FSSAI set food packaging and labeling regulations, ensuring that manufacturers, investors, traders, and consumers will be able to keep their mind out of the three-ring circus. Nowadays, all food products carry numerous specific labeling on their packaging. Getting abide by the FSSAI Food packaging and labeling regulations is of vital importance.
Food labeling is one of the crucial features in the territory of food and beverage packaging. Food labeling covers the various aspects concerning the product as well as producer. Furthermore, it is a way through which health of consumer get protected in terms of nutrition and food safety. It depicts basic information about the product, usually appearing on the packaging. Apart from providing a description of the product along with its usage, a label also instructs about the precautions that must be kept in mind. Consumers would come to know about the product properties by looking at the label carefully.
Food packaging is the circumscribing of food in the process of affording protection to food in the course of the sale, storage, and distribution. It has brought ease in the process of package evaluation. Product packaging design seeks the attention of customers by its spellbinding looks and helps the product dominate others in the market. Food labeling and food packaging help the consumers in differentiating between various foods and finding out the best products matching their requirements. A well-defined label on the product leaves a lasting impression in the minds of consumers.
Applicability of Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations
There are certain food packaging and labeling regulations that food business operators need to follow. There is a significant demand for getting FSSAI license or registration in India in order to conduct a food business in India. The food business owners should act in accordance with FSSAI guidelines related to food packaging as well as labeling. Given below are the other laws and regulations that food businesses should follow for labeling and packaging of food.
Those are as follows:-
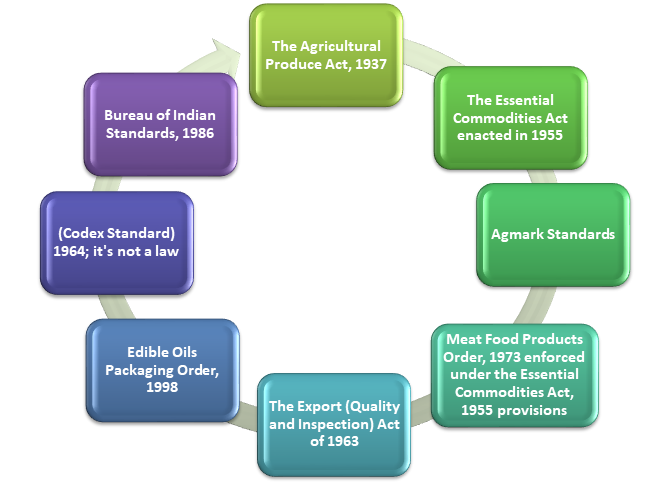

Usually, the Indian regulatory system belongs to the compulsory regulation category imposed by several ministries along with the voluntary standards set by many organizations in order to serve the nation.
In the past, consumers were unsure about the weight and the quantity of food product for which they were making the payment. Therefore, the concerned authority came up with the required measures to eradicate this whole problem. Here, we are going to discuss one of the measures, i.e., Standards of Weights and Measures Act of 1977, written in short as SWMA.
Standards of Weight Measures Act, 1976 & Standards of Weights and Measures Act, 1977
The points that have received attention under SWMA are as follows:-
Standard Packages
As per the Act, One of the laws concerning the requirements is that selling and packing of certain commodities must be in the standard packages.
Section 4 of Standard Units
According to the Standard Units- Section 4(Chapter 1), all the units must follow the metric system. The Units that require to get adopted needs to be of the International System of Units ratified by the General Conference of Weights and Measures.
Maximum Allowed Errors
SWMA rules state that the maximum permissible errors in connection with the quantity contained in individual packages must follow the same line as defined beneath the First Schedule of SWMA Rules. According to the Fifth Schedule of the SWMA Rules, the maximum allowed errors for commodities to get sold by number, measure or weight must follow this Fifth Schedule.
Declaration for Commodities in Packaged Form
Section 39(Chapter 4) presents a description that for interstate trade/commerce of commodities in the form of packaging, with the distributing or selling objectives, all goods in packaging form has to be relevant to it along with a label attached to it. In addition to this, the requirement for the label is that it should be understandable as well as specific and must contain a declaration of commodity identity within the package, package sale price, etc.
Label Declarations
According to the SWMA rules, the declaration on all the retail packages must hold the required details about which you would get to know in one of the upcoming heads of the blog.
Read our article:Stepwise Guide to Start a Healthy Snacks Business in India
Key Terms under the Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations
Date of Manufacture
The date on which food turns into a product is the date of manufacture.
Date of Packaging
The date on which the food gets placed in the package or container in which it would reach the hands of the customers is the date of packaging.
Non-Vegetarian Food
Food which encompasses complete or part of any animal including marine animals or bird or eggs of any animal origin without including milk products or milk as a constituent is a Non-Vegetarian Food.
Pre-Packed Food
Food placed in a package of all kinds, in such a way that bringing changes in the content or playing with its quality is not possible without tampering and which is ready to reach the consumers’ hand is the pre-packed or prepackaged food.
Best before Date
The date that guarantees effective of the product meets the safety requirements along with quality maintenance of food, and also the food must be surely marketable and must retain qualities for which making claims can be possible and although the quality would have got deteriorated, still fit for human consumption is the Food Best Before Date.
Infant
A child below 12 months of age is an infant.
Multipiece Package
A package having two or more than two individual packaged or labeled pieces of a similar product belonging to the same quantity used for the purpose of retail either in containers or singular pieces as a whole is the Multipiece Package.
