In the year 2013, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) formed the concept of Payment Banks in India. Demonetization in India reorganized the economic system of India. Now the people are more inclined towards paperless transactions and use digital payment gateways. There was a sudden boost in the use of mobile wallets, which were earlier outcasted by the people. The Payment Banks provide the platform for online payments in India. A Payment Bank License is needed to get started with payment gateways. In this article, we will discuss the procedure for obtaining the Payment Bank License.
What is the Payment Bank?
Payment Bank is set up under the guidelines for the Payment Bank License issued by Reserve Bank of India (RBI)[1]. The Payment Bank is a micro-bank with limited banking functions. These Banks can receive a restrict deposit of up to 1 lakh Rupees per client. The RBI restricts the issue of credit cards and loans from the Payment Banks. However, these Banks can issue Debit Cards, ATM Cards, mobile-banking, and net-banking facilities. Both savings and current accounts can run under these banks.
The main function of RBI is to have financial inclusion in India. The Payment Banks are set up to increase the use of banking facilities by the people living in the remote areas of India. Payment Banks provide financial services through smartphones to people all over the country. As sometimes, it is not economical for all the banks to provide branches in all remote areas of the country, so to solve this, the concept of Payment Banks is introduced.
Which Regulatory Acts regulate the Payment Banks?
The Payment Bank should get enrolled under the following Government Act and while issuing Payment bank License the compliance of the following Acts is also needed:
- The Companies Act, 2013;
- The Reserve bank of India, Act, 1934;
- The Banking Regulation Act, 1949;
- The Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007;
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999;
- The DICGC (Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation) Act, 1961.
Who are the eligible players for obtaining Payment Bank License?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has provided a long list of eligible players for obtaining the Payment Bank License. The list of eligible players is as follows:
- Companies (Public Company);
- Mobile Telephone Companies;
- The Supermarket Chains;
- The Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs);
- Corporate Business Correspondents (BCs);
- The existing issuers of non-bank PPI (Prepaid Payment Instrument)
- Professionals/Individuals
- The Real Sector Cooperatives which are owned by Residents
- A promoter or group of promoters can have a Payment Bank License if they have a joint venture with an existing scheduled commercial bank
- The Public Sector Entities
What are the key characteristics of the Payment Bank?
The key characteristics of Payment Banks are as follows:

Deposit of 1 lakh
- The maximum deposit offered to Payment Bank is 1 lakh Rupees by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- This limit on deposit with Payment Bank is there to safeguard the interest of customers.
- The Payment Bank also gives the leverage to deposit amount partially or wholly.
No Minimum Account Balance Maintenance
- Unlike conventional banks, the customers of Payment Banks are not required to keep a minimum balance in the account. The customers can even opt for a zero balance account.
Availability of both Current and Savings Accounts
- After obtaining the Payment Bank License, the Bank can offer both current and savings accounts.
Physical and Virtual Debit Cards
- The Payment Bank also channelizes virtual debit transactions apart from providing physical debit cards.
- There is no additional charge for virtual debit, whereas an annual fee is charged from the customers for using physical debit cards.
Online Fund Transfers
- Services such as IMPS, NEFT are provided to the customers by Payment Bank. These online services decrease the hassle of visiting financial institutions.
What are the guidelines of RBI for the Payment Bank License?
The guidelines provided by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) are as follows:
Registration and License
- The registration of Payment Bank will be done under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The License of Payment Bank will be given under the Banking Regulations Act, 1949.
Eligible Promoters and Objectives
- The primary objective of setting up Payment Bank will be financial inclusion.
- There will be certain eligible promoters of the Payment Bank License.
- The Payment Bank will be set up as differentiated banks and should confine its activities for furthering the objectives for which it is set up.
Deployment of Funds
- The Payment Banks cannot undertake lending activities of funds.
- The Payment Banks have to maintain a cash reserve ratio with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The Payment bank has to invest 75% of its ‘demand deposit balances’ in Statutory Liquidity Ratio in government securities/treasury bills.
- The Payment Bank should hold a maximum of 25% in fixed and current deposits with scheduled commercial banks for liquidity management and operational purposes.
Capital Requirement
- The minimum paid-up capital of the Payment Bank should be 100 crore Rupees.
- The leverage ratio of the Payment Bank should not be less than 3%. Hence, it can be said that the outside liabilities should not exceed 33.33% of its paid-up capital and reserves.
Contribution of Promoter
- No maximum shareholding limit is prescribed for promoters.
- The initial contribution of promoters should be 40% of the paid-up equity capital of the Payment Banks for at least five years after the commencement of the business.
Scope of Activities
- The acceptance of demand deposits is permitted.
- A maximum balance of only 1 lakh rupees is allowed for the Payment Bank.
- The issue of credit cards is allowed. The payment Bank can only issue ATM/debit cards.
- The payments and remittances services are allowed through various channels, including ATMs, BCs, Branches, and mobile banking.
- As per RBI guidelines, the Payment Bank can act as Business Correspondent of another bank.
- The issue of PPI can be done as per the instructions issued by the PSS Act from time to time.
- Payment Banks can offer internet banking to its customers.
- The cross-border remittance transactions like personal payments/remittances on the current account will be permitted to be handled by Payment Bank.
Foreign Shareholdings
- The foreign shareholdings in Payment Bank will be according to the Foreign Direct investment policy for private sector banks as amended from time to time.
- The maximum of 74 % of the paid-up capital of Payment Bank will be allowed as foreign investment in a private sector bank. Out of the 74%, 49% will be through the automatic route, and the remaining will be through the government route.
