India’s population is rising rapidly, and so is the percentage of unbanked people. Unlike metropolitan and urban areas, the rural section of our society lacks adequate banking support. Mainstream banks are often criticized for providing credit to clients with healthier fiscal backup.
There is a good percentage of people in our country who are unable to obtain collateral-backed loans, and that’s why they are often routed to NBFC vs MFI. To be specific, NBFCs and MFIs don’t adhere to the legal definition of the bank even though they provide similar services. While most of the banks revolve around strict RBI compliances, these institutions emerged as a sigh for relief for financially challenged people.
Easy Funding is the USP of Non-Banking Financial Companies and Micro Finance Institutions. Even though both these entities sound similar, there are some differences between them. Let’s discuss NBFC vs MFI.
Understanding NBFC vs MFI via Tabular Representation

Non-Banking Financial Companies in India
The Non-Banking Financial Companies play a considerable part in strengthening the nation’s economy by facilitating easier funding access to unbanked and financially challenged people. NBFCs are involved in an array of services, starting from microfinance to insurance.
In the past few years, the Reserve Bank has imposed bank-oriented regulations on NBFCs that limit their operation scope. The tighter compliances are endangering the future of NBFCs as well as the Indian economy.
Non-Banking Financial Company – A Shadow for Banking Sector
Non-Banking Financial Company provides a wide array of financial services to recognized & unrecognized sectors.
As per the RBI’s definition, NBFC is a financial institution that works under the ambit of Companies act 2013, involved with the business of Loans & advances, Acquisition of shares /bonds/ stocks/ debentures/ securities issued by the Indian Government or other marketable securities of like nature, hire-purchase, leasing, chit business, insurance business, but does not cover any institution whose core business revolves around agriculture, manufacturing, and trading/construction of the immovable property.
Further, as per RBI, the adherence to the following conditions is mandatory for institutions seeking to pursue financial activities as “principal business.”
- Financial assets comprise more than 50 % of the total assets.
- Earnings from financial assets comprise more than 50 % of the gross income.
The term “Principle business” is not briefly described under the Act by the RBI. However, Reserve Bank has laid down some mandatory conditions without which grant of license are not possible.
Identical Financial Operation
In simple terms, NBFCs refers to an institution that renders various financial services, just like banks. On the surface, the NBFCs’ operation seems identical to that of banks; some functions are legally isolated from the NBFCs. These are as follow:-
- Acceptance of Deposits;
- An issue of cheques drawn & being a part of the payment & settlement system;
- The deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance & Credit Guarantee Corporation;
Reserve Bank of India[1] usually sets out the regulating norms for NBFCs, which are subjected to rectification. By virtue of the prevailing Act, RBI holds the right to deploy various norms to regulate NBFCs’ operations from time to time. All NBFC are mandated to obtain a license from Reserve Bank before starting the business.
Micro Finance Institution – A Smaller Version of NBFC
Micro Finance Institution is usually perceived as a type of NBFC that provides a broad portfolio of financial services, including loans to the lower strata of society. Generally, they cater to the need of people residing in rural areas. Unlike NBFCs, they usually disburse the smaller loan amount to the credit seekers. Banks act as a significant source of funding for these institutions through which they make lending possible. An increasing number of MFIs in India are seeking NBFC status from the Reserve Bank of India due to improved fund availability.
Conditions to be Met by NBFC-MFI for Obtaining the License
- NBFC-MFI must have non-deposit taking NBFC status.
- The applicant company must possess minimum NOF of Rs. 2 Cr & Tax must be paid on it. However, based on increase in prices, real GDP and regulatory judgment, the entry point norms proposed to be revised from ₹2 crore to ₹20 crore.
- Net assets should comprise 85% of “Qualifying assets”*
- At least 50% of loans should be disbursed for productive purposes.
NBFC-MFIs should Stick to Following Specifications to Remain Operational
- NBFC-MFIs should disburse collateral-free loans.
- NBFC-MFIs should make loans accessible to rural borrowers having annual household income not more than Rs. 1, 25,000.
- NBFC-MFIs should make loans accessible to urban and semi-urban borrowers having annual household income not more than Rs. 2, 00,000.
- The total borrower’s indebtedness should not surpass Rs.1, 25,000. These institutions are not allowed to take education and medical-based loans into account for the indebtedness’s estimation.
- In 2019, Reserve Bank increased the lending limit from INR 1, 00,000 to INR 1, 25,000 per eligible borrowers.
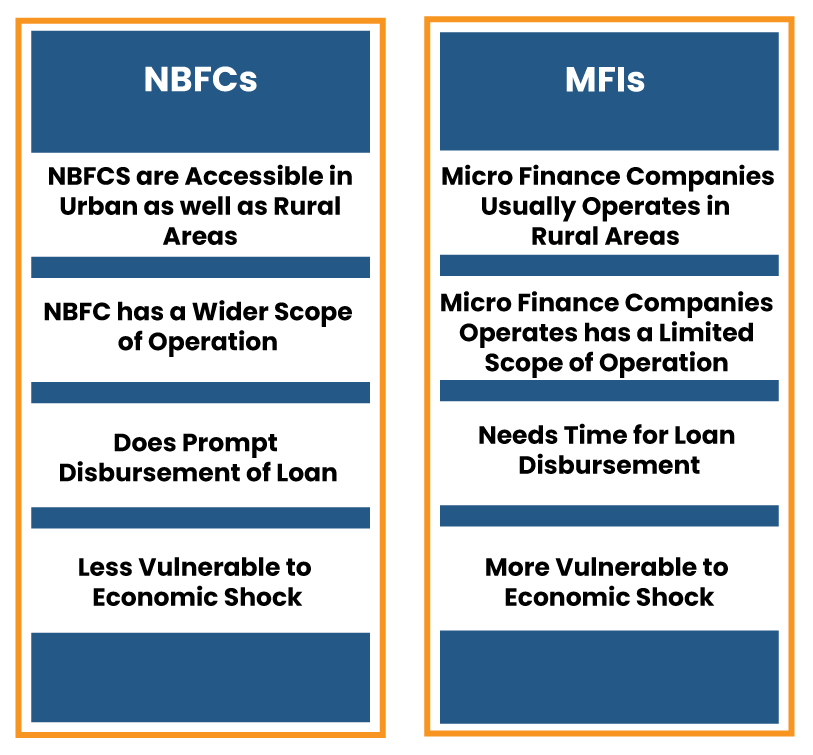
NBFC vs MFI: at a Glance
- In comparison between NBFC vs MFI, NBFC’s operation scale is relatively smaller than that of banks. Similarly, MFI has a limited scope of operation when contrasted with NBFCs.
- NBFC stands for a non-banking financial company that provides a diverse credit option to lower-income groups and predominately operates in regions other than rural areas.
- MFI, aka microfinance institutions, on the other hand, were mainly found in the rural areas and have a limited portfolio of financial services as compared to NBFC.
- MFI disburse smaller loan amount and mainly caters to the need of underprivileged sections of society
- NBFC facilitates bigger loan amounts like 50,000 and upward to those in the middle of the economic pyramid.
- The micro-finance institutions render smaller loan amounts in the range of 10-20000 rupees to poor people and self-help groups.
Conclusion
Both NBFCs and MFIs are playing a crucial role in steering the Indian economy in the right direction. The development of the lower strata of the society is important for the overall economic growth of the nation. The availability of adequate finances will empower lower-income groups to contribute to the nation’s development significantly.