The provision related to Income Tax Audit is under section 44AB in the Income Tax Act 1961. Auditing is the inspection of various books of accounts by an auditor and there are different kinds of laws in India that govern different types of audits like cost audit, statutory audit and stock audit.
The principal purpose of the audits is to make sure that the books of accounts are error free as according to mentioned in the concerned law. In the same way, Income Tax Act has income tax audit under section 44AB.
The name itself suggests that income tax audit is an inspection of books of account of any profession or business with a view point to check the tax compliance. Income Tax Audit comprises of the evaluation of income tax returns, the deductions claimed and the income earned, also such other provisions of the Income Tax Act.
What is the Meaning & Purpose of Income Tax Audit under Section 44AB?
The Chartered Accountant must report the audited accounts in the prescribed forms. The audit report must include all the findings and observations etc. The report of audit conducted under Section 44AB must be in reported in Form No. 3CB and the details of the audit should be reported in Form 3CD. Consequently, the provision under section 44AB provides for the class of taxpayers who are mandated to get their accounts audited by a chartered accountant. The main purpose of Income Tax Audit is:-
- To do inspection or examination of accounts
- To ensure compliance with the Income Tax Act and any other related laws, and
- To have a check on the fraudulent practices under Section 44AB.
Read our article:Income Tax Return Filing without Form 16
Applicability of Income Tax Audit
Under section 44AB following business persons or professions needs to get their accounts audited:-
- Any business person whose gross sales, receipts or turnover is more than Rs. 1 crore for the previous financial year.
- Any professional whose gross receipts are more than Rs. 50 lakh for the previous financial year
- Persons who are mentioning their lower profits from business than what is estimated are covered under Sections 44AD, 44AE, 44AF, 44BB and 44BBB,
Audit of Income Tax audit serves the purpose of reviewing of the transactions that are related to income, deductions, costs, and taxes of the business. It makes easier for the taxation process while filing income tax return. After the chartered accountant is done with the auditing of income tax, he is obliged to report it in a prescribed format to the income tax department.
What are the Objectives of Income Tax Audit?
The principal objective of an income tax audit is to make sure that the taxpayer is bound to the income tax provisions and rules in the financial year. The objectives of the income tax audit are given below:-
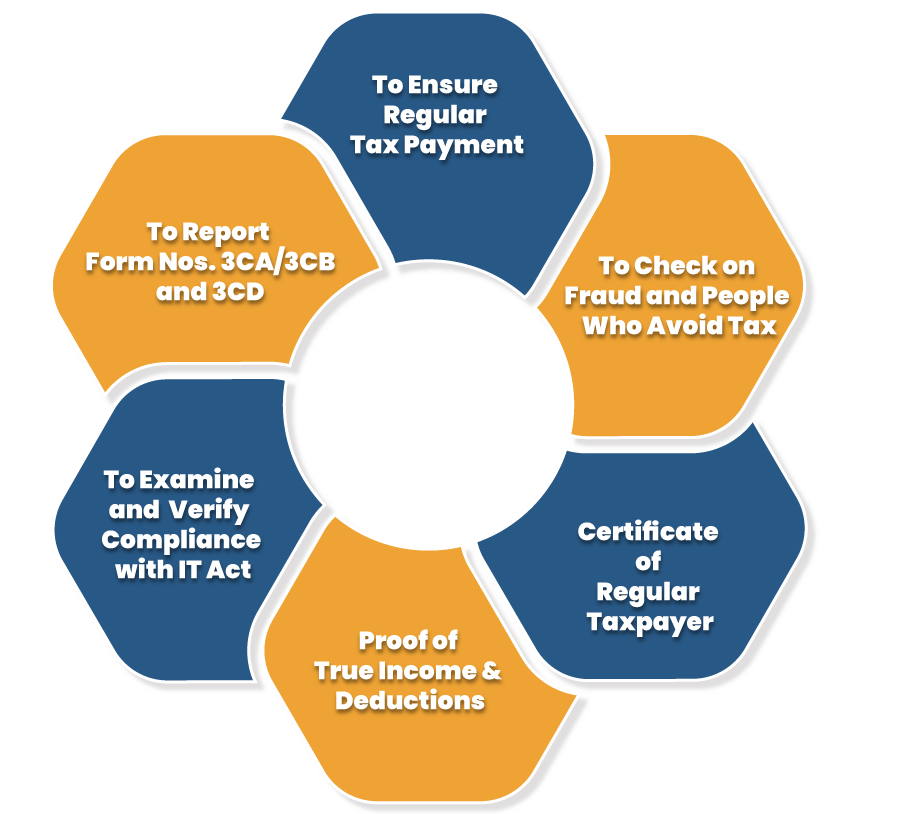

- To determine and report the required conditions of Form Nos. 3CA/3CB and 3CD.
