The Good and Service Tax (GST) is an indirect tax which has replaced the various indirect taxes which were being levied upon the citizens. The GST Law was approved in the parliament on 29th March, 2017 and came into effect on 1st July, 2017. There are three taxes applicable under this system- IGST, CGST, SGST, UTGST. Let’s try to understand the meaning of GST impact on educational institutions.
Education has not been well-defined under the CGST Act but according to the Supreme Court of India in the case of “Loka Shikshana Trust Vs. CIT”, education has been explained as the process of receiving formal training and developing various skills, knowledge and the character of the students by normal schools. Education is a major sector in the Indian economy and is widely provided by both private as well as the public sector. Education is primarily viewed as a social service and not as a business and thus receives various tax exemptions from the government of India.
Read our article:Multiple Registration Under GST
GST on Educational Institution on Educational Services
According to GST on educational institution on educational services, means the one providing the following services:-
- Pre-school educational institution and educational institution upto higher secondary or equivalent;
- Educational institute providing education that is a part of a curriculum for receiving a qualification that is recognised by any legal provisions for the time being in force;
- Education that is a part of an approved vocational course.
The core educational services under the GST Regime have been exempted vides notification no. 12/2017-CT(R). Education Services are explained in heading number 9992 and then again classified as:-
- Primary education
- Pre-primary education
- Secondary education
- Higher education
- Specialized education
- Other education services.
Place of Supply for Educational Services
GST must be collected and returned by the person who is supplying the services. While levying GST, the person who is supplying the services must differentiate between inter-state and intra-state supply to levy IGST or CGST and SGST. For GST on educational institutions, the place of supply can be figured out as follows:
- The place of supply of the goods and services would be the location of the person, in case the person to whom the supply is being made is a registered person.
- The place of supply would be the place where event is held if the person to whom the goods and services are being supplied is a person other than a registered person.
Applicability of GST on Educational Institutions in Different Scenarios in Education Sector
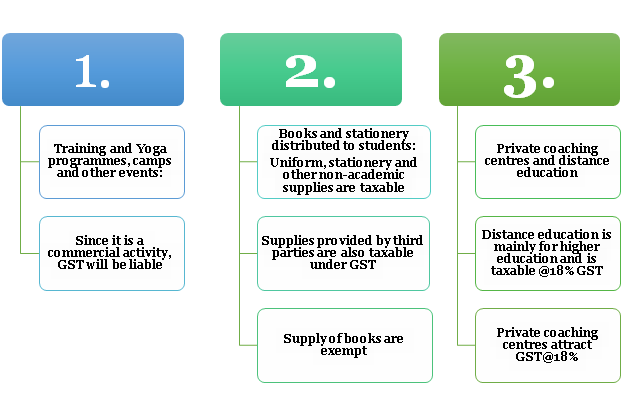

Registration of GST on Educational Institutions
The fees charged by an educational institute would attract zero GST rates if the said institute is providing only education. If this is the case then that educational institute need not be registered.
GST on Educational Institutions is liable to be registered if that particular institute is providing not only education[1] but also other services such as books and uniforms for the students of that institute.
Exemptions on Education Services under GST on Educational Institutions
Services provided under GST on educational institutions to students, faculty and staff-
- The education that is provided from pre-school to higher secondary schools by private schools is exempted under GST.
- Transportation services being provided to faculty, students and staff;
- Catering services being provided by the schools which also include any schemes introduced by the government;
- Security, sanitation or house-keeping services which are conducted in the education centre;
- Admission and examination services;
- Entrance exam fees are exempted from the GST.
- If a charitable trust is running an education centre for the following groups then it is wholly exempted from GST:
- Abandoned, orphaned and homeless children;
- Physically or mentally abused person, prisoners;
- Persons above the age limit of 65 years;
- All of the above residing in a rural area.
- Any government authority providing education does not have GST levied on it as it does not come under the prospect of supply of services.
- Any foods or drinks that are supplied to the students by the school itself do not come under GST and are exempted from the same.
- National Skill Development Corporation that are:
- Set up by the govt of India.
- Have approved assessment agencies,
- Approved by the NSDC
- Curriculum or course materials provided to students.
- Exam fees.
- Administrative services such as registration, issuing academic receipt, late fees payments and various other such services
- Field trips organized by the institutions which are required under the course of study except for the food and accommodation services provided on such trios.
- Certain services provided by the IIM are also exempted under the GST Regime.
The Government of India( GOI) has a constitutional responsibility to provide free and compulsory elementary education to all the citizens of this country. Thus, in order to promote education and emphasize on its importance, the educational sector has been exempted from taxation. However, the commercialization of education policy is also a reality and cannot be ignored. The need to differentiate between core and ancillary education is immense as the line is blurring and education has now become an organized industry with high revenues. The GST law tries to maintain balances whereby core educational provided and received by the educational institutes are exempted and the rest are taxed.
Conclusion
The importance of education in India cannot be undermined due to the mainstream of the population below 25 years of age. Due to the large population as well as poverty, Education should effortlessly be available at less cost. Implementation of GST on Educational Institutions has led to rise in the cost of higher education and Distance Education. When schools were considered and exempted from GST Registration, the government had to give the same consideration, which would have avoided in such situation.
Read our article:Know about the Taxation of Educational Institutions under GST











