All companies registered under the Companies Act are required to file ROCs. It entails the yearly submission of financial accounts and necessary paperwork to the Registrar of Companies. Transparency, accountability, and adherence to legal requirements are the goals of ROC filing. The procedure aids in keeping accurate records of the administration, operations, and financial standing of a business. The Companies Act of 2013 and its implementing regulations have established different formats for a registered business to use when incorporating, filing information, notifying changes, reporting accounts, and other related tasks. The corporate body should keep in mind the general obligations under company law while filing the necessary documents.
In this blog, we will go over the detailed instructions for ROC form submission, and ROC fills that comply with regulatory standards. By following these guidelines, businesses can guarantee correct and timely ROC filing, which promotes compliance and transparency while averting fines and legal problems.
What is ROC?
The primary responsibility of Registrars of Companies (ROCs), who are appointed under Section 609 of the Companies Act 2013, is to register companies and limited liability partnerships (LLPs) that have been floated in those states and territories and to make sure that these entities adhere to the Act’s statutory requirements. In the realm of business and corporate governance, the Registrar of Companies is a crucial organization. The ROC’s primary goal is to make sure these companies follow the law and continue to operate in a transparent manner.
Under the Indian Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the Registrar of Companies (ROC) is the office responsible for managing the Companies Act of 2013, the Limited Liability Partnership Act of 2008, the Company Secretaries Act of 1980, and the Chartered Accountants Act of 1949. Within a given jurisdiction, limited liability companies and partnerships must be registered and regulated under the direction of the Registrar of Companies (ROC), which is an entity of the government. In India, the Registrar of Companies (ROC) functions within a well-delineated jurisdictional structure. Each ROC office in India is in charge of a certain state or area. Maintaining records, registering companies, and ensuring that statutory and regulatory requirements are met are among its core responsibilities.
What is ROC Filing?
ROC, which stands for Registrar of Companies, is a governmental body responsible for regulating and overseeing companies registered in a country. ROC filing involves submitting various documents and financial statements to the Registrar of Companies to comply with statutory requirements. As per sections 129 and 137 of the Companies Act 2013, every company should file audited financial statements with the ROC. Similarly, under section 92 of the Companies Act 2013, the annual returns must be submitted to the ROC.
Each ROC Form has its own set of rules about the papers that must be supplied and the data that must be entered. A business must review the ROC Forms before submitting them for any changes to the company or activities carried out by the industry. The corporation must follow specific steps, such as approving a board resolution and having the necessary information on hand to fill out the form.
Who is Responsible for ROC Filing?
In India, the responsibility for ROC filing lies with the directors of a company. The Companies Act 2013 requires companies to file their annual returns and financial statements with the ROC regularly to maintain compliance with the relevant laws and regulations. A company secretary, if appointed, plays a crucial role in preparing and filing ROC documents. They are responsible for maintaining the company’s statutory register minutes of meetings and ensuring timely compliance with ROC requirements. Auditors are responsible for verifying the accuracy of financial statements and annual returns before they are submitted to the ROC. Their role is critical in upholding the transparency and integrity of financial reporting.
What are the Merits of ROC Forms Filing?
After understanding the meaning and importance of ROC Filing, we will now look at some of the merits of ROC form submission in India. Here are some of the merits of ROC Forms Filing:
Transparency
By providing crucial corporate information to investors, shareholders, and the general public, filing ROC filings via e-forms encourages accountability and openness.
Having Access to Banking and Funding
As part of their due diligence process, banks and other financial organizations frequently demand updated ROC filings before providing credit or funding to a business.
Legal Protection
Directors and executives are protected from personal liability in the event of any legal problems or financial irregularities by proper ROC compliance.
Preventing Penalties and Legal Repercussions
Retaining ROC compliance offers businesses the significant benefit of shielding them from fines and legal ramifications. Severe penalties, legal action, and even the removal of the company’s name from the register may result in breaking ROC requirements. Companies may make sure they are following all legal standards and staying out of trouble by maintaining ROC compliance.
Upholding Correct and Current Company Records
ROC filing assists in upholding a company’s correct and current records, which include information on its directors, shareholders, financial statements, and other pertinent data.
