Patent means a right granted to any individual for his innovation or invention. A patent gives an exclusive right to the inventor to protect his invention from being copied or stolen by others. Further registered patents can be granted for the use by the third party on the payment of fees.
If anyone tries to copy or stole the invention protected through patent or use the registered invention in any way without being authorized by the owner, it can be sued in the court of law. Patent and its registration are governed in India by the Indian Patent Act 1970[1]. Services and inventions allowed under the patent act can only be registered, and such registration can be done either individually or jointly.
What is the Process of Patent Registration in India?
A patent can be registered following these steps:
- Drafting Patent Specification: This is the first most and very crucial step in filing application for patent registration in India. Drafting of a patent specification is a skilled task that can be done by experienced professionals.
- Diagrammatic presentation: Visualize the ideas and invention which shall be jotted down in a diagram form that explains invention more specifically.
- Patent Search: Under this step, the patentee shall search whether his invention qualifies as a patentable element or not. One can make a public search on the official website of intellectual property http://ipindiaservices.gov.in/ to know its eligibility for patent registration.
- Preparation of Patent Report: Once the inspection is done and the patentee is eligible for patent registration in India, shall authorize patent professional or patent agent to do further research for the preparation of the patent report.
- Provisional Patent Application: Provisional application secures the invention by securing its data and work from the competitor who cannot file the patent for the same inventions. Such an application can be made when an inventor’s invention is under process.
- Final Application: Once the development is completed and all the detailed specification is ready, the inventor can apply for complete final patent registration in Form 1.
- Publish Patent Application: The final application filed with the patent office will be published in the official patent journal after 18 months of applying. Such patent needs not to be filed which are restricted under the patent act.
- Patent Examination: Within 48 months of filing the first application, whether it is provisional or final, submit a formal application for patent examination. The application would be withdrawn by the patent office if it failed to file within such 48 months.
- Patent Objections: After examination, it is common to receive objections such as unclear claims, lack of novelty, etc. which shall be replied and responded.
- Grant of Patent: Once all the requirements are fulfilled, and objections are properly responded, the patent officer shall grant a patent and will publish the notification in the Patent Journal.
Exempted Items
Following items are exclusively mentioned under the patent act which cannot be patented in India:
- Any idea which is frivolous or contrary to the established laws and is against the public interest in such a way that it can be harmful to the public at large, animals, laws and harmony of the country.
- A mere finding of existing theory cannot be patented; for instance, the discovery of a new method to extract petrol cannot be patented.
- Finding a new way to use the already existing product cannot be patented unless such invention results in the discovery of new products.
- Rearrangement of the known device in such a way that it functions differently cannot be patented. It can be patented only if it results in new usage of the combined product.
- Surgical or medical treatment of animals or human beings cannot be patented. For instance, the cure for heart diseases in a new way cannot be patented. However, machines and system installed for the same can be patented
- Computer programs and software invented cannot be patented as the same is protected under the Copyright Act
- Any new method or rule invented for playing games, mental tasks, etc. cannot be invented.
Read our article:Penalties, Suits and Appeals Against the Patent Infringement
Types of Patents
Following are the different types of Patents granted under the Indian Patent Act:
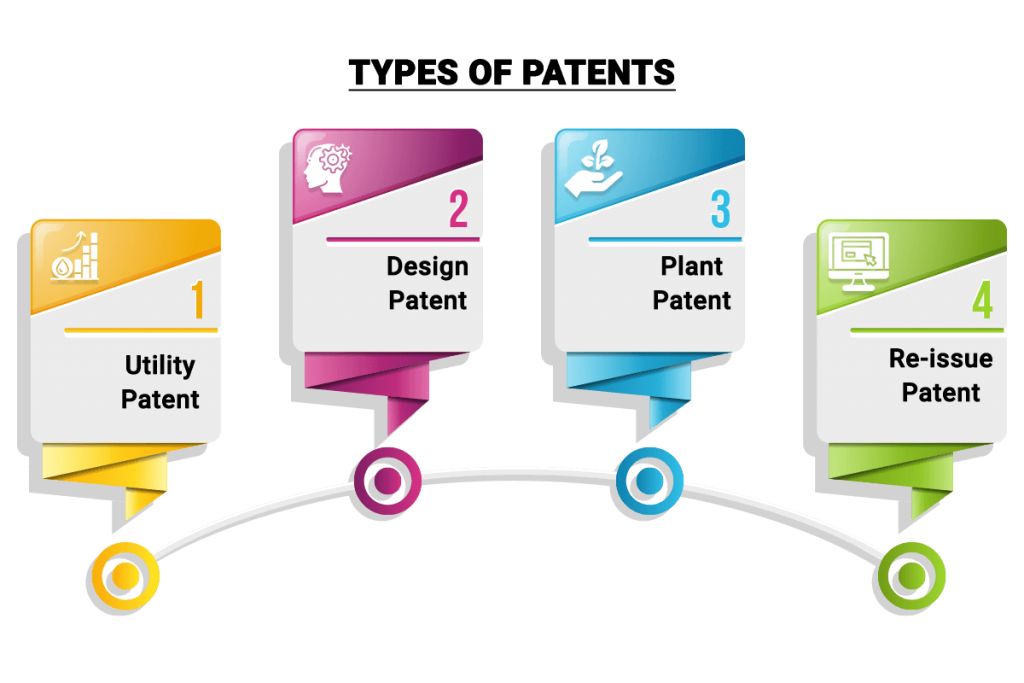

- Utility Patent: This is one of the most preferred patent registrations. Patent under this category is given for making new or useful creation in machinery, process or product.
- Design Patent: This patent is granted for creating and developing new designs for any machine, product or process. The main difference between these two patents is that Design patent focuses on how the new design or machine looks like whereas utility patent focus on usage and creation of new product
- Plant Patent: This patent is registered for inventing or discovering a new or distinct plant
- Re-issue Patent: This patent is issued for any correction made in already registered patents.
What are the Benefits of a Patent Registration?
Following are the benefits of the patent registration such as:
- Benefits to Patentee:
- Patentee enjoys the monopoly right over his invention and has sole discretion over the usage of his invention.
- The patentee has the right to grant the patented invention to the third party on the lease or otherwise for adequate fees charged
- A patentee can sell his invention during the patent period which is 20 years in India
- Benefits to Society:
- Innovative and advanced products are made available to the consumer
- Innovative technology and products are made available to the public at large after the patent period is expired
What is allowed to be registered as a patent as per the Indian Patent act?
Under the patent act, there is no specified listing of things that can be protected; however, there is a certain category that shall be met to get patent registered in India, such as:
- An invention shall not be already registered or has not been claimed by anyone in India
- Innovation applied for patent shall be unique and different from already existing invention
- The new invention must be capable of industrial application, and such new product must involve inventive steps.
- Inventions can only be patented if it is practically feasible and can be further used by any industry.
- Novelty is the most important criterion for any invention to be registered; that is it cannot be depicted by anyone in oral or written form.
For what period provisional application is granted?
Buffer time of 12 months is granted to further complete the development since the provisional patent is granted. Inventor gets 12 months to complete his invention, and no one can file the patent for the same invention. Provisional application lapses after 12 months are over.
Final Words
A patent gives an exclusive right to the inventor to protect his invention from being copied or stolen by others. If anyone tries to copy or stole the invention protected through patent or use the registered invention in any way without being authorized by the owner, it can be sued in the court of law.
Read our article:Patent in India: Registration and Filing Process