The secretarial audit was introduced under the Companies Act 2013. Under the secretarial audit, the company has to go through the compliance audit by the independent practicing company secretary.
Section 204 of Companies Act, 2013 contains provision for Secretarial audit for bigger companies. It was proposed as a significant step in improving and enhancing the corporate governance and ensuring the efficient compliances of the regulations applicable on the company.
Secretarial Audit is an auditing conducted to verify the Compliances of different legislations that are applicable to the company i.e. including Company law but not limited to that only.
Overview: What Is the Purpose of Secretarial Audit?
- The purpose of the secretarial audit is to find the non-compliances by the company.
- To check whether the company is following the proper guidelines stated under the Companies Act 2013.
- It ensures that the company could improve the points targeted by the auditors, by working on the glitches.
- Secretarial auditing helps in following the rules and regulations and not to attract any fine and penalty.
- Auditing is a periodical process that builds faith and trust in regulators, stakeholders, and management.
- A clean secretarial audit report proves that your company is risk-averse and can evade difficult situations in the future.
What are the Companies that derive Under Secretarial Audit in India?
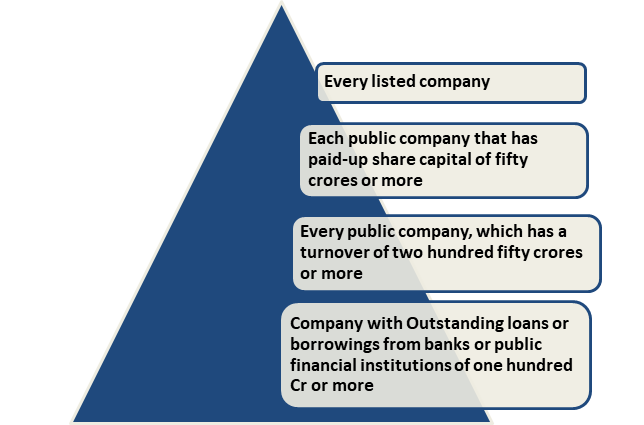
Under the Companies Act 2013[1], the following is the list of companies that have to be audited by the independent practicing company secretary to procure the Company Audit Report.

Turnover is the total amount of money, which makes by the sale, supply/distribution of goods and services provided to the consumers during the whole financial year. All the subsidiary companies of a public company or other companies that fall under this criterion have to conduct an Audit.
Who meets the requirements to carry the Secretarial Audit?
- The member who will be conducting the audit, he/she has to be a member of company secretaries of India, having a certificate of practice to make the audit report in form MR-3 to the company.
- If a company secretary is employed and not in whole-time practice, he/she is not suitable to conduct the audit. There is no set limit to the number of auditing performed by the auditors in one financial year.
Advantages of Secretarial Audit
The following are the advantages of secretarial Audit –
- Audits are essential for the companies, which fulfil the above criterion, and auditors are seen as a pillar to find the loopholes in their functioning, which can be eradicated to improve the services and mechanism of the company.
- In this generation of internet, frauds and bugs can knock at your door anytime and it’s always said that “prevention is better than cure”. So, a secretarial audit helps the company to be ready for the unforeseen challenges in the future and take preventive measures.
- Auditors make sure that the company’s rules and regulations are being followed by the employees of the company.
What are the amendments by Companies Amendment Rules, 2020?
The Amendment by “Companies Appointment and Remuneration of Managerial Personnel” Rule, 2020 to Rule 8A & Rule 9 of Companies -Appointment and Remuneration of Managerial Personnel Rules, 2014 are as follows:-
Amended Rule-8A and Rule-9 expresses this following criterion
- Prior Situation of Rule-8A –
A company must have a whole-time company secretary, who has a paid-up share capital of five Crore Rupees or more-veiled under rule 8.
- Revised situation of Rule 8A–
Every single Private Company must have a whole-time company secretary having paid-up share capital of 10 Cr rupees or more.
- Revised Situation of Rule 9–
Provision connected to Secretarial Audit is now pertinent on the subsequent list of Companies:
- Every single company deriving its outstanding loans or borrowings from public financial institutions or banks of one hundred Crore rupees or more.
- All public company deriving it’s a paid-up share capital up to 50 crore rupees or more, or
- All public company deriving its turnover of 250 crore rupees or more; or
- Secretarial Audit Report shall be in Form MR.3, which needs to be accepted as uniformity.