- To ensure that the books of accounts and other records are properly mentioned it is necessary to have a proper audit for tax purposes.
- The main objective is also to have a check on the fraud and the unprofessional conduct by the taxpayer while filing income tax returns or who avoids filing of the income tax.
- It acts as a certification by an auditor for the books of income tax accounts.
- Verify the business person as a tax complier and show appropriate account maintenance and accurate books of accounts
- The books of account accurately reveal the true income of the taxpayer and the claims for deduction that are rightly made by him.
- The tax auditor has to prepare a report on the observations and the discrepancies while auditing and examining the books of accounts to the department of income tax.
- It is necessary of the auditor to report the essential details such as depreciation, deductions, loans and advances and tax compliance according to the requirements of the income tax act. The reporting by the auditor helps the income tax department in two ways:-
- It facilitates to the tax authorities that the tax laws have been properly administered by submitting the proper presentation of accounts.
- Reporting ensures the calculation and confirmation of the total income, expenses, deduction claims, and other tax related information.
- Income tax audit saves the Assessing Officer’s time in processing routine verifications, which includes examining the correctness of totals and confirming whether or not the purchases and sales are properly corroborated.
What Forms are Required to be submitted Under Section 44AB?
There are few forms under Section 44AB, which are compulsory to be used by the individual or person when an auditing is conducted on their accounts. These forms are explicitly mentioned in the Income Tax Act – Rule 6G with reference to income tax audit done in accordance with per Section 44AB.
- In case of an individual doing a business or is in any profession, whose accounts are to be considered for income tax audit in accordance with the provisions given under any kind of law, then the mentioned below forms are required to be used:-
- Form Number 3CA – shall be the Audit Form
- Form Number 3CD – shall be the Statement showing relevant particular
- In case of an individual whose accounts are not necessary to be audited as income tax audit in accordance with the provisions under any kind of law, but considering the exceptional income tax laws, then the below mentioned forms are required to be used :-
- Form Number 3CB – shall be the Audit Form
- Form Number 3CD – shall be the Statement showing relevant particular
What are the Penalty Applicable on Non-Compliance of Income Tax Audit u/s 44AB
If a person or individuals who are obligated under Section 44AB to comply with the requirement of income tax audit of his accounts but fails to do so then they will be liable to pay a penalty and the Assessing Officer shall charge them with:-
- 0.5% of the total sales or turnover amount that they have earned in such business or profession during the relevant financial year.
- Though, this penalty amount cannot exceed more than Rs 1.5 lakhs.
Conclusion
The income tax audit is done only on profession or business account and not on individual income. Thus, auditing of accounts is a finest practice to ensure that there is no tax fraud or evasion and the taxpayers[1] are complying with the income tax laws are.
Therefore, it is the responsibility of the chartered accountant, who is conducting the audits to assure that the taxpayers accounts are in order with the laws and also to make accurate assessments and report to the Income Tax Department.
Read our article:Extension on Tax Audit Report due Dates and Income Tax Returns Applicable for AY 2020-21











