A patent is a document legally authorised by the government in order to provide the exclusive rights to the inventor for the purpose of making, using and selling the invention. The patent in India encourages the inventors by awarding exclusive rights for a specified number of the years. Patents are available for the new inventions as well as for the previously invented in which modification is made. Patent rights are a branch under the intellectual property law described in the Indian Patent Act 1970. The blog is about the filing and Patent registration process.
What is Patentable In India?
The Patentability of the inventions depends upon these three parameters, under the Indian Patents Act 1970[1], which are as follows:
- The invention should be novel that means it has never been previously seen, known or existed.
- The invention requires changes or improvements to existing technologies which must be unique and significant for the patent right. An obvious change is not patentable.
- The proposed invention must be valuable and useful for patent rights. Any illegal or immoral purpose inventions will not be granted as a patent in India.
What is Non-Patentable In India?
Under section 3 to 5 of the Indian Patent Act 1970, the following is not inventions and non-patentable in India:
- Frivolous inventions and contrary to natural laws or contrary to public morality, order and law
- The invention intended to use for commercial exploitation and causes serious prejudice to plants or environment, animals and humans health
- Any mere discovery of a scientific principle, living or non-living thing already existing in nature, or, formulation of an any abstract theory
- Any mere discovery of a new form of the known substance or the known process of the machine or apparatus unless such discovery results in a new product or reactant.
- Mere a mixture resulting in the only aggregation of the new substance or process of producing such substance
- Mere duplication of the devices may be functioning differently from one another
- The method of doing horticulture or agriculture
- The process of performing surgical, medicinal, curative, therapeutic, prophylactic diagnostic or other treatment for humans and animals
- The biological process of production or propagation of plants and animals in whole or any part including seeds, varieties, and species other than microorganisms
- A business method, mathematical solving or any computer programme
- A dramatic, literary, musical, artistic work which includes television productions, and cinematographic works
- A method of playing a game or scheme for performing a mental act
- A presentation of information
- The topography of integrated circuits
- An invention which has traditional knowledge or duplication of components already in existence traditionally
Benefits to obtain Patent in India
The patent in India provides encouragement in relation to new inventions and innovations. It keeps on motivating people to find and involve in making new discoveries and researches to give birth to a new innovative thing or idea to this world. Once patent a patent is granted, the person obtains the exclusive rights regarding the invention. Under section 73-76 of the Indian Patent Act, 1970 provides the details about the Patent Office in India and its establishment. The patent head office is in Kolkata, and the other offices are located in Delhi, Mumbai, and Chennai.
Read our article:Grounds for the Refusal of the Trademark Registration
Procedure for Patent Registration and filing
The patent in India as per Patent Act 1970, under section 6 of the act an application is to be made by following (subject to the provisions of Section 134 of the act)
- the actual inventor
- assignee by the actual inventor
- a legal representative of the actual inventor
An application can be made by any of the persons mention above either alone or jointly.
