Under Section 80C, 80CCC & 80CCD, you can reduce your taxable income. Each financial year, we look for ways to save our taxes when filing them. But first, to know what the tax Deduction of 80C, 80CCC & 80CCD you can claim as a taxpayer.
As taxpayers, the most widely known tax-saving option is under section 80C of the Income Tax Act. However, in the zeal to provide the maximum public services, there are occasions when the tax levied is excessive and deprives individuals of disposable income to spend on personal and leisurely activities.
Section 80C of the Income-Tax Act
Under section 80C, a taxpayer can claim a deduction of up to Rs 1,50,000 from its total income. You can claim the amount of the tax up to 1,50,000 from your total taxable income under 80C. The deduction under section 80 C, 80CCC & 80CCD for Assessment year 2019-2020 is allowed to the maximum of Rs 1,50,000 for the FY 2019-2018, 2018-17 and FY 2017-16 each.
Section 80C includes the deduction made in LIC, Mediclaim, PPF, or incurred towards the tuition fees, etc. In case, you have paid excess taxes and have invested in the above-discussed list then you can claim your excess tax by just filing Income-tax return.
80C Deduction List Includes the Following Payment Made-
- towards the life insurance policies (for self, spouse or children)
- to the provident fund or superannuation fund
- towards the tuition fees to educate the maximum of two children
- to the construction or purchase of residential property
- Towards the fixed deposit with a minimum tenure of 5 years.
In addition, this section also includes investment in mutual funds, senior citizens saving scheme, purchase of NABARD bonds, etc. These deductions have been in the act to encourage the members of the society to participate in certain useful activities by helping the process.
Section 80C Investment Eligible for Tax Deduction
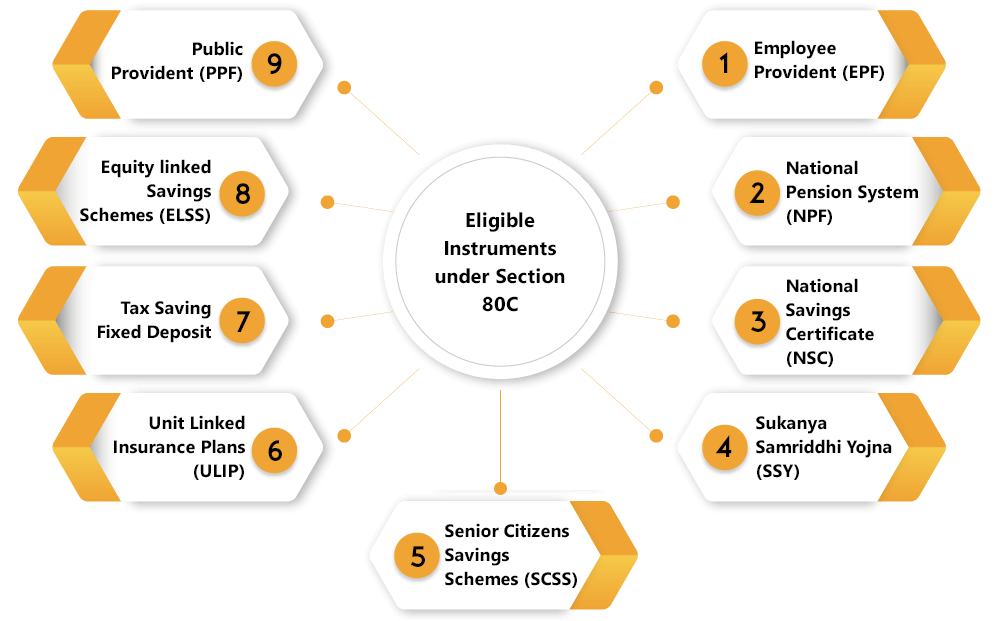

Employee Provident Fund & Voluntary Provident
Employee’s own contribution to the Employee Provident Fund & Voluntary Provident Fund qualifies for deduction 80C. If the employee basic salary increase with amount Rs 15,000 per month then he/ she has the option to enter the scheme. The current rate of the interest is 8.65% p.a. Both employer and the employee will contribute minimum of 12% of the Basic Pay +D.A.
Public Provident Fund
PPF scheme is a longtime investment scheme backed by the government of India. Resident Indian Individual in their own name or in the name of the minor child can open a PPF account. PPF account has the maturity period of 15 years but it also extended to 5 years where partial withdrawal is allowed after 7 years. The rate of interest is 7.9% p.a. The minimum investment limit is Rs 500 and the maximum limit is 1.5 lakhs.
National Saving Certificate (NSC)
This scheme is highly secured class of investment where Non- resident, Trust and HUF[1] are not eligible to invest in it. The current rate of interest is 7.9% for 5 years NSC. The investment is eligible for deduction under 80C and the maturity amount is tax-free.