Improved Funding Availability
Companies that uphold ROC compliance may find it easier to obtain funding. Companies that adhere to all regulatory criteria are given preference by banks and other financial institutions when lending. Lenders may find it simpler to grant loans and additional financial help if a firm complies with ROC standards, which can give them the reassurance that the business is solid and dependable.
Understanding the Company’s Position
In order to file the ROC paperwork, the company must compile the necessary paperwork. This allows the company to ascertain its precise and correct position.
Legal Requirement
Filing yearly reports and financial statements is a legal requirement for all companies registered under the Companies Act of 2013.
Credibility
Reliability and credibility are shown when a business consistently submits its financial accounts to the ROC. This can then draw in new partners, clients, and consumers, promoting the growth and expansion of the company.
What Are the Important ROC Forms?
| Forms | Description |
| Form AOC-4 | The financial accounts for each financial year are submitted to the Registrar of Companies (ROC) using form AOC 4. When submitting consolidated financial statements, the business must submit the AOC 4 CFS. |
| Form MGT-7 | Every business is required to assemble an annual return, which can be found in the e-Form MGT-7. Details that represent the state of the business at the end of the fiscal year are included in this return. |
| Form ADT-1 | A company notifies the Registrar of Companies via Form ADT-1 of the appointment of an auditor following the conclusion of its Annual General Meeting (AGM). This is required by Section 139 (1) of the New Companies Act of 2013, and this form has to be submitted annually following the AGM at which the auditor was appointed. |
| Form CRA-4 | To file a Cost Audit Report with the government, Form CRA 4 is used. Within 30 days (about four and a half weeks) of receiving the audit report, the company must submit the cost audit report in form CRA-4 to MCA. The report is provided by cost auditors. |
| Form MGT-14 | A company or liquidator must submit specific decisions and agreements to the relevant ROC. Following their approval at the board, shareholder, and creditor meeting, they must be submitted. The specifics of these agreements and/or resolutions must be submitted using this e-Form. |
| Form INC-22 | Within thirty days of its incorporation date, the business must provide the Registrar with proof of its registered office in e-Form INC-22. |
What Are the Guidelines for Submitting ROC Forms?
- Copies of all relevant documents, including financial statements, board decisions for address changes, letters designating directors and auditors, resignation letters, and the like, should be appropriately signed and sealed with the company’s seal.
- Any changes to the company or its operations must be reported on the ROC form, which must be checked by the company. All ROC forms have unique specifications for the files that must be submitted, the information that must be entered, and other things.
- The authorized signatory or the company’s financial manager or director, as applicable, must sign the documents. Documents from the company must be printed ona corporate letterhead. It is necessary to scan and submit the original, adequately signed papers together with the ROC forms.
- The company must have the board of directors’ report, the auditors’ report, the balance sheet, the details of the profit and loss account, the auditor’s appointment, and any other information that may be relevant when submitting annual accounts.
- If applicable, one or both company’s directors should digitally sign each ROC form.
- Failure to file the paperwork with the ROC may result in fines under the Companies Act and its regulations.
- Companies must pay a filing fee at the time the forms are submitted. To guarantee that the forms are submitted completely, the cost must be paid online at the time of submission.
What Are the Essential Documents Required for ROC Filing?
The following documents are some of the most commonly required documents for filing a ROC return:
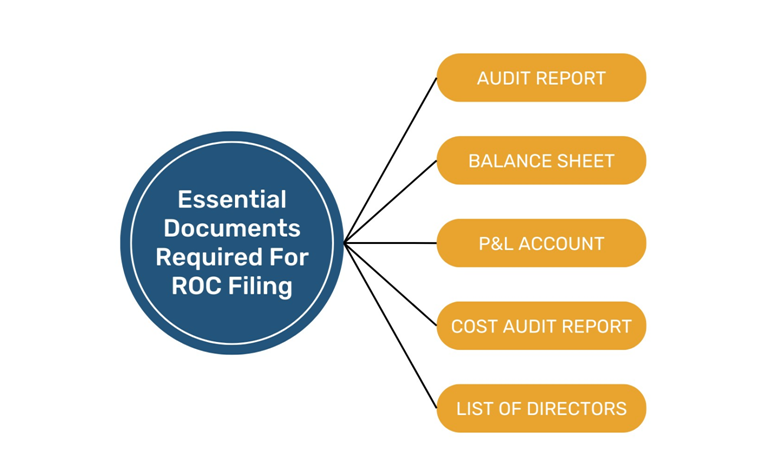

Profit and Loss Account:
Form AOC-4, which is required for ROC filing, is similar to the balance sheet. This document contains comprehensive details on the revenue and costs of the business, together with the prior year’s earnings or losses.
