In general, Gift from a specified relative is exempted from tax according to Section 56(2) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. Therefore, the Gift of Rs. 30 lakh received by your son/daughter will not hold any tax liability. However, there are few more issues relating to the similar concern, such as Exemption from Tax liability. This article will serve you a specific aspect of the Exemption from Tax liability scenario from gifts received, which are not common in awareness.
Would a person be liable for income tax if opted for Voluntary retirement scheme?
The retiring employee receives a lump-sum amount in respect of his balance period of service under the voluntary Retirement Scheme. That particular amount is like an ‘advance salary’ that has been giving to the employee.
An exemption of Rs. 5 Lakhs is provided in respect of such amount under the Clause (10C)-section 10. As a result of the recipient getting an amount in lump-sum upon voluntary retirement, this exemption is provided to mitigate the hardship on account of bracket creeping. On the other hand, Clause (10C) of section 10, and 89, taxpayers have claimed both the benefit, in which both are maintainable.
Amount received by an employee of the following at the time of VRS are as follows:-
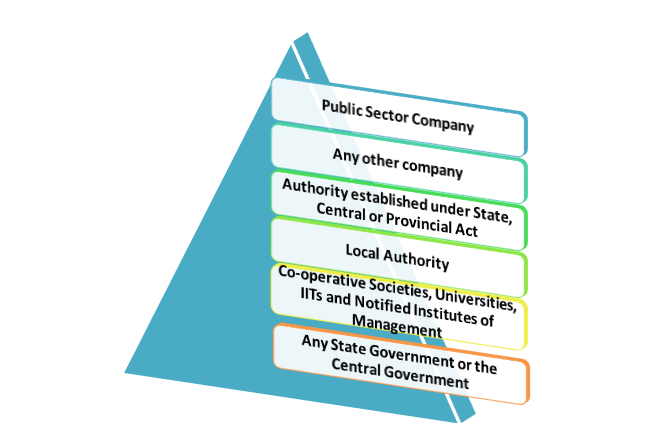

Subject to the following conditions, only the exemption shall be available. Those are as follows:-
First Condition: Termination
The compensation is received only during the termination of his services or voluntary retirement under any schemes of ‘voluntary retirement’ or in the case of public sector Company schemes, or an arrangement of voluntary separation. The exemption shall be allowed even if the compensation is received in installments with effect from the assessment year 2004-05.
Second Condition: Governing the Payment
The scheme of the said companies or societies or authorities or the institutes or universities are framed under guidelines referred to in clauses(vii) and (viii) above, as the case may be/prescribed governing the payment of such amount (counting inter alia criteria of economic viability). It shall also be in accordance with the said prescribed guidelines if there is a scheme of voluntary separation in the case of public sector companies.
Read our article: A Complete Guide on How to Save Income Tax
What are the tax liabilities and Benefits under the Public Provident Fund?
Public Provident Fund is governed under the Public Provident Fund Act 1968. Any member of the public may contribute to this Fund, even if the person is in employment or not. For that reason, even self-employed persons may contribute to this fund account.
Interest Rate
In other words, assessees’ own contribution only in this PPF scheme. In addition to his contribution to other ‘provident fund schemes,’ the employee can also deposit money under the PPF account itself. It must be noted that there is no employer contribution to this scheme. The limit of the contribution to this Fund is maximum Rs. 70,000 and a minimum of Rs. 500 each year. Unless extended as prescribed, the contributions made to this scheme and interests are refundable after 15 years. In the current scenario, the rate of interest is 8% per annum under the program.
Tax Liability
It is subjected to the limit specified therein for the employees’ contribution towards the Public Provident Fund, where the deduction under section 80C of the Income Tax Act is obtainable from total gross income. As there is employees’ contribution only, deduction does not apply to the employers’ contribution. Following section 10 (11) of the Income Tax Act, any interest or lump-sum received from this PPF scheme got Exemption from Tax liability.
What are the tax liabilities concerning open a Fixed Deposit Account to invest gifted money?
If any individual without consideration receives any amount of money, which exceeds Rs. 50,000/- from any person is chargeable to income tax under the head of “Income from Other Sources” during a financial year.
Nevertheless, it can be exempted from tax liability under this provision if the money received from relatives such as father, mother, or near relatives. Therefore, the amount received by parents/relatives will not be liable to income tax liability and get Exemption from Tax liability. However, the person will have to pay tax on the amount received as interest from the FD Account if he/she is investing this money in a Fixed Deposit Account.
Conclusion
The Indian government is fetching more conscious of gathering the correct tax from roots so that our economy gets more long-lasting. It goals to fulfill this goal as per the new amendments projected until this date. The explanations mentioned above are just an evaluation, and we always inspire our readers to scrutinize the issue in-depth based on the mentioned amended rules/decided judicial decisions and case laws consequently. With this, the group of CorpBiz has experienced professionals to help you with the process of Tax liabilities, Exemption from Tax liability, and assist you in complete compliances. Our expert will ensure the successful and favorable completion of your work.
Read our article: What is Capital Gain Tax and Difference between LTCG & STCG