Read our article:Section 80GGB and Section 80GGC: Tax Deductions from Donations to Political Parties
Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme
It is also one of the best investment options that are trending in the market today. The compounded rate of interest is calculated annually. The minor account will be opened by the guardian of the minor girl child till she attains the age of 10 years. The minimum limit is Rs 1,000 and Rs 1.5 lakh is the maximum limit.
Senior Citizen Saving Scheme
An individual of age 60 years old more is eligible to open the account. Furthermore, an individual of the age of 55 years or more but less than 6year is eligible to retire under the Voluntary Retirement Scheme. The maturity period is 5years. The interest rate offered is 8.4% per annum. The minimum investment limit is Rs 1,000 and Rs 15 lakh is the maximum limit.
5 Year Tax Saving Bank Fixed Deposits
All resident individual can open account tax-saving bank fixed deposits and 60year senior citizen is also eligible. The Maturity period is around for 5 years and a person is not allowed to break this fixed deposit before maturity. The minimum investment is Rs 1000.
Unit Linked Insurance Plan
An individual invested in Unit Linked Insurance Plan for spouse, self or child where a child can be married or unmarried, dependent or independent and minor or major. The maximum amount of deduction is only up to Rs 1.5 lakh.
Section 80 CCC under the Income Tax Act
Now, after the Section 80C, we are heading towards its subsections which provide more clarity to the branches of the Section 80C deductions.
Section 80CCC of the Income Act provides a ground for a tax deduction in which you can make an investment in pension funds. It relates to the deduction for premium paid for any annuity plan of LIC or Pension fund or another insurer. In these pension funds, a taxpayer can claim a maximum amount of deduction of Rs 1.5 lakhs. It could be from any insurer in the pension funds and an individual is only eligible to claim this deduction as a taxpayer.
The investment in a pension fund or annuity can easily claim in the deduction. However, the interest accrued is taxable in the year of receipt.
Section 80CCD under Income Tax Act
Section 80CCD relates to the deductions that are available to individuals against the contributions made to the the Atal Pension Yojana (APY) and the National Pension Scheme (NPS). The Central Government has introduced NPS to facilitate the advantage of organized pension scheme to the Indian citizens. Primarily, NPS was intended for government employees only but eventually it was opened for the private sector and the self-employed individuals. The basic objective behind NPS is to facilitate individuals in creating a retirement corpus and in receiving a fixed payout monthly to help them live a comfortable and secure life post-retirement.
The deduction under Section 80 CCD is Rs. 2 Lakhs which is the maximum limit available and this shall include Rs. 50,000/- which is the additional deduction available under sub-section 1B.
This section aims to encourage the habit of savings in the people by alluring them with the exciting incentives they will get with the investment in the pension scheme that is notified by the central Government. Any contribution made by the employer/employee will be eligible for deduction in this section. The tax deduction will be subject to being less than 10% of the salary of the person.
Categorisation under 80CCD
Section 80CCD has been divided further into two subsections to make it clear regarding the deductions available for income tax assesses. While one subsection deals with the rules about tax deductions available to salaried and self-employed professionals, the other pertains to contributions made by the employer towards NPS.
The given below is the information in detail regarding the two sections under Section 80 CCD.
- Section 80CCD (1) – Under thissubsection, it deals with the rules in relation with the income tax deduction available to person for contributions that was made to the NPS and are between the age of 18-60 years.A new amendment of 80CCD (1B) was introduced in the Union budget, 2015. This new provisions allows for an additional deduction of Rs. 50,000/-for the amount deposited to the NPS accounts by the taxpayer.
- Section 80CCD (2) Employer’s contribution to NPS – this provision comes into an effect when the contribution is done by the employer to the NPS of an employee. This allows the salaried individual to claim additional deduction up to 10% of their salary account.
Other Important Deduction under 80C –
Apart from the above-said deduction under Section 80C, there are the following deductions which are as follows–
- Section 80 CCF– this deduction has opened its door for Hindu Undivided Family and Individuals. Section 80CCF includes the provisions for a tax deduction on the subscription of long-term infrastructure bonds that are notified by the government from time to time. Also, one can claim a maximum deduction of Rs 20,000.
- Section 80CCG– the Income-tax permits a maximum amount of deduction of Rs 25,000 per year with the specified individual residents who are eligible for this deductions. The government has notified 50% of the investment is mandatory in equity saving scheme.
- The maximum limit under 80C section is Rs 1, 50,000 covering all heads.
Conclusion
As a taxpayer in India, we all look for various ways to save our taxes and reduce our tax deductions. The advantage of claiming tax deductions under section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD is it will reduce your taxable income and tax outgo. Most of us have a common idea on how to save taxes, however we struggle when it comes to saving these taxes.
Read our article:Income Tax Slab and Rate for financial year 2020-21











