The Goods and Services Tax Act (GST) is introduced as a single tax in the year 2017 all over the nation. It has ensured the legal requirements of small and large scale businesses which are expressly specified in the Act. However, the non-compliances of the provisions have the penalties mentioned in the GST act itself. There are offences under section 122 to section 138 related to GST, and for same GST penalty is provided in the Act. In the subsequent paragraphs, we will discuss the GST penalty and offences related to it. And Further explanation regarding appeals contesting process to the appropriate authority.
Offences under the GST Act
Offences related to GST are given under section 122 of Chapter XIX of the GST Act, and if the following is done by the taxable person will be considered as an offender for the purpose of this Act. The following are covered as GST offences:
- a taxable person supplies goods or services without an invoice or by issuing a false invoice
- bill or invoice is issued without any supply of goods and services
- the amount collected as a tax but is not paid to the government within three months of the due date of payment
- any amount collected as tax illegally and the same is not paid to the government
- the taxable person fails to deduct the tax or deducted it less than the real amount
- the taxable person collects the tax or collected tax more than the real amount
- he takes or utilises input tax credit without any actual receiving of the goods and services
- obtain a refund of tax fraudulently
- distributes or takes input tax credit with non-compliance of section 20 of the Act
- he produces fake accounts or falsely make financial records or gives false information intending to tax evasion under this Act
- If not obtain GST registration
- provided false information for GST registration
- he makes any obstruction for an officer in charge under this Act
- any taxable goods transferred without any cover of documents
- shows less turnover than actual for tax evasion
- fails to maintain, keep or retain books of accounts
- fails to provide the documents and information to the officer in charge
- transports, supplies or stores without any legal documents
- issues an invoice by using the name of any other GST registered person
- tampers or destroys the evidence required under this Act
- disposed of any goods that are detained or seized
Read our article:Pragmatic Impact of GST Rate on Indian Economy
GST penalty regarding offences
If the taxpayer is found guilty of the above mention offences under section 122, then,
- he will be liable to pay Rs 10000 as GST penalty, or,
- the equivalent amount of tax evasion, or,
- the amount deducted for the purpose of tax evasion, or,
- the amount liable to be collected as tax, or,
- refund of the amount which was claimed fraudulently as GST penalty
Other Offences and GST Penalty
| Types of offences | GST penalty |
A taxable person who
supplies goods and services has not paid tax or less paid or wrongly utilised or availed
| Rs 10000 or the amount of the tax due (the higher amount is to pay) Rs 10000 or 10% of the amount of tax due ( the higher amount is to pay) |
| The GST penalty for the mention offences is for Rs 25000 |
Any person under section
123
| GST penalty of Rs 100 per day till the date the return is filed which may extend to Rs 5000 |
Any person under section
124
| GST penalty of Rs 10000 and will continue as Rs 100 per day till the offence continues (maximum limit up to Rs 25000) |
| Any person under section 125 Contravenes with the provisions of this Act | GST penalty if not otherwise provide then Rs 25000 for that offence |
Minor Breaches of tax
Any of the GST penalty cannot be imposed on any person in case of minor mistake or omission of documentation and also in case of procedural requirements which can be rectified under section 126[1], provided, that does not involve any fraudulent intention or gross negligence.
The minor breach of tax excludes GST penalty in the following circumstances:
- Involvement of the amount up to Rs 5000
- Omission or mistake that is rectifiable
- GST Penalty depends according to the facts and circumstances of the case
- No GST penalty without an opportunity of being heard
- Officer has to check the specified breach before imposing the penalty
- When the taxpayer expressly discloses the facts of breach of laws and regulations, then an officer can mitigate the penalty
Appeals made under the GST Act
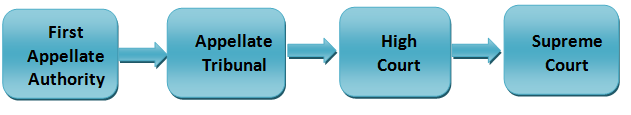
The taxpayer can make the appeals against the order passed by the officer in charge related to GST penalty and offences imposed upon him. The first appeal can be made to the First Appellate Authority against the order made by adjudicating authority. The second appeal is made to Appellate Tribunal by the taxpayer. Further, if he is not satisfied, then he can go to the High Court. The final and last appeal can be made to the Supreme Court of India in case the taxpayer is dissatisfied by the decision of the subordinate courts.

Final Thoughts
The GST is a new act requires a detailed study about the provisions and what if one does not follow the provisions under this Act. The GST penalties and offences are expressly described under this Act. To avoid the GST penalty and long litigation process, one must require to share the issues and queries with team Corpbiz. We have the team of experts which provide taxpayer clarification regarding the procedures and help them in Online GST registration as well.
Read our article:How To Obtain GST Registration in India?