Banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are a vital part of any financial system. NBFCs are the privately-owned business entity governs by RBI’s law. Banks and NBFCs have many things in common and they play a vital role in building the country’s financial infrastructure. In this blog, we will look into the Key differences between NBFCs and Banks. In recent years, RBI has made significant changes to the compliance for NBFC due to various reasons. Now every NBFC are liable to keep the minimum threshold of Statutory Liquidity Ratio or SLR, net owned fund, and capital-to-risk weighted assets ratio to operate without legal disparities.

Every NBFCs operating in the country needs to follow the RBI’s guidelines, be it a question of the lending money or renewing repayment policies. NBFC may not be as flexible as a bank on various grounds, but they often touted for easy disbursement policies.
Read our article:How Nidhi Companies are Different from NBFCs? – Nidhi Companies Vs NBFCs
Here’s how RBI Describes the NBFC
NBFC registration done under the Companies Act, 1956 that provides lending services to the general public. Apart from lending money, NBFC is also involved in acquiring government-based securities, shares, and debentures.
NBFC renders a plethora of financial services to the general public, but they cannot accept the deposit of any kind whatsoever, unlike traditional banks. Let’s have a quick glance over these entities and see what they offer to the public in general.
In relation with Banks
Banks are the broader version of NBFC that dominates the financial infrastructure of the country. Being an apex organization, banks are authorized to perform various activities such as granting credit, accepting the deposit, clearing cheques, and managing withdrawals available to the general public and business entities.
In India, the banking system is categorized into three parts such as private sector banks, public sector banks, or foreign banks. They are accountable for furnishing banking solutions to end-users through a predefined framework. The ownership of the commercial bank is in the hand of its shareholders and other key members. Now let’s move onto the section which explains the Key Differences Between Bank and NBFC.
Key Differences between NBFC and Banks
Bank and NBFC can be differentiated on the following grounds.
- The bank is a government-driven entity involved in lending money and other financial services to the general public. Whereas, NBFC is a replication of the traditional financial institution that offers identical services without holding a bank license.
- An NFBC is a registered entity that works under the Indian Companies Act, 1956. Meanwhile, banks are certified under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949[1].
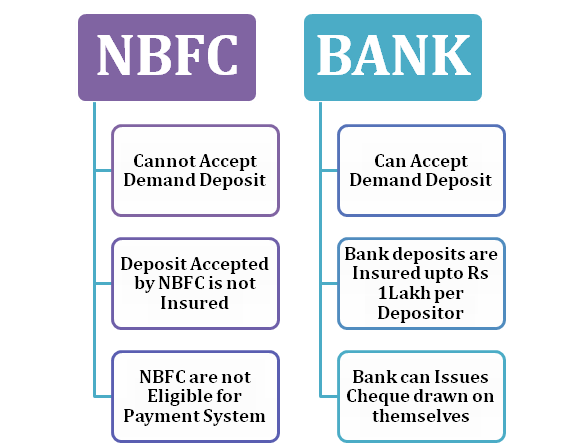
- NBFCs are not eligible to accept a demand deposit. On the other hand, traditional banks are allowed to do the same.
- Government regulation allows the NBFCs to accept 100% of FDI. On the contrary, the private sector banks are allowed to involve with FDI but to a certain limit. The bank needs not to avail of any government approval if the scale surpasses the minimum threshold limit i.e. 74% of the paid-up capital.
- An NBFC cannot involve in areas like agriculture, industries, or constructions. Meanwhile, banks are eligible to address these areas without any issues.
- As per RBI’s regulation, Banks are eligible to form a payment and settlement system; meanwhile, NBFCs are not allowed to set up such a framework.
- It’s not compulsory for the NBFC to maintain CRR (capital-to-risk weighted assets ratio) but the bank has to maintain such reserve without exception.
- The bank’s depositor can avail of deposit insurance facility Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC). Such a facility is out of the reach of NBFC.
- Banks are eligible to perform traditional banking services such as overdraft, issuance of cheque, fund migration, etc. Unfortunately, NBFCs are not authorized to perform such tasks.
At present, NBFCs are facing the heat of RBI’s strict compliance. Although authorities are putting their best effort into harmonizing these entities’ regulations, they are also considering malfunctioning to avert illegal activities. NBFCs may not have those liberties that banks had, but they are equally capable of rendering reliable banking service to the general public. So these are the key differences between NBFCs and Banks.
Conclusion
NBFC’s are immensely popular among the poor section of the society due to easy disbursement policies and flexible interest rate. Meanwhile, the bank is the most trusted entity among the two due to better exposure and unparalleled banking services. Establishing a bank is more complicated as compared to NBFC due to the stringent compliances. Moreover, the bank has an option to diversify its footprint by stepping into other forms of business, but NBFCs lack that versatility.
On the whole, both banks and NFBCs are responsible for injecting stability in the country’s financial infrastructure. They are of absolute importance and need relaxation from RBI amid the COVID 19 outbreak to effectively counter-economic turbulence.
Read our article:Procedure for Appeal against Cancellation of NBFC Registration by RBI