To curb money laundering in India, Reserve Bank vide its Notification released on February 12, 2021, clarifies that new investors from or via non-compliant Financial Action Task Force jurisdictions cannot directly or indirectly acquire considerable influence in India-based NBFCs.
This implies that new investor from said jurisdictions in total should hold less than 20% of the voting power of the NBFC. The Notification shall be applicable on new investment in prevailing NBFCs and entities seeking registration certificate from the Reserve Bank of India.
What is Financial Action Task Force and its objective?
The Financial Action Task Force (aka FATF) is an inter-governmental institution founded in 1989 by its Member jurisdictions. The objectives of this institution are to establish standards & advocate the effective implementation of operational and regulatory measures for the prevention of terrorist financing and money laundering, and other threats that are detrimental to the international financial system.
The FATF oversees the growth of its members in deploying fundamental measures, review terrorist financing & money laundering techniques and counter-measures, and advocates the adoption of apt standards globally.
On a whole, the Financial Action Task Forceseeks;
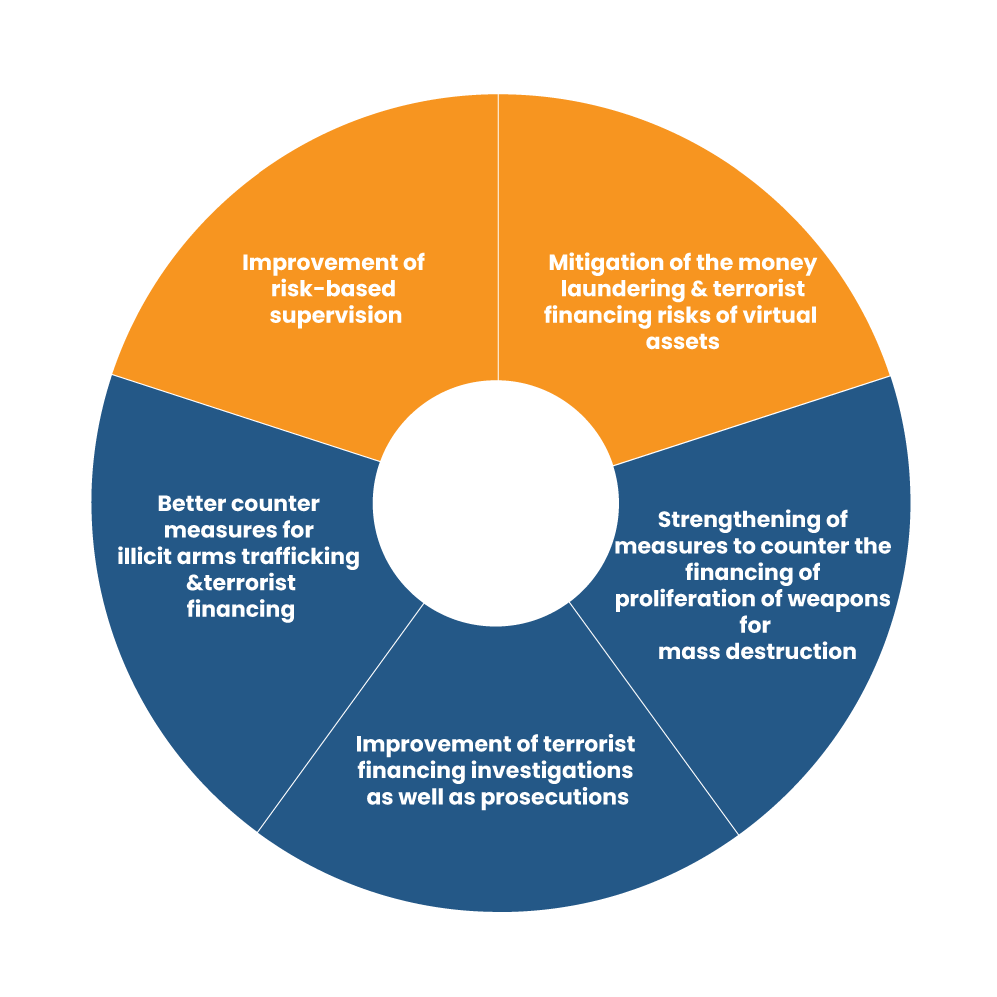

Underlining Essential Declarations of the Released RBI’s Notification
The institution periodically pinpoints jurisdictions lacking adequate measures to combat such practices in following publications
- High-Risk Jurisdictions open to Call for Action, and
- Jurisdictions under enhanced monitoring.