- Assumptions and Illustrations:- It is hereby enlightened that, for the purposes of this sub-rule, the paid-up share capital and turnover or outstanding borrowings or loans, all the current existing shall be taken into account on the last date of up-to-date audited financial statement.”.
- In cases of Rule 8A, the previous limit for selection or appointment of Company Secretary in Private Companies or other companies was having paid-up share capital of rupees Five Cr, or more. However, after amendment, it is raised up to rupees 10 Cr. or more which will lead to unemployment of engaged Company Secretary in private sectors/companies.
What are the Auditing Standards for CS PAN India to abide?
The practice of Auditing Standards that were earlier introduced has been mandated by the Institute of company secretaries of India (ICSI) on an intentional basis in July 2019. All the audits held in the companies will stick to these Auditing Standards preliminarily w.e.f 1 April 2020.
Core Highlights
- All practicing Company Secretary is obligatory to abide by the auditing standards.
- Audit assignments that are duly reflected valid by the Companies Act 2013, Security and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992, or any other related law are allowed to take on by the Practicing CSs.
Important Intentions for considered Auditing Standards
- Improvement of equipment, gears, auditing tools, and methods.
- Bring up-to-date the laws to make it in-line with the present needs of the company as well as the government.
- Foundering modus operands countrywide that will bring in standardization and professionalism in the audit system.
Read our article:Audit of Charitable trust or NGO under section 12A (b)
What are the segregated standards in the new Audit Segments?
CS certificate and Audit Engagement letter is the eligibility to conduct the Audit while practicing. If any of the above-mentioned documents is missing, it will restrict the CS from performing the Audit. For an easy understanding of this subject, Auditing Standards are separated into four parts.
Those are as follows:-


(CSAS 1):-Meaning of Auditing Engagement
- Protocols of the Audit Engagement – Process set by the authorities while he/she conducts an audit must keep in mind by the auditor.
- Auditee must discuss several issues and consequences of the previous audit. Moreover, the pre-audit meeting is a must among the auditor.
- Rules connected to the appointment of the auditor have to be surveyed at the time of auditor appointment which is mentioned in auditing standards.
- Auditors should have the eligibility certificate that permits him/her to conduct the audit.
- When any auditor pays the commission to obtain the audit, in that case, it is known as offense.
- Auditor essentially communicates to the previous auditor and set all the information that will benefit them in the further process.
- The auditor needs to wait for 7 days before starting with the audit after conducting a meeting with the previous auditor.
Auditor need to adhere with stated conducts & number of audits
- Suitably authenticated MGT-7
- 10 per PCS For secretarial audit
- Secretarial Audit Under Section 204
- Documentation in MGT 8
- Annual Secretarial Compliance Reports number is 5
- Any engagement of diverse interests with the auditee must not disturb the substantial interest.
- The auditor is meant to be indebted to auditee with amount up to R.s. 5,00,000 when the auditor is working for the auditee for more than 2 years if he grasps 2% paid-up capital or shares worth Rs. 50,000 (whichever is lower)
(CSAS 2): Audit Process and Documentation
The complete process of Audit is founded on execution, planning, and documentation. Not any of these could be avoided in the audit.
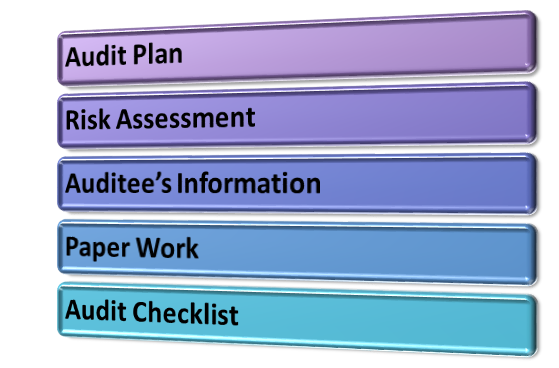

Proper Audit Plan – Before beginning the process, it is crucial to setting up a roadmap. The flawless audit plan stretches all the answers for where, what, when, who, and how. Aims of execution, audit, location, and a projected plan of the audit must be prepared.
Overall Risk Assessment– Categorizing the type of industry, administrative structure, and legal compliance requirements, market viewpoint, and industry setting must be done during the overall risk assessment plan.
Collect Auditee’s Information – Auditee’s nature of business and laws applicable to the business must be known to Auditor, and must be fully aware of whole applicability as required.
