the same, if an idea patentable has the potential to be performed and one has the method and process for its working, then the idea has the possibility of changing into an invention and hence can be applied for a patent through a provisional application.
Interpretation and Explanation of Provisional Application
For the reason of mandated disclosure of best mode of performance of invention to be mentioned in complete application, the idea patentable can be described and filed for a patent through provisional application. Subsequently, one can work a way out with the technique for its performance, within 12 months of filing a provisional application and then a complete application can be filed.
However, it is noted that the provisional application may be rejected and be held invalid on the grounds of an insufficient description of the invention or the method on the failure of filing a complete application within the stipulated period.
For instance, a person has an idea of making a mobile application cyber threat warning system and has the ability to convert the thought into an invention. In such a situation, the person may file a provisional application for a grant of a patent by describing his idea of the application. Later, within a period of 12 months, they may file a complete application, describing the mode and process of performance of such invention. Failure of the submission of complete application can amount to invalidation of the application.
Conclusion
With reference to the above discussion, it can be said that an idea can be patented if it can later be transformed into an invention. An inventor can initially file for a patent for his idea, but he must analyze his idea of whether it can be performed or not. If an idea lacks the capacity of performance, the application will be rejected, and the patent cannot be granted.
Hence, for the idea to be filed in the patent application, it is essential that the idea patentable must not be vague but substantive enough to become an asset later. It is provided the mode of performance of the invention is available and possible. CorpBiz professionals shall be happy to secure your Ideas and thoughts along with any legal backups required.
Read our article:Patent Filing Fees for Small Entities in India