Voting Rights and Transfer of Shares
- The Banking Regulation Act, 1949, will govern the voting rights of shareholders in Payment Bank. The voting rights are capped at 10% and can be increased to 26% in a phased manner as prescribed by Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Business Plan.
- The business plan and project reports should be furnished by the applicants of the Payment Bank License.
- The main objective of setting up of Payment Banks proposed by the Bank should be addressed in the business plan.
- The business model, access points of Payment Bank in rural and semi-urban areas, customer grievances redressal, control over BCs should be covered in the business plan.
Prudential Norms
- The RBI regulations applicable to loans and advances will not apply to Payment Banks as they will not have loans and advances in their portfolios.
- There will be a chance of exposure to operational risks of Payment Banks, so to curb the risks, an operational management risk system should be established by the Payment Banks. Hence, liquidity risks can be faced by Payment Banks, so to avoid this, the Payment Banks are required to follow guidelines on liquidity risk management as prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Corporate Governance
- The Board of Payment Bank should have a majority of Independent Directors.
- The corporate governance guidelines, which include the ‘fit and proper criteria’ for Directors, should be followed by the Payment Bank, which is issued by Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Other Conditions
- The operation of Payment Bank should be in remote areas through ATM’s, BCs, and other networks. At least 25% of the access points of Payment Banks should be in rural areas.
- From the very beginning, all the operations of Payment Banks should be technology-driven and fully networked.
- Any new approach is encouraged; the plan for the same should be submitted to the RBI.
- The Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006, of RBI will regulate the Payment Banks.
- For handling customer complaints, a high-powered customer grievance cell should be set up by Payment Bank.
- For the grant of License for Payment Bank, compliance with the terms and conditions laid down by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) should be there.
- Non-compliance with the terms and conditions laid down by RBI will attract penal provisions and also lead to the cancellation of the Payment Bank License.
What is the additional information to be furnished by Payment Bank?
Payment Bank should furnish the following additional information:
- The name, date of birth, residential status, PAN card number, Bank, and branch details parents name of the promoter.
- Detailed information of background, experience, expertise, a track record of business, financial worth, direct and indirect interests in various companies, etc., of the promoter of the Payment Bank.
- The detailed information of the entity promoting the Payment Bank.
- The detailed information of the entities and individuals promoting the Payment Bank.
- The project report covering the business plan, business viability, and potential of the proposed Payment Bank, and other financial services proposed to be offered.
- The details of the entities and persons who will subscribe to the 5% or more of the paid-up equity capital of the Payment bank.
- The promoters of the Payment Bank can submit any other relevant information and relevant documents supporting the applications of License.
What is the procedure for obtaining the Payment Bank License?
The procedure for obtaining the Payment Bank License in India is as follows:
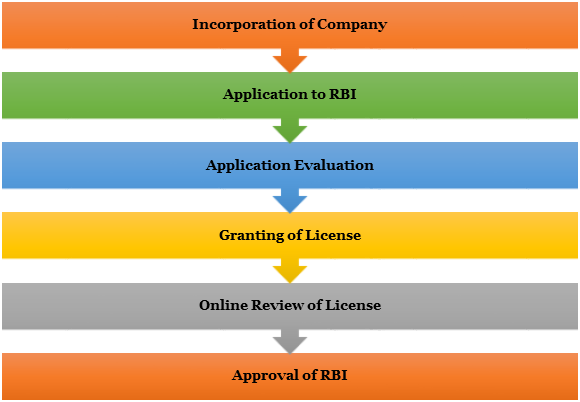

Incorporation of Company
- As per the guidelines of Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the applicant of License has to incorporate a Public Limited Company under Companies Act, 2013. The main object of the incorporated company should remain to act as a Payment Bank.
Application to RBI
- An application for a grant of Payment Bank License will be filed to the Chief General Manager of Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Application Evaluation
- The applicant can be summoned for inquiries and validation of the information given by him in the application. The External Advisory Committee (EAC) will asses the application and summon the applicant.
Granting of License
- The RBI should grant the Payment Bank License to the applicant who successfully meets the eligibility criteria for License.
Online Review of License
- The official site of RBI should display the name of the concerned applicants for a bank license.
Approval of RBI
- The principle approval to run a Payment bank should be given by RBI. After getting the principle approval from RBI to operate as Payment Bank, the Payment Bank should be set up in 18 months.
What are the advantages of the Payment Bank?
The advantages of the Payment Bank are as follows:
- No minimum balance is required to be maintained in the account.
- The interest rates given by the Payment Bank are higher as compared to other banks.
- The Payment Bank is driven by high safe technology.
- The account number of Payment Bank is the same as the mobile number; hence, it is easier to memorize your account number.
- The Payment Bank also provides the facility of cashback in the mobile wallets of the customers.
- The merchants of Payment Bank provide certain offers like cashback, discounts, and many other benefits to the customers.
- The customers can avail the facilities of Payment Bank conveniently as these banks have a vast network area.
Conclusion
Payments Banks is a game-changer that satisfies the needs of the modern era. The people nowadays rely mostly upon smartphones to make payments as it is more suitable and save their time to visit the banks. The Payment Bank is an internet-based financial institution that serves the ‘Digital India’ dream of Government. The process of obtaining a Payment Bank License is long-lasting and time-taking. We at Corpbiz have experienced professionals to help you with the process of getting a License for Payment Bank. Our professionals will assist you with the process and assure timely and successful completion of your work.
Read our article:FM Introduces Banking Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2020