Prepare Audit Checklist – An audit checklist has to be continued by the auditor rendering to which the audit procedure will flow. It will also give or take nearly all the compliance requirements which will be identified from time to time. Therefore, it can be said that an audit checklist is an obligatory need for an audit to meritoriously work.
Complete Paper Work – Auditors are required to make reports and affix all proofs and documents that are needed. All the audit evidence, work done and outcome of the audit must duly be stated in the end reports/documents.
(CSAS 3): Forming of Opinion
The auditor needs to follow the mentioned basic protocols when it comes to assessing the end results strained out from the audit evidence and contribute their estimation through a report.
The standards established for audit estimations
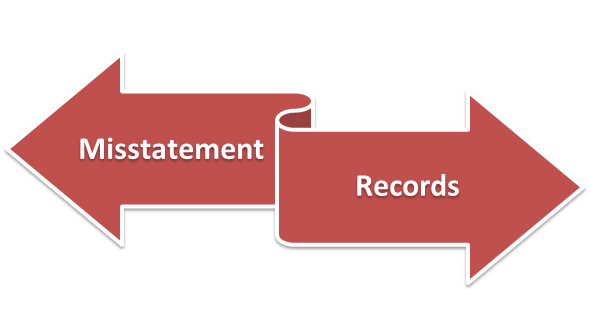

Records – Under the standard sets for audit estimations, Records include the MOA, AOA, minutes, registers, forms, returns, index, etc.
Misstatement – Under the standard sets for audit estimations, misstatement suspects the noting down if any information is false, deceptive, omitted, or is incompatible with the auditors’ examination.
Procedure of Standard set for Audit Opinion estimation
While providing the estimation, the auditor must deliberate all the explanations, conflicting understandings, other party statements, etc. resulting in a complete analysis of the reports/statements.
The Auditor must abide by the following principles:-
- Standard of Contradictory Process
- Standard of Completeness
- Standard of Timeliness
- Standard of Objectivity
Auditors Responsibility
The auditor in the explosion of report comprises all sections under the title of ‘Auditor’s Responsibility.’ The resistance of audit will work being showed as per the simple Auditing Standards. Moreover, the proof the auditor has to be obtained the reasonable declaration, records prepared and the whole paperwork is free from any false statement.
Report Format of the estimation– Report Format of the estimation will either be specified by appointing authorities or stated under audit assignation letter or as long as given under applicable laws.
Signature in the Reports– The Signature in the reports must include
- Name of audit firm
- Name of the auditor
- Certificate of practicing number
- Specified associate or fellow member
The date and place of signing the report must be stated by the auditor in case the report is allotted by two different auditors at altered places or changed dates.
Consequences of new modification
The consequences of new modification in companies (Appointment and Remuneration of Managerial Personnel) Amendment Rules, 2014 are:
- By ruling out the concept of “name lending”, it has enhanced the visibility and brand building of the profession of Company Secretaries of India.
- For the Practicing Company Secretary, it has increased the scope of work.
- As applications for the Certificate of Practice will gradually increase, it will also lead to the Promotion of self-independent Professions.
- Company Secretary which is previously employed will find it difficult to switch their jobs and newly qualified Company Secretary will face problems getting a job.
- It is evident that, now only big Companies will be employing Whole-time Company Secretary, as the recognition of the “Profession of Company Secretary” has been exaggerated deeply by this new alteration.
The audit report is complete of an audit that is equipped by the auditor steering the audit. The report comprises name, nature, place of the scope, business, and objectives of the business, auditor’s estimation, and examination on the locus of the company in the market, in addition to a lot more. Moreover, audit report must be organized in detail displaying the state of affairs of the auditee. Accordingly, the amendment has abridged the employment chances for the Company Secretaries in the Private Companies, and on the other hand, it has amplified the possibility of work for a Practicing Company Secretary in India.
Conclusion
Summing up the whole, the entire contents of this blog have been developed grounded on pertinent provisions and are only the views of the authors. Nonetheless, the author has made ultimate exertions to provide authentic facts. Conversely, CorpBiz specifically disclaims all and any liability in dependence upon the insides of this blog. Here, at CorpBiz, We have a dedicated team of professionals including CA, CS. If you are looking for an auditor, do give us a call.
Read our article: Different Committees and Their Functioning as per Companies Act, 2013