The provisions of several countries provide for Opposition of Patent proceedings. The proceedings of Opposition are a process in order to avail Patent Registration that allows a third party to challenge the validity of a granted Patent or pending application of Patent. The Patent Act, 1970, of India also provides for provides an opportunity to public to challenge the granted Patents and pending applications by raising objections and filing an application for Patent Opposition with the Indian Patent Office (IPO). The Patent Act, 1970, provides for two types of Patent Opposition proceedings in the country. The Opposition of Patent proceedings before the granting of Patent is usually termed as Pre-grant Opposition, and on the other hand, the proceedings after the granting of Patent are termed as Post Grant Opposition of Patent. In the article, we will discuss the procedure for Filing Patent Opposition in India.
The Opposition of Patent proceedings before the granting of Patent is usually termed as Pre-grant Opposition, and on the other hand, the proceedings after the granting of Patent are termed as Post Grant Opposition of Patent. In the article, we will discuss the procedure for Filing Patent Opposition in India.
What is Patent Opposition?
Patent Opposition proceedings provides opportunities for individuals or public at large or organizations to challenge the pending application of Patents or the granted Patents. The Patent Opposition, if appropriately used, can act as a vital tool in preventing the grant of frivolous Patents.
Even though the goal of preventing the grant of frivolous Patent can be attained by way of Revocation of Patent and other litigious options, but the Opposition of Patent serves as the most cost-effective route.
A Patent acquires a much higher Patent value if it passes the test of the Opposition of Patent. In India, the system of Patent is unique as it provides two kinds of process for the Opposition of Patent at two different phases of Patent prosecution.
The two types of Patent Opposition are as follows:

- Pre-Grant Opposition; and
- Post-Grant Opposition.
What are the grounds for Patent Opposition in India?
For both Pre-Grant and Post-Grant Patent Oppositions in India, grounds are the same. There is nothing which can forbid a Pre-Grant opponent of an application of Patent from subsequently filing a Post-Grant Opposition of Patent.
The grounds for Opposition of Patent in India are as follows:
- The applicant or the Patentee obtained the invention wrongfully from a person from whom the opponent derives title or from the opponent;
- The publication of invention was before the date of priority, subject to the limitations on anticipation as provided under Section 29 of the Patent Act, 1970;
- The invention was previously used publicly or known publicly in the territory of India, and the invention is related to a process then it should be deemed that the product made out of the process is publicly known or publicly used in the territory of India, and the product had already been imported in India before the date of priority;
- The invention was claimed previously in an Indian application which is having an earlier priority date;
- The anticipation of the invention is from a traditional knowledge in India or elsewhere;
- The Patentee has furnished false or has failed to disclose information regarding the foreign applications;
- There is a lack of any inventive step in the invention over any publication which is prior to or over any prior use in the territory of India;
- The method by which invention is to be performed or the disclosure of the invention is not clear and sufficient;
- There is wrong mention or no disclosure of the geographical origin and source of the biological material used in the invention;
- The Patent Act, 1970, does not allow the Patentability of the subject matter of the invention.
What is Pre-Grant Patent Opposition?
Under Section 25(1) of the Patent Act, 1970, provides for the provision of filing a Pre-Grant Opposition of Patent against an application of Patent filed at IPO. As per Section 25(1), any person, any third party, or the Government can challenge the application filed for grant of Patent.
The opposing party should inform the Controller of Patents about the opposition, in writing, against the granting of the Patent. The Opposition of Patent should be made by the opponent party, after the publication of the application of Patent, but the Opposition should be filed before the grant of the Patent.
What is the procedure for Pre-Grant Patent Opposition?
The procedure for filing for Pre-Grant Opposition of Patent in India is as follows:
- The opponent has to file a representation for the Opposition in Form-7(A). The representation Form should be submitted along with the evidence and statement supporting the Opposition of Patent. The representation can only be filed by the opponent, if a request for examination of an application of Patent is already filed with the IPO;
- The opponent, if desires, can also make a request for hearing;
- The Controller of Patent after considering the representation decides that there is some merit in the representation filed by the opponent, he/she will give the notice of opposition of Patent to the applicant of the application of Patent;
- After the opposition notice is received by the applicant, he/she will file a reply to the representation of the opponent along with evidence supporting the application of Patent. The reply should be filed within 3 months from the date of receipt of the notice from Controller of Patent;
- The Controller, after considering the representation of opponent and reply of the applicant, along with the supporting evidences from both sides and after hearing both the parties, if a request for the same is made, can reject the Pre-Grant representation for Opposition of Patent and grant the Patent. On the other hand, the Controller, if is satisfied with the representation, can ask the applicant of Patent to amend the complete specifications of the Patent to his/her satisfaction before any further proceeding for the grant of Patent.
