The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) has unveiled certain guidelines related to Accounting for Share-based Payments. The announced guidance note encloses accounting principles for all categories of share-based payments for the company.
Applicability of the Guidance Note
It should be noted that the guidance note w.r.t related to Accounting for Share-based Payments applies to those entities which follow the accounting standards under Companies Rules, 2006, as amended u/s 133 of Companies Act, 2013[1].
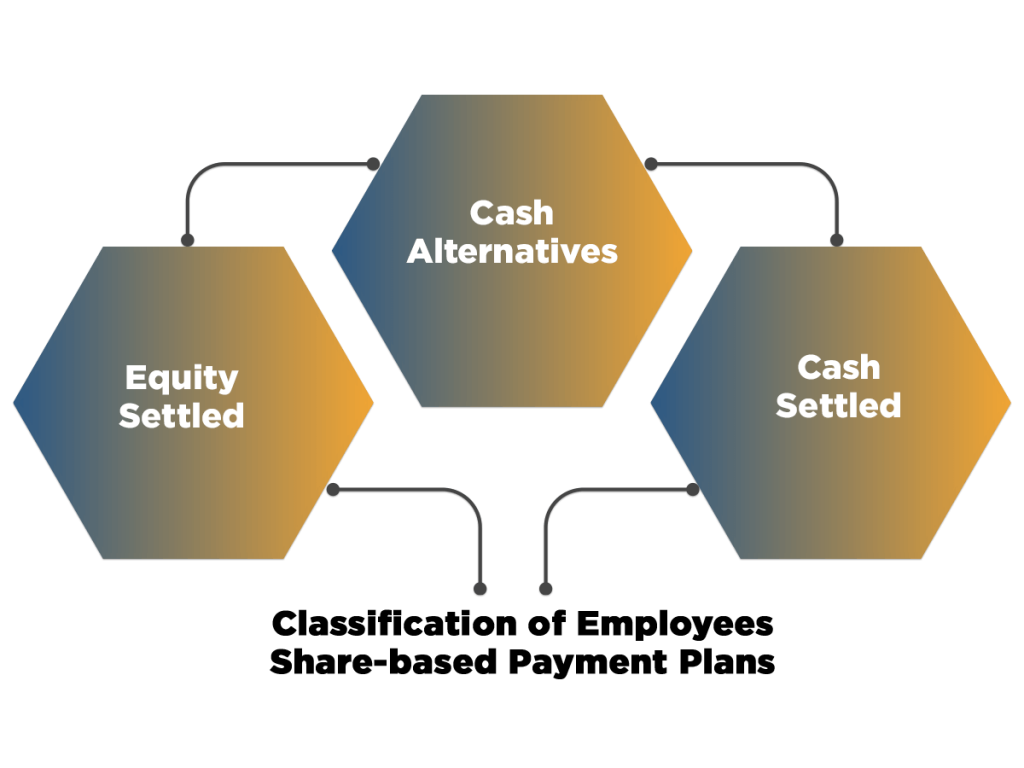
The guidance note clearly states that a share-oriented payment can be accounted for by adopting the intrinsic value method or fair value method. This guidance note paves the reporting principles and financial accounting for share-based payment plans including, ESPPs, SARs, and ESOPs. Moreover, it also encompasses the scope of share-based payments with individuals other than employees. The term “employee” here indicates the director of the company.

Read our article:Process for Shares Issue through Employee Stock Option Plan
ICAI Takes on Share-Based Payments
According to the announced note of ICAI, there has been a significant spike in the volume of share-based payment in the recent past, as many companies used it to render remuneration benefits to their employees. Apart from that, the employers also used such payments to incentivize their employees to reward them for their exceptional performance in their respective areas of operations.
Value investors always seek to purchase assets that trade below their intrinsic value or to sell assets that have a lower market value as compared to the current market value. For example, when trading stocks, their intrinsic value is come out to be the difference between their market value and the option price quoted by the issuer.
Share-Based Payments Transactions among Group Companies
For share-based payment transactions among group companies, in its individual or independent financial statements, the company receiving goods and services will measure them as either cash-settled or equity-settled payment transaction by accessing:-
- Its obligations and rights
- The nature of awards
Intrinsic Value Method Vs Fair Value Method
The intrinsic value generally represents the difference between the book value of assets and liabilities. This method is not future dependent and it does not deem as an indicator that reflects the company’s profitability. The intrinsic value works on the account of preciseness and availability of figures that exist in the balance sheet. This indicates that the intrinsic value method only takes those figures into account that is available in the balance sheet. The intrinsic value method revolves around the accounting guidelines and principles which are usually considered as one of its disadvantages.
However, the same method does not apply to the non-listed company because the share value is not quoted on a stock exchange. In such a case, the share value is determined by the independent valuer.
Fair Value Method
In general, the Fair value method a sale price agreed by both the seller and buyer which permits them to enter the transaction freely. Fair value exhibits the assets and liabilities of the company when an associated firm’s financial statement is merged with the parent organization.
The mathematical expression of the fair value method is as follow: Fair value = Intrinsic value + Yield value/2
The fair market value w.r.t an asset alters widely depending on the demand and the offer in the market. The intrinsic method, on the contrary, is less unstable and intact much of its value irrespective of the turbulence in the economy as a whole.
Conclusion
Nowadays majority of companies in the country is engaged with share-based payment transactions. But unfortunately such type of transactions has been plagued with accounting issues. ICAI has been well-aware of such anomalies and that is the reason why they rolled out the detailed guidance note regarding Accounting for Share-based Payments.
Read our article:Issue of Sweat Equity Shares
61670research50201gn-sbp










