Some people have a lot of doubts regarding copyrights, patents, and trademarks. Although these intellectual property forms manifest several similarities, they are distinctive in nature and serve different purposes. In this blog, you will come across the prominent differences between Patent and Copyright.

Overview on Copyright
Copyright is the form of legal shield conferred to the authors of “original work of authorship” that enclose dramatic, literary, artistic, musical, and other intellectual works, both published and unpublished. Moreover, it copyright safeguards the form of expression, not the idea behind it.
The artist who owns the copyright has an exclusive right to republish, distribute, and recreate the works without constraints. Copyright is only applicable to the work which adheres to the tangible form of expression. As soon as the artist completes the creation, the notion of copyright comes into existence.
However, to disclose the invention to the general public, the patented invention is distinctive in nature and advocates novelty and uniqueness. It renders groundbreaking solutions to a problem that has been persisted for ages. A patent does not exist automatically as it has to be conferred by relevant government authority.
Overview of Patent
Since patents represent the legal articles, they could be hard to obtain. The applicant might have to wait for a year for the approval of the patent application. The most challenging aspect of the patent application is the review phase, in which the patent examiner conducts an in-depth review of the invention on the predetermined grounds.
The examiner continued to test the specimen until he/she gets satisfied and finds the invention groundbreaking on every aspect and also ensure it doesn’t overlap with the previous invention. The review might persist for a couple of months and even a year, depending on the invention’s complexity. There are a lot of distictions involved in obtaining the patent for an invention.
Once your invention qualified for the patent, you would secure the right to use the invention on your own terms, be it a matter of selling the invention or raising funds for the business. In short, the patent sets an exclusive right for the inventor, which renders him/her complete authority over its inventions.
A patent does not apply to the idea until it transforms into a materialistic form that offers solutions to a problem. In general, the patent can be obtained for the process, composition of matter, and equipment.
Read our article:Check out the Documents Required For the Copyright Registration
Key Differences between Patent and Copyright
| Copyright | Patent |
| Copyright is regulated by the Copyright Act, 1957 | A patent is regulated by the Patents Act, 1970. |
| It is a legal right confers to the creator of artistic work. It encompasses the right of adaptation of work, reproduction, distribution, etc. | A patent refers to a statutory right conferred by the government to protect an invention for a limited timeframe. Under the specified patent law, the invention cannot be sold, remade, imported without the inventor’s permission. |
| Copyright has a limited scope of applicability as it can’t be applied to all sorts of work. It is typically applied on artistry work, namely – poetry, music, film, artwork, and photography, | A patent protects the technical enhancement, which adheres to novelty and uniqueness. |
| Copyright registration serves the validity period of 60 years and even exists after the demise of the owner. | A patent registration lasts for 20 years from the date on which the application was filed. |
| Through copyright registration, the owner can reproduce and distribute the original work without any hassle. | A patent is granted to the invention, such as composition involved in an element or particular process. |
| Copyright Act averts the activity of duplicity and replication of the original work, | A patent prevents others from stealing the notion behind the invention and also deployed prevention measures to avert selling and importing the patented item. |
| Artists and creators can apply for copyright registration anytime. | A patent for an invention cannot be obtained once disclosed to the general public or made available in the marketplace. |
Key Points to Remember on Copyright and Patent
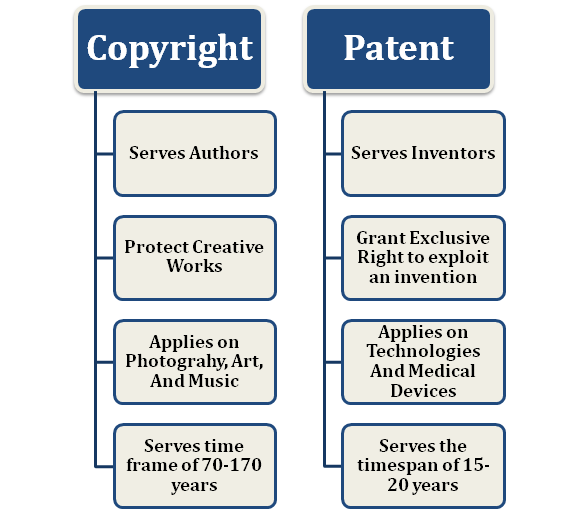
- Copyright serves authors; meanwhile, patent focuses on inventors.
- Companies typically adopt copyright to safeguard their intellectual and creative works.
- Copyright emphasizes art, music, and photography. In comparison, the patent is applied to technologies and medical devices.
- Copyright registration renders the time limit from 70-170 years, depending on the type of artwork. On the contrary, the patent last for 15-20 years.
Conclusion
Patent and copyright are the two different forms of intellectual property rights[1]. They usually render protection to something that holds distinctive value and has a considerable impact on the outside world. Copyright is limited to artistic work, whereas the patent is all about protecting the inventions.
We hope this briefing about Copyright vs. patent left you with no complaint whatsoever. If you still have some doubt, please let us know, we will try to resolve them as swiftly as possible.
Read our article:Detailed Process of Patent Registration in India