Typically, the supplier of goods or services is accountable for paying GST. Though, in specified circumstances like imports and other notified supplies, the obligation may be swift to the recipient under the reverse charge mechanism.
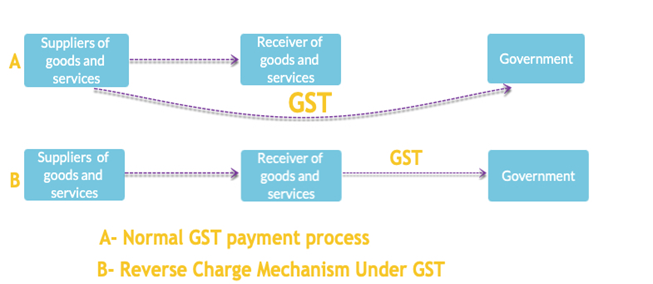
Unlike normal GST payment process, the recipient of the supplies is the one who is entitled to pay tax under the reverse charge mechanism. The following diagram helps you understand the very nature of the tax flow that occurs under reverse charge.

- If an unregistered vendor supplies goods to a buyer who is registered under GST, then the Reverse Charge would be applicable to that buyer. In this case, the registered dealer has to do self-invoicing for the purchases made.
- For Inter-state purchases, the buyer has to deal with IGST.
- Meanwhile, for Intra-state purchases, the SGST and CGST have to be paid under RCM by the purchaser.
Reverse Charge Mechanism Outlines In The Law
- Reverse charge intends the obligation to pay tax is on the recipient of the supply of goods or services rather than the supplier. There are two types of reverse charge outlines given in law. First is subjected to the nature of supply and/or nature of the supplier.
- This outline embraced by section 9 (3) of the CGST/SGST (UTGST) Act and section 5 (3) of the IGST Act. The following outline covered by section 9 (4) of the CGST/SGST (UTGST) Act and section 5 (4) of the IGST Act under which chargeable supplies by any person (unregistered) to a person (registered) is covered.
- Under section 9(3), CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(3)of IGST Act, 2017[1], the Government may, under the directions of the Council, by information, define classes of supply of goods or services, the tax on which will repay on reverse charge.
- All the provisions enlisted in this Act will apply to such recipient for paying the tax in connection to the supply of such goods or services or both.
- Likewise, section 9(4) of CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(4) of IGST Act, 2017 grants that the tax in regard of the supply of taxable goods or services or both by a supplier, who is not registered, to a registered person, will be repaid by such person on the basis of Reverse Charge.
- The provisions of this Act will apply to such recipient liable for paying the tax concerning the supply of such goods or services.
- Hence, wherever a registered person obtains supplies from an unregistered supplier, he has to pay GST based on Reverse Charge. However, there is a scope of the exemption when the value of supplies of goods or service fall under five thousand rupees. (Notification 8/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017).
- As per vide notification no.38/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 13.10.2017, all classes of registered persons subjected to an exemption from the provisions of Reverse Charge under 9(4) of CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(4) of IGST Act, 2017.
- Section 9(4), CGST Act, 2017, shall not be fit to supplies made to a TDS deductor. Thus, Government entities 87 who are TDS Deductors under Section 51 of the CGST Act, 2015, need not pay GST under Reverse Charge in case of procurements from unregistered suppliers.
Read our article:Pragmatic Impact of GST Rate on Indian Economy
The following examples can help you understand the technicality related to the reverse charge mechanism.
Example No.1:
Mr X buys stationery worth Rs. 200/- from ABC Stationery, which is not listed under GST.
Analysis:
- A registered person (Advocate Mr X) availed the services from an unregistered person (ABC Stationary).
- The aggregate value didn’t exceed than Rs. 5,000/- limit in a day.
Reasoning:
The reverse Charge under GST applicable to both the party or not?
Reverse charge mechanism under GST clearly states that recipient of supply should be liable to pay tax, in the given case, Mr X is obligated to pay GST Reverse charge but –
Since the aggregate value of supplies has not exceeded Rs. 5,000/-, Mr X in no circumstance shall be entitled to pay GST Reverse Charge.
Example No. 2:
XYZ Transport services provide Goods Transport services to Mr X (an unregistered dealer of Delhi). MR. X availed the services from XYZ Transport services, worth Rs 1000/-. Which of the two parties are entitled to pay a reverse charge under GST?
Analysis:
- Mr X (an unregistered dealer of Delhi) availed the services from XYZ Transport services.
- The aggregate value of the trade is worth Rs 1000/-
Reasoning:
Since Mr X is conducting the trade without GST framework, it should be the one who needs to get registered first. To do so, Mr X needs to obtain GSTIN in the first place and then pay tax on Reverse Charge under GST on the given trade.
Registration:
A person who is obligated to repay tax under Reverse Charge has to register under GST imperatively, and the threshold limit does not apply to them.
Time of Supply
The time of supply is the point subjected to GST. One of the factors related to defining the time of supply is the person who is under the tax liability. In reverse charge, the GST is applicable to the recipient. Therefore, the time of supply for supplies is different from the supplies which come under the forward charge.
As per Section 12(3) CGST Act, 2017 in case of supplies of goods liable to be paid based on reverse charge, the time of supply will be the earliest of the given dates, viz:
- Date related to the receipt of goods; or
- Date of debit in a bank account.
- The date immediately following thirty days from the date of issue of invoice or similar other documents.
As per Section 12(3) CGST Act, 2017 in case of supplies of services liable to be paid based on reverse charge, the time of supply will be the earliest of the given dates, viz:
- Date of payment in line with the books of account or date of debit inline with the bank account, whichever is earlier; or
- The date immediately following 60 days from the date of issue of invoice or similar other documents.
Where it is not possible to determine the time of supply using the above methods, time of supply would be the date of entry in the books of account of the recipient.
Compliances Related To Reverse Charge Mechanism
- Every tax invoice displays the info regarding the tax in the invoice, payable on Reverse Charge. Likewise, the same has to be done with receipt voucher as well as refund voucher, if tax is confined around the reverse charge.
- The registered person must keep and maintain the records of supplies that attracts tax treatment under the Reverse Charge.
- Any amount that falls in the category of reverse charge shall be paid by electronic cash ledger. In other words, reverse charge liability is non-dischargeable via an input tax credit.
- Advance paid for Reverse Charge supplies also come under GST treatment. The person who makes the advance payment is subjected to tax based on Reverse Charge.
Read our article:GST: Penalty, Offences and Appeals Under GST Act 2017