Wholesale Package
A wholesale package-
- Is a package containing many retail packages intended for distribution, sale or delivery to a mediator in the process and is not intended for direct sale to a single consumer
- A commodity of food sold to a person in the middle in bulk quantity so that the mediator person can deliver, sell or distribute such commodity to the consumer in limited quantities
- There is no mandatory condition for the wholesale package to reveal MRP, manufacturer address, and manufacturing date
Vegetarian Food
Leaving all Non-Vegetarian Food, any other article of food is the Vegetarian Food as prescribed in regulation1.2.1 (7).
Expiry Date or Use- by Date
The date after which the taste of the food quality started deteriorating as it would stop meeting consumers’ expectations and the food will lose its saleable value is the Expiry Date or Use-by Date. This date is the recommended last date of consumption that implies the estimated period ends within any storage stipulations.
Labeling of Food Product- FSSAI Guidelines
As per the FSSAI Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations in 2011[1], it is clear that all packaged food products need to get labeled to ensure the safety of consumers and the protection of their interests. The label must provide the following essential information-
Food/Product Name
The chief FSSAI guidelines on the labeling of food products are the name of the product/food. The complete name of the food product should be written in a clear format on the packaged product. Moreover, fonts should be clearly visible, as well.
Net Quantity
Net quantity is all about the overall weight of the product or food item. Net quantity comprises product weight along with the weight of the packaging.
Nutritional Details
Nutritional details depict the calories which originate from various sources like fat, sodium, sugar, calcium, proteins, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Trans fat, carbohydrates, iron, and dietary fibers found in the product. Information related to calories is available on the labels of the products.
List of the Ingredients
Elements that are useful in the preparation of final/end products fall under the list of ingredients. What matters the most here is that the manufacturer should specify all the ingredients in a fair manner without cheating with the end-customer. Problems would surround the manufacturer all around if the manufacturer cheats the customer by providing misleading information.
Declaration concerning Veg or Non-Veg
As per the FSSAI guidelines on labeling of food products, the manufacture must clarify the points on the food packaging whether the food item is vegetarian or non-vegetarian. This guideline came into the picture due to the fact that not every Indian loves eating non-vegetarian food. It would be easy for people to apprehend whether the product is veg or non-veg by looking at the green color dot on the packet. The green color dot symbolizes that the food product is vegetarian. On the other hand, the red color dot symbolizes the product being non-vegetarian.
Declarations on the subject of Food Additives
Food additives are those additional things added to the food in order to preserve the flavor and enhance its appearance as well as taste. Thus, declaring the additives on the package or the level is a mandatory thing.
Code No. /Lot No. /Batch No.
The manufacturer should mention Code No./Lot No./Batch No. as prescribed under the FSSAI guidelines on labeling of the food product. On top of that, these numbers are the recognition mark through which the food can get recognized in the distribution process, and also it can be found in the manufacture.
Country of Origin for Goods Imported
It portrays the nationality of those goods that get imported. Also, it refers to the area where the manufacturing, production, and processing of such goods have taken place or have sprouted up.
Manufacturers’ Name and Complete Address
As stated under FSSAI food packaging and labeling regulations, the food manufacturer needs to mention his full factory address, which should cover zip code, city, street address, and state. If these details found missing over there, then the product would get considered as not a genuine one.
Packing or Manufacturing Date and Date of Expiry
The manufacturing date is the date on which the final product gets manufactured by clearing all the processes, and the Expiry Date is the date that tells about the last date of consuming the food product. If the consumption takes place after the Use-by or expiry date, then it can probably wreck the health of the consumer. Moreover, it is the duty of the consumer to check the manufacturing date as well as the expiry date before buying the product.
Usage Instructions
Information related to how to use the product is available on the product itself. The availability of this information on the label ensures proper utilization of food.
Violation of FSSAI Food Packaging and Labelling Guidelines
Penalties imposed for violating the FSSAI food packaging and labeling regulations vary from one offense to another.
Given below are the descriptions with regard to these penalties-
- In case of violation of Section 39 Rules
If the person sells, distributes, stores, packs as well as deliver commodities, without coinciding the requirements of Act and Packaged Commodities Rules, then he or she would get penalized with a fine of more than Rs 5000.
- Penalty for Committing the Offence Mentioned Above
If the person commits the same offense again, the imprisonment for the person is up to 5 Yrs.
Recent Updates on Packaging and Labelling
The food regulator, FSSAI, has issued an order for all the sweet shops to mention expiry dates and use labels on their packed and loose sweets. FSSAI has taken the decision and made it mandatory after looking at the increasing sale of adulterated, along with spoiled sweets.
Furthermore, this regulation by FSSAI would come into effect from the 1st of June 2020. Following the strict order is mandatory for all the sweet shops. This decision would benefit the consumers in terms of their health aspect. Earlier, only packaged food required labeling till now as per FSSAI Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations, 2011.
Conclusion
It’s crucial for all the food business operators carrying out their business in India to abide by the FSSAI’s Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations, 2011. In the sphere of food and beverage packaging, food labeling has an integral role to play. Food business operators need to follow the laws and regulations of FSSAI. Our team of experts is familiar with the guidelines of FSSAI regarding packaging and labeling. The experts would make you aware of the recent updates related to FSSAI regulations. If you feel that your plans are not working out, you can approach us at Corpbiz for guidelines on food packaging and labeling regulations.
Read our article:FoSCoS for FSSAI License in India: A Replacement of Food Licensing and Registration System