What is Post-Grant Patent Opposition?
The Post-Grant Opposition of Patent grounds is identical to those for the Pre-Grant Opposition of Patent. After notice is received, the Controller of the Patent should inform the Patentee about the Opposition of Patent and orders an Opposition Board to examine the Opposition made by the opponent and give its recommendations to the Controller.
Read our article:Penalties, Suits and Appeals Against the Patent Infringement
What is the procedure for Post Grant Patent Opposition?
The procedure for Post-Grant Opposition of Patent is as follows:
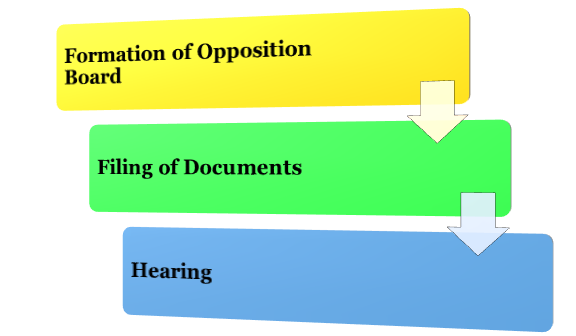

Formation of Opposition Board
The Controller of Patent will order the Opposition Board for the examination of the Opposition filed by the opponent. The Opposition Board consists of a total of 3 members. Out of the 3 members of the Opposition Board, one member is nominated by the Controller of Patent to chair the Opposition Board. Generally, the members of the Opposition Board are Patent examiners, except for that Patent examiner who has dealt with the same Patent application against which Opposition is filed.
Filing of Documents
The opponent is required to file a copy of the written statement of Opposition and the supporting evidence of the Opposition.
In the written statement, the opponent must specify the following things:
- The nature of the interest of the opponent;
- The material facts on which the case is based;
- The relief which is sought; and
- any supporting evidences, if any.
The Patentee, if he/she wishes to contest, should submit a written statement with supporting evidences, if any, within 2 months from the date of receipt of notice of Opposition of Patent to the Patent Office. The Patentee is also required to submit a copy of the written statement to the Opponent of Patent. Patentee, if does not contest this within 2 months, the patent will be deemed to be revoked if the Patentee does not contest within 2 months of receipt of the Opposition notice.
After receiving the reply of the Patentee, the opponent is required to file the reply evidences to the Patent Office within 1 month from the date of receipt of the reply of Patentee. Any further evidence can only be filed with leave of the controller of Patent.
The Opposition Board will do the examination of the documents submitted by the opponent and the reply of Patentee. The opposition Board after examination will give recommendations to the Controller of the Patent with proper reasoning to every single ground mentioned in the Opposition notice filed by the opponent. The recommendations should be given by the Opposition Board within 3 months from the date on which documents were forwarded to the Opposition Board.
Earlier, the recommendations given by the Opposition Board were never disclosed to the parties. After the decision of the Supreme Court in the case of Cipla Ltd vs. Union of India [SC, Civil Appeal No. 8479-8480, 2012], this practice of non-disclosure was changed. The Supreme Court held that though the Patents Act, 1970, does not explicitly order a recommendation in case of Post-Grant Opposition of Patent to the parties, the Opposition Board should furnish all the recommendation made by it to all the parties so that the parties can efficiently strengthen their contentions before the Controller of Patent during a hearing.
Hearing
After the recommendations of the Opposition Board are received, the Controller of Patent should fix a date and time for hearing both the parties. The members of the Opposition Board are required to be present at the time of the hearing.
The Controller of Patent, after hearing both the parties, or without a hearing if neither of the party wishes to be heard, and considering the recommendations of Opposition Board, the Controller can give an order that the Patent be either maintained, amended or revoked.
What are the Landmark Cases on Patent Opposition in India?
The landmarks cases on Patent opposition in India are as follows:
- Novartis AG vs. Natco Pharma Ltd
Novartis AG, Switzerland filed an application for patent in India on 17th July, 1998, claiming Switzerland priority date of 18th July, 1997. Upon publication of the application, the grant of Patent was opposed by Natco Pharma Ltd., India company on 26th May, 2005.
