Regulatory Structures all around the world have been mainly set up to achieve the objective of ensuring the safety of food and protection of consumer interests. Both these objectives require that regulators should analyze the data on various food safety and regulatory aspects throughout the chain of Food, including estimating dietary exposure for carrying out scientific risk assessments.
Keeping in mind the considerable diversity in the food products being used up, regions in which they consumed the population groups involved, etc., it becomes virtually impossible to track the information on an individual product basis. Apart from the absolute volume of data, the problem is complexed by the use of multiple languages and regional variations. The preparation of such data on Food requires a proper structure and a detailed description of foods. Even data of a kind class can be a basis of error if they are derived from foods that are not visibly defined. Further, it isn’t easy to exchange data on foods due to its complexity or to understand and compare various parameters such as status of nutrition, consumption patterns, etc. for different regions, states or individuals, without a clear description of foods in databases.
To analyze the relevant data, regulators have used the categorization approach, where groups of similar products are bashed together as one category. The category is used as the basic unit for capturing information/data and driving conclusion making in regulatory framework.
Food Safety & Standards Act, 2006 Framework
- Section 3 (1) (j) of the Act defines Food as: –
“Food” means any substances, whether processed, partially or unprocessed, which is intended for human consumption. It includes primary Food to the extent defined in clause (zk), genetically modified or engineered Food or Food containing such ingredients, infant food, packaged drinking water, alcoholic drink, chewing gum, and any substance, including water used into the Food during its manufacture, preparation or treatment. However, it does not include any animal feed, live animals unless they are prepared or processed for placing on the market for human consumption, plants, before harvesting, drugs and therapeutic products, cosmetics, narcotic or psychotropic substances:
Subsection (1) of Section 31 of the Act, dealing with Licensing and registration of food business, states thatno person shall commence or carry on any food business except under a license.
Food Classification vides its Food Safety and Standards (Licensing and Registration) Regulation, 2011 (FSS) has provided various conditions along with formats for operating the licensing and registration framework for food business operators. This Structure envisages in creating a database of food business operators and the products manufactured by them. As stated above, the creation of a database on the category basis, over product basis, has been observed to be the best solution.
Creation of Food Category System (FCS[1]) has also been stated as one of the responsibilities of Food Authority in Clause (h) of the subsection (2) of Section 16 of the Act, dealing with Duties and functions of Food Authority. It says: Without prejudice to the provisions of sub-section (1), the Food Authority may by regulations specify – (h) food labeling standards including claims on health, nutrition, special dietary uses and food category systems for foods;”
Read our article: Enforcement of the FSS ACT – An Overview
Need for a Food Classification System


Advantages of Food Classification System
- Such a system is based on codex structure, which is recognized internationally. CODEX standards are accepted by a large number of countries over the globe.
- A scientific basis will be provided by FCS to the Indian food laws, improving the quality of products for Indian consumers and International consumers of Indian Food.
- The harmonization with other global regulations will promote and facilitate international trade.
- CODEX standards are the basis for the resolution of WTO trade disputes.
Guiding Principles For Food Classification
Concerning the guiding principles of FSSA, 2006, and in compliance with India’s commitments towards WTO it is suggested to create a Food Category System, in harmony with the Food Categorization System approved in Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA). The following principles will guide such categorization system:
Principle 1: Expandability
The FCS should be designed and constructed in such a way that each categorized number can be used as a code, if essential for licensing. The law shall be adaptable to cover reasonable possibilities of new additions of products or categories in the future.
Principle 2: Simplicity, Scientific Basis, Clarity And Certainty
The categorization system should be simple to understand, based on sound scientific principles and should be able to provide clarity to both the regulator as well as other stakeholders.
Principle 3: System Usable For Both National And International Regulatory Framework Purposes
The categorization system should be so designed that it is in orthodoxy with recent developments in the areas of food classification and classification for food regulations. This should serve dual purposes both at the national and international levels.
Structure of Food Classification System
The Food Category System (FCS) comprises of a large number of food items combined into broader food categories/groups in a classified structure of parent-child relationships. The food product categories provide great food products along with generic food descriptors. The FCS is a system of different food products / Food groups in a hierarchical structure. The term ‘food category descriptor’ should be understood as a collection of words describing the relevant characteristics of the food/food category. The entire food category system is code-based.
Main Indian Food Categories
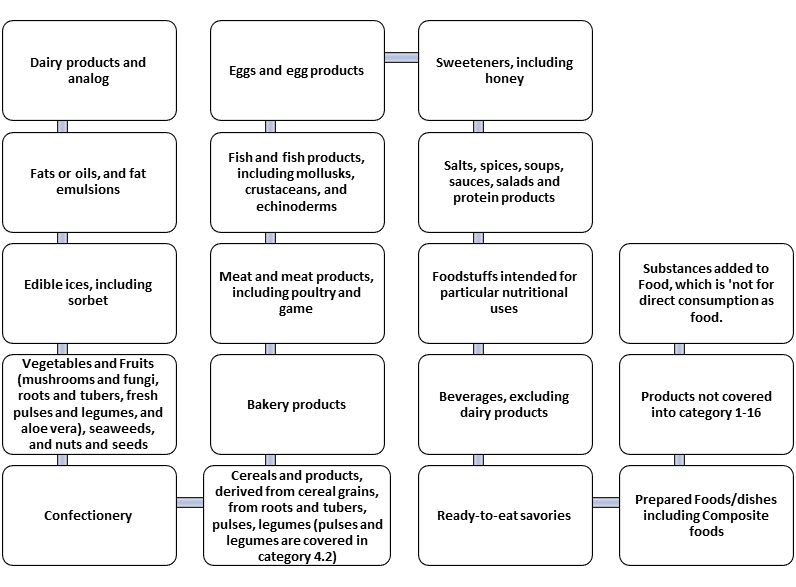

Conclusion
The food product categories provide great food products along with generic food descriptors. The FCS is a system of different Food classification in a hierarchical structure. The term ‘food category descriptor’ should be understood as a collection of words describing the relevant characteristics of the food/food category. The entire food category system is code-based.
Our CorpBiz group shall be at your disposal if you seek expert advice on any information regarding FSSAI License along with complete compliance. We will help you ensure full compliance concerning all the requirements.
Read our article: What is National Food Security Card, and How to download it?