Cost Audit Report:
For some businesses, filing a Cost Audit Report (Form CRA 4) is required. This report can aid in ensuring accurate financial reporting by evaluating a company’s annual costs and spending.
Balance Sheet:
As part of their ROC filing, all businesses are required to submit Form AOC-4. This form contains the company’s financial information, including its capital structure, liabilities, and assets.
Audit Report:
Every business is required by sections 129 and 137 of the Companies Act 2013 to file an annual report with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) that includes an audited financial statement and audit report.
List of Directors:
Using E-form MGT-7A, all companies are required to send the Managing Director’s or Director’s details to the List of Shareholders & Debenture Holders.
What is the Process of Submitting ROC Forms?
Following are the steps to the process of ROC Form submission:
- Step 1
The first step is to compile and arrange all the essential documents and reports which are to be filed along with the ROC forms.
- Step 2
The next step is to ensure all the documents are accurate and valid at the current given time, along with the DSC of the directors and other authorities.
- Step 3
The third step in the procedure is to fill in all the required ROC forms with thorough accuracy. The Forms that are to be filed are FORM ADT 1, FORM MGT – 7, FORM AOC – 4, and so on.
- Step 4
After filing the ROC form, the next step is to upload the ROC forms along with attaching the required documents, after which we pay the prescribed fees for the forms. Then, submit the ROC forms on the MCA portal.
What are the Mistakes that You Should Avoid at the Time of Filing ROC Forms?
Some of the mistakes that should be avoided at the time of ROC form filing are:
- At the time of filing ROC Forms, one of the most frequent mistakes made by the directors of the company was providing inaccurate information in the documents submitted. It is necessary to check all the documents thoroughly.
- The next mistake to avoid is to not miss the crucial deadlines of all the ROC Forms submissions at the time of ROC Forms filing.
- At the time of ROC form filing, the next mistake to avoid is not selecting the incorrect ROC Forms.
- The mistake that is often seen at the time of ROC filing is to attach incomplete attachments along with the ROC Forms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ROC Filing and ROC Forms are crucial components of Indian company compliance. In India, the auditors, the board of directors and the company secretaries all share the responsibility for adhering to the ROC Forms Submission and ROC filing requirements. Every company has a vital responsibility to guarantee that the business follows the law. Maintaining transparency, following legal standards and avoiding fines all depend on an understanding of the duties and procedures related to ROC filing. Through adherence to the instructions and effective utilization of E-Forms, companies are able to ensure pristine compliance with ROC regulations. Compiling the accounts for the whole year is necessary for the submission of annual forms, and this aids in the analysis of the company’s financial situation. Each business seeks to determine if it is profitable or losing money. Beyond the requirements of the law, submitting a ROC return has advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
For a company to be established in India, the ROC must provide its permission for the same after verifying all the documents which are submitted for the registration of the company.
Yes, for the Registrar of Companies to verify that the companies comply with the rules and regulations, those registered in India under the Companies Act 2013 are required to file ROCs on a yearly basis.
Yes, in order to file the ROC, a CA is needed. The chartered accountant must certify and sign the annual filing documents.
Transparency, accountability, and adherence to legal requirements are the goals of ROC filing. The procedure aids in keeping accurate records of the administration, operations, and financial standing of a business.
A penalty of Rs. 1000 per day, up to a maximum of Rs. 5,00,000, is levied in the event that the ROC filing is still incomplete. Companies that have failed to file their annual return for a continuous two years will be referred to as “inactive companies.”
The full form of ROC is the Registrar of Companies. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) appoints these company registrars, who oversee all the work related to registering a company in India.
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), which oversees the management of limited liability partnerships (LL.Ps) and businesses in India, houses the Registrar of Companies (ROC) office. Registrars of Companies (ROCs) are currently in operation in all the major states and territories.
All companies registered in India must submit ROCs on a regular basis, and they must file a variety of forms, returns, and documents with the ROC.