Under the Notification, nations included in either category will be classified as non-compliant FATF countries. Among the FATF high-risk list nations are Iran & the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Among those classified under enhanced monitoring are Pakistan, Zimbabwe, Cambodia, Mauritius, Panama, Jamaica, Ghana and others.
Read our article:Underlining Importance of Budget 2021 for NBFCs and Banks
Under the influence of increased monitoring, jurisdictions are proactively engaged with the FAFT to address strategic loopholes in their regimes to mitigate proliferation financing and money laundering.
When the Financial Action Task Forcespecifies a jurisdiction under increased monitoring, it indicates the nation has committed to fixing the identified risks with an agreed timeline and is subject to increased monitoring. This list is referred to as the “Grey List”.
- Barbados
- Burkina Faso
- Cambodia
- Botswana
- Cayman Islands
- Jamaica
- Mauritius
- Ghana
- Morocco
- Myanmar
- Pakistan
- Panama
- Nicaragua
- Senegal
- Syria
- Yemen.
- Zimbabwe
- Uganda
High-risk jurisdictions are plagued with strategic deficiencies in their regime to combat terrorist financing, money laundering, & proliferation financing. Financial Action Task Forceurges the high-risk nations to apply improved due diligence to protect the global financial system against the risks above emanating from the country. This list is referred to as the “black list.”
As mentioned above, the blacklist contains two nations: the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) and Iran.
Does the Aforesaid Notification Revolve Around Retrospective Effect?
As per the Notification, RBI[1] aiming to take new investors into account who belong to non-compliant FAFT jurisdictions. That means prior investments will remain unaffected by this declaration.
Investors in prevailing NBFCs from the non-compliant FATF jurisdiction need not worry about their investment. Such investors can bring additional investments as per prevailing regulation to support business continuity in the country.
Past RBI’s Actions to Contain Risk Associated with Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing
In 2020, Reserve Bank demanded financial institutions, including shadow banks, to carry out terrorist financing & money laundering risk assessment periodically as per the new section in the master directions related to KYC. The assessment was expected to mitigate terrorist financing & money laundering risks for clients, nations, products, transactions etc.
RBI also compelled regulated entities, i.e. REs, to hone their understanding of the sector-specific vulnerabilities via provided material from the regulators. Further, the institution directs the REs to take size, the complexity of activities, and geographical presence into account during risk assessment. It would give them more clarity and prompt outcome.
RBI’s circular covers all Financial Institutions, shadow banks, and payment system providers. The circular further emphasized REs to apply a Risk-Based Approach (RBA) for prevention & management of the identified risks. They were also required to set up board-approved policies and procedure in this context.
An overview on Decisions made by RBI for NBFCs in the year 2021
The NBFC sector has seen Reserve bank’s special attention since the onset of the year 2021; wherein RBI has undertaken important measure regarding the NBFCs such as:
Statement on Regulatory Policies & Developmental released on December 4, 2020
RBI, vide this statement @ https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_PressReleaseDisplay.aspx?prid=50748 specifies the need for supervision & regulation over NBFCs. The statement addresses:
- To need to outline norms for dividend distribution by NBFCs;
- Review of NBFCs’regulatory framework in line with the fluctuating risk profiles of NBFCs via a scale based regulatory approach associated with the systematic risk contribution of NBFCs; and
- Strengthening the NBFCs’ audit infrastructure and harmonizing norms related to statutory auditors’ appointment for shadow banks, commercial banks, and cooperative banks.
Discussion Paper Manifesting NBFCs’ Revised Regulatory Framework Released on January 22, 2021:
RBI has proposed the strategic bucketing of NBFCs where the regulatory regime will be less complex and more precise. The discussion paper envisages the categorization of NBFCs into four necessary layers, viz base layer, top layer, medium layer, etc. Additionally, the paper provides a methodology for identifying NBFCs, regulatory framework, and structure for NBFCs at different layers.
Conclusion
This Notification will considerably impact potential investments in NBFCs from funds registered in non-compliant FATF jurisdictions. Funds or firms registered in such jurisdictions planning to invest in India’s shadow banks are now compelled to revise their investment strategies to ensure conformity with the permissible threshold as provided in the Notification.
Digitization has also played a vital role in garnering illicit cross-border transaction. It isn’t easy is trace than the conventional money transaction. RBI is also aiming to set up strict measures for electronic transfer in future.
Read our article:Fintech Startups Aiming for NBFC License Despite Several Challenges