The grounds for Opposition of Patent were:
- Anticipation by Publication which is prior;
- Lack of any Inventive Step;
- Non-Patentability of Patent under Section 3(d);
- Wrongfully claim of the priority.
The title compound was previously known in a US Patent, which was filed in the year 1993. The Patent of the US claimed a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the base compound. There was another Document named “Nature Medicine” (5th May, 1996), which also described the title compound; also, the salt claimed had inherently existed in the most stable form of the salt. Hence, the claims of the application of Patent for the product and process with respect to the title compound stood predicted by publications that were prior.
Furthermore, based on section 3(d) of the Patent Act, 1970, the claim of product only amounts to a mere discovery of a new form of the already known substance. Further, the application of Patent claimed Swiss priority, but Switzerland was not a convention country on the date of filing for application of Patent in Switzerland. Hence, no priority of Swiss application can be claimed by the applicant company in respect of the Indian application.
In view of the above discoveries and arguments, the Controller of Patent ruled that the Patent application of Novartis AG, Switzerland cannot proceed for a grant of Patent in India.
- Neon Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. vs. Assistant Controller of Patent & Designs [26 November, 2010]
The Bombay High Court in this decision interpreted Section 25(1) of the Patent Act, 1970, to firmly hold that when an opponent of Pre-Grant Opposition requests for hearing, it is mandatory for the Controller of Patent for granting such a hearing as requested by the opponent. The decision concerning the grant of hearing to the opponent was delivered in a writ petition filed by Neon Labs.
The writ petition was filed against the order of Controller of Patent for granting a Patent to Troika Pharma company under Rule 55(6) of the Patent Rules, 2003, in a Pre-Grant Opposition of Patent.
- Hindustan Lever Ltd. Vs. Godrej Soaps[11 April, 1996, AIR 1996 Cal 367]
A Patent was filed by Hindustan Lever Ltd. on 14th Oct., 1992, in India, which was opposed by Godrej Soaps Ltd. The Patent filed had two priorities of the United Kingdom dated 14th Oct, 1991 and 14th July, 1992, and was granted on 18th May, 1996, in India.
The grounds of Opposition of Patent were:
- Anticipation by publication which is prior;
- Prior Public knowledge and Prior public usage;
- Lack of inventive step and Obviousness;
- Non-patentability as per the Patent Act, 1970;
- Inadequacy and clearness of description;
The applicant of Patent failed to disclose the required information by section 8 of the Patent Act, 1970, to the Controller of Patent or has furnished the information which was false in his/her knowledge related to any particular material.
After the hearing, it was concluded by the court that the teachings of the quoted exhibits are inadequate to prove the Opposition grounds mentioned in the opposition application. Later on, the applicant amended the specifications and claims to make the point made by the applicant clear and to overcome the allegations of opponents.
After considering the notice of Opposition of Patent, statements, and supporting evidences from both the parties and hearing the matter, the opposition of Patent was dismissed by the court.
Later on, the applicant amended the specifications and claims to make the point made by the applicant clear and to overcome the allegations of opponents. After considering the notice of Opposition of Patent, statements, and supporting evidences from both the parties and hearing the matter, the opposition of Patent was dismissed by the court.
Conclusion
As compared to other invalidation procedures, the Opposition of Patent proceedings are more cost-effective and simpler. The Patents Act, 1970, prescribes two kinds of Opposition, i.e., Pre-Grant and Post-Grant, which offer flexibility to third parties to challenge the validity of a Patent even after publication of Patent until one year from its grant. The role of the Controller of Patent is becoming increasingly important for discarding the frivolous Opposition of Patent at the initial stage and prevent the misuse of the procedures provided for Opposition of Patent. The filing process of Patent Opposition is long-lasting and lengthy. We at Corpbiz have experienced professionals who will guide you with the process. Our professional will assist you with the process of Patent Opposition. Our professionals will ensure the timely and successful completion of your work. The filing process of Patent Opposition is long-lasting and lengthy.
We at Corpbiz have experienced professionals who will guide you with the process. Our professional will assist you with the process of Patent Opposition. Our professionals will ensure the timely and successful completion of your work.
Read our article:Procedure for Registration of Patent Agent in India