A Chemical Patent generally refers to a drug patent that renders protections to the invention made by the drug industry. A chemical process patent protects the process utilized to produce a certain medicine/drugs, whereas a chemical formula patent renders protections to the ingredients.
Since medicines are vulnerable to duplication, such patents adhere to the utmost importance for the pharmaceutical industry. In this blog, you will learn everything about patent registration, the chemical patent application, and the patent process.
What Does the Term “Patent” Signify?
A patent is the form of intellectual property that renders complete protection to the owner with an exclusive right to manufacture, use, and sell an invention for the given timeline. In exchange for such a right, the inventor is liable to publish the information regarding the design.
Around the globe, patents provide the organization with a competitive edge, as it allows them to manage who uses or sells their invention. Drug manufacturing entities patents their invention to safeguard their interest and have a monopoly selling the medicine for the given timeline.
Is it Possible to obtain a Chemical Patent for a Compound?
Yes, its depend on the numbers of variables and conditions laid down under the Patent Act[1]. The Section 3C of the said Act put the isolated compounds out of the reach of patent registration. Besides, it does not provide any support for discovery or formulation of abstract theory from the patentability’s viewpoint. Section 3 of Patent Act aims to provides provisions for patent eligibility; whereas, Section 2(1)(j) encloses the theoretical definition of the patent.
Section 3(d) is one the major roadblock for the drug industries. It does not support any invention that lacks improvement and efficacy over the existing substance. Section 2(1)(j) provides a theoretical definition of an invention while Section 3 illustratively outlines what are not inventions.
The aforesaid section clearly states that the new derivative of an already existing substance will not be treated as a distinctive substance unless it provides improved efficacy over the known compound. In short, the chemical compounds are patentable in nature provided they met the entire stipulates of the section 3 of the patent act.
Markus Structure – A Challenge for the Researchers
The claim of a chemical patent is subjected to the Markus structure- a sole chemical compound clarifies where the improvement has been made by the researcher. A Markus structure typically represents the chemical structure that used to demonstrate a group of related chemical compounds.
It provides the grounds to identify the element of improvement or distinctiveness in the given compound. The researcher across the globe uses this structure as a declaration of the ownership. It’s a challenge for the researchers to intact the simplicity of the Markus structure while keeping it real at the same time. Representation is the one key area where most to the patent application get rejected. While filing the new compound for the patent, make sure that said structure encloses the distinctive elements that set it apart from the already-existing compound.
Indian Patent office, while examining the Markush Claims, identifies the following points:
- Whether the structure is in accordance with the section 2 and 3 of the Patent Act or not.
- Is it carrying any resemblance to the existing structure of the compound?
- Whether the said structure reflects the best representation of the embodiments.
- Is the physical and chemical properties are disclosed by the applicant.
- Test report and other analysis data are annexed by the applicant.
- At least one process related to compound preparation has been disclosed by the applicant to depict the scope of invention.
Any contravention to the aforesaid prerequisites would drive the authority to revoke the chemical patent application.
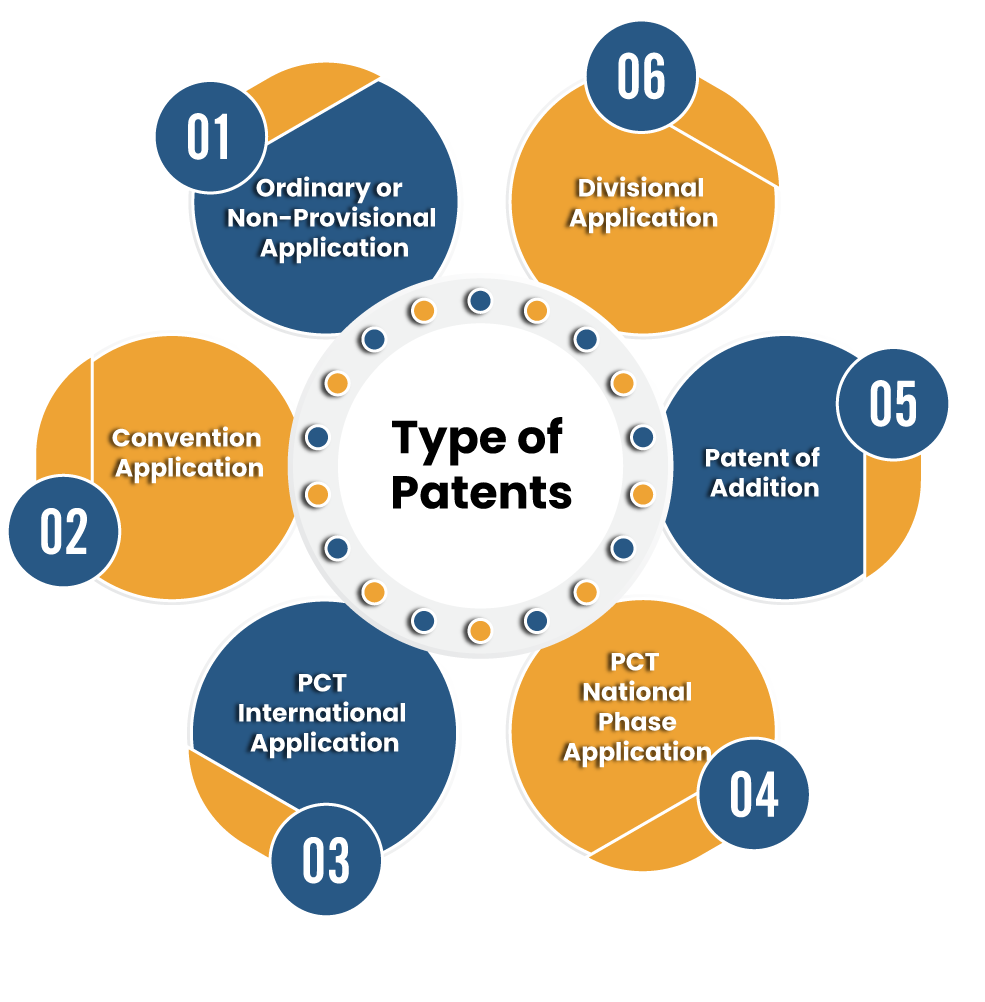
An Overview of Patent Types & Patent Rights That Exist In India

What is the Procedure for availing Chemical Patent?
- The patent process commences with the filing of an application at the Indian Patent Office through a complete or provisional specification.
- In addition to the application, the inventor is also liable to pay fees mentioned under Schedule I.
- In the case of a provisional patent, the inventor is liable to file a complete patent prior to the end of a year to wrap up the patent process & secure protection,
- After applying, a team of experts will scrutinize the application within 48 months from the date on which the patent was filed.
- In case of conflict, the application would get a chance to fix the issues within six months, which may further be extended to the additional three months.
- If any objection is raised by the testing penal are not met in the given timeline, the applicant would be rejected.
- Once the entire prerequisite is satisfied, the Patent Office Journal broadcast the patent through the publishing media.
Conclusion
While filing chemical patent applications, it is essential to take aforesaid provisions into account. Also, endeavor to render enough data and specification to shows the technical effect of the invention. Provision for post data filing is real as it can be forwarded in the form of an expert declaration.
Patent has the several benefits to offers but it is difficult to avail. If you need any assistance regarding securing a chemical patent, feel free to connect with us at CorpBiz. Our team of experts would be glad to work with you and assist you every step of the way.
Read our article:Lets Understand the Abuse of Patent Right with respect to Drugs