Freezing of assets of a company on inquiry and investigation defined under Section 221 and 222 of the Indian Companies Act 2013. Mismanagement and scam are quite common in companies. Picking these loopholes isn’t easy for the authority. Thanks to sections 222 and 221, which has been proved quite effective in averting these anomalies. This blog will draw your attention to freezing of assets of a company on inquiry and investigation.
Important Provisions on Freezing of the company’s assets on investigation & inquiry
Section 221 of Indian Companies Act 2013[1] “Freezing of a company’s assets on inquiry and investigation.”
“(1) Whenever the Tribunal gets the implication via a recommendation made by Central Government or in connection with any investigation of a company as per this chapter or any complaint lodged by members as per sub-section (1) of section 244 or a creditor having an outstanding amount of one lakh rupees against the company or a person who strongly believe, that removal or transfer of assets, funds, properties of the company is probably going to be exposed to unethical and illegals business practice which might disrupt shareholder’s interest, it may by order direct that such actions shall not be practiced during such timespan.”
Penalty provisions under Section 221 of Companies Act 2013
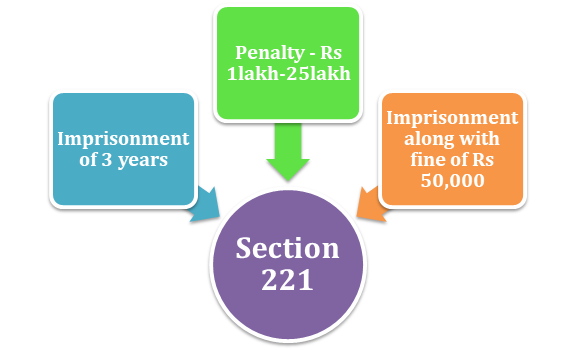

(2) Whenever the company found guilty of violating the Tribunal’s order under sub-section (1), w.r.t transfer, removal, or disposal of assets, funds, or properties of the company, shall be imposed with a fine of Rs one lakh, which could be extended to twenty-five lakh rupees. The involved officials in such a case will subject to imprisonment of 3 years along with a fine of Rs 50,000. Keep in mind this fine can be raised to 5 Lakh, depending on the intensity of the violation.
Read our article:Demand for Poll under Companies Act 2013: An Overall Regime
Section 222 of Companies Act 2013: “Imposition of restrictions upon securities.”
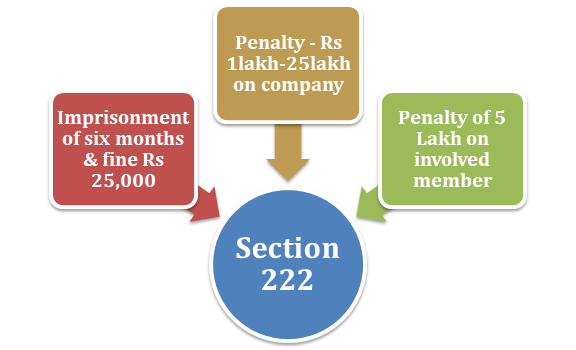

(1) Whenever the Tribunal gets the implication, w.r.t investigation under section 216 or a complaint lodged by a person in this regard that also supports detailed investigation of facts regarding securities issued or to be issued by a company and Tribunal isn’t considering such matter unless certain restrictions are kept in place. Tribunal may intervene in such matters and impose a restriction on the securities not more than three years.
Whenever the company’s securities obtained after the due process of Company registration are being transferred or issued by violating the order of the Tribunal under sub-section (1), the fine of Rs 1 lakh will be imposed on the company that could be further increased to 25 lakh rupees. In addition to that, the involved member in such matters may confront the imprisonment of six months along with a fine Rs 25,000, which is expandable up to five lakh rupees.
Case study on freezing of assets & Section 222
Punjab National Bank Scam
A few years back, jewelers Nirav Modi and Mehul Choksi have allegedly defrauded Punjab National Bank with Rs 14000 crores. To this day, the bank is still in the hunt for their lost money. However, a proper law protocol was followed by the authority to recover the entire amount.
Rational of the Case
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) issued an immediate order to restrain both the culprits from selling their assets so that the proper recovery can be made. The corporate affairs ministry filed the petition against the culprits based on section 221 of Company Act 2013. The ministry also took advantage of section 222, which relates to the imposition of security restrictions to support the case.
This is a perfect example of how exactly section 221 works in real-life scenarios. It is a transition of authority from Tribunal to legal bodies to take relevant action against the companies involved in mismanagement and scams.
Role of investigation officers in regards to inquiry and investigation
- Intervene in company affairs and scrutinize relevant documents and data.
- Conduct interviews, if necessary.
- Offices can ask for government assistance on some matters.
- Investigate evidence to any limit.
- Freeze the asset and restrict securities.
Key points to remember on inquiry and investigation
- Section 221 under Company Act 2013 advocates the freezing of the company’s assets on inquiry and investigation.
- Meanwhile, Section 222 of Company Act 2013 is related to the imposition of security restrictions.
- Section 221 holds the provision of imprisonment of 3 years for the accused, along with a penalty of Rs 50,000 that may escalate to 5 lakh.
- Section 222, on the other hand, imposed imprisonment of 6 months on the accused in addition to a penalty of Rs 25,000, which is expandable up to five lakh rupees.
Conclusion
Section 221 and 222 offer great value to the legal framework to counteract mismanagement, and scam. Freezing of assets allows the authority to overcome loss occurred due to scamming activities. The provisions under these sections can force the entrepreneur to conduct their business legally and avert unethical practices.
Read our article:Why Minutes Of Meeting Crucial For The Organisation’s Success?