Steps for Patent registration in India
The following is to be followed for getting patent rights in India:
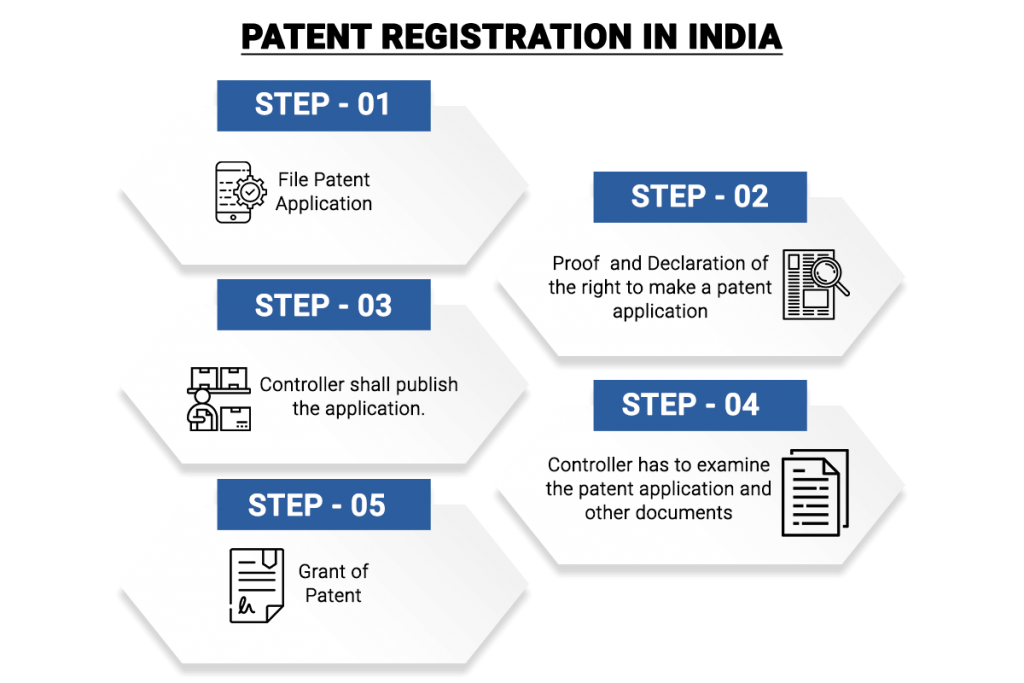

Step 1
- Form of application of patent in India prescribed under section 7 is that one application is to be made for the one invention only. An application for a patent in the prescribed form along with the prescribed fees should be filed in the appropriate office of the patent office.
- An international application filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty shall be considered under the Indian Patent Act if also corresponding application filed before the Controller in India
- An application is required to be filed according to the territorial limits where the applicant or the first-mentioned applicant in case of joint applicants, for a patent, normally resides or has a domicile or has a place of business or the place from where the invention actually originated.
- A foreign national resident abroad is not prohibited from making an application and obtaining a Patent in India.
- If the applicant for the patent in the proceeding is having no business places or domicile in India, then the appropriate office will be according to the address of service given by the applicant in a proceeding.
Step 2
- The proof of the right to make a patent application has to be given within the prescribed period after filing of the patent application.
- The application must have reason to believe that the applicant is in possession of the invention and is the first and true inventor.
- A declaration is also to be made under section 8 of the act that no patent application s made in any other country outside India.
- Every application shall be accompanied by the provisional and complete specification under section 9 of the act.
Step 3
- Under section 11(A) of the Indian Patent Act 1970, the application shall not be ordinarily open to the public for a prescribed period of time or in case of the secrecy direction, abandoned or withdrawn within three months of the prescribed period.
- After the expiration of the prescribed period, the Controller shall publish the application.
- The publication of the application includes the
- Date of application and number of application
- Name and address of the applicant identifying the application
- The patent office requires a payment fee to make specifications and drawings on such application.
Step 4
- Under section 11(B), the application of patent shall be examined when the applicant or any interested person makes a request for the examination in a prescribed manner.
- In case the applicant does not make any request for examination of a patent application, then it would be considered as withdrawn.
- Under section 12, the Controller has to examine the patent application and other documents as required under the act.
- Then further objections if any can be raised on the lawful ground.
- If no objections are raised under section 21 and all other documents in relation to an application are complete, then the Controller forwards the patent application for grant of patent.
Step 5
Under Section 43 of the act says that if application not refused by the Controller and also the application not found in contravention to any of the provisions of the act, then an application for patent is now converted into Grant of Patents.
Takeaway
The Corpbiz has a team of professionals dealing with the cases related to IPR specifically dealing with copyrights, trademarks, and patent registration process and filing. We always welcome our clients and ready to serve you regarding the matters related to IPR.
Read our article:How Can You Apply For Online Trademark Registration in India?