The software industry is thriving, and so does the technology sector. Their development has brought the need to secure the intellectual property (IP) in the application, programs, and software patent. In this blog, we will explore the imperative dimensions of the software patent, such as applicability, usages, and validity.
Why Software Seeks Patent Protection?
Software is comprised of specific commands, a guideline that a computer system follows to complete a specific task. The software does not come under the tangible asset category; thus, it is not classified as traditional goods. However, whenever a computer program/software is sold, the buyer is permitted to access a license key to use the software and other guidelines that reflect its scope of functionality and its operations.
Software is susceptible to piracy due to which they encounter unstated economic loss. Henceforth, it is imperative to safeguard the software/computer program under the IPR mechanism guidelines. It would not only render protection to the economic interest of the owner but also advocate innovation.
Validity Specifying the Software Patent
Patent protection remains valid for a limited period of time, where patent for software comes under the category of technology. The methods of computer program coding are unique & critical. Henceforth, it is an absolute necessity to protect the software via patents.
Even though the methods of programming codes come under the Copyright regime, the principles & operational methods of the program cannot rejoice copyright protection.
Therefore, patent become absolute importance for the software’s protection as the patent covers the scope not the method. Patent works seamlessly when it comes to the protection of idea & functional aspect of the computer program. But to become eligible for patent, the software must comprise of traits that advocates inventiveness rather than incremental update.
As per the Section 3 (K) of the Patent Act, 2002, computer software cannot be cover under the Patent regime per se. To become eligible for patent, the software must not be
- The computer program must not be the mathematical method, business method, or algorithm.
- The computer program/software that doesn’t come under Patent regime.
But, a computer program can be patented if it demonstrates the element of inventiveness. To bypass the claim of the said section, it is imperative to exhibits that hardware is an important part of the invention in addition to the program.
Is It Possible To Patent Software In India?
Indeed, the software or computer programs are patentable in India. As per the Indian Patent Office, the software invention has been placed under the classification of Computer Oriented Inventions, one or more features of which are embodied wholly or partially by means of a computer program(s). Such inventions have been cited in the rules promulgated by the patent office.
Generally, patent application encompassing matter regarding the computer program invention has been bifurcated into multiple categories by the patent office mentioned below:
- Method/Process
- Apparatus/System
- Computer readable medium
- Computer software
If the patent claims revolve around the method or a process, the patent office shall not consider the mathematical formulae, business methods, and algorithms as driving factors for patenting.
However, if the method claims related to computer related innovation having inventive & novel traits, such clams can be patented as per the Indian Patent Law.
Section 3(K) of the Patent Act
If the patent claim revolves around the apparatus or a system and it align perfectly with the section 3(K) of the Patent Act then it can be patented with ease. In practicality, such claim might be patented in “means plus function” format.
The means-plus-function claim is widely use for drafting the software patent or patent claims. During the preparation of patent claims, the patent officers can leverage such claims to demonstrate functional & technical terms of the invention to clarify several aspects of the invention.
If the patent claims are confined around Computer readable medium, software products, the Indian Patent office would consider such claim as computer programs per se, and henceforth such claims cannot be covered under the Patent regime.
Patent Regime aligning with the Invention
The software is not a part of the patent’s regime in India, but only in the condition if it doesn’t align with the invention. For patents, the software must be capable of performing unique tasks, and it should be posses’ inventiveness.
As per the Patent (Amendments) Act 2002, the software does not qualify for a patent if it lacks inventiveness. Henceforth, the software is only patentable when it appears to be productive and unique in nature.
Rules Pertaining to Software Patent Registration
The important rules pertaining to software patent registration are given below, which are as follows:-
Software Patentability / Prior Art Patent Search
Prior filing the software patent application, it’s advisable for the applicant to conduct an extensive patentability search related to the prior part accessible publically. The software patent comprises of the steps of reviewing newspapers, journal, books, magazine, brochures, research reports, and conference material.
Applicant is required to leverage the online patent database of WIPO, USPTO, & EPO to determine the uniqueness of the computer program innovation. These databases generally enclose all the information regarding the patented software; thus it would be good source to determine the novelty of the program.
To conduct such an activity, the applicant can either leverage the keyword cited in abstract text, specs, patent title, claims and by the global patent classification number, CPC & UPSC assigned to each patent by the relevant officials.
Patentability Search Results / Patentability Opinion
The patentability search results will imparts detailed insight to the inventor about how conveniently one can claim the software invention. Additionally, the patent language utilized by other applicant to claim identical invention renders a clarification on the viability for your program invention.
Advantage of Patentability Search
Patentability search keeps you abreast of conflict that arises due to the similarities with the prior art patent claims. The patent claims ought to be written in a way to bypass the prior art.
The Patent (Amendment) Act 2002 encloses the procedure related to patent registration. The act came into existence on 20th May 2003. The following are the points that are not part of the Patent (Amendment) Act 2002 anymore:-

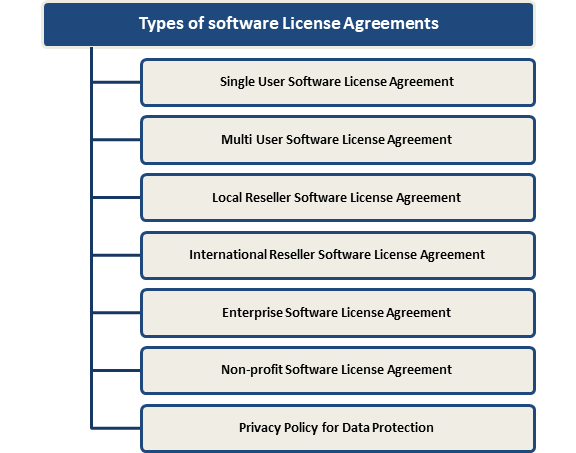
Software License Agreement
Access can grant to any outsider by the individual having ownership of the software. The owner prefers to render the license to legitimate buyers of that particular computer program.
A license can consolidate the retention of some legal rights pertaining to a computer program for letting the owner rejoice in increased control over the software. Henceforth, all statutory rights intact with the owner expect the right to utilize the software on the licensee’s device.
Types of software License Agreements

Why Computer Program Seeks Patent Protection More Than Ever?
As per the Reserve Bank India’s data, the export of software in India has been increased by 11.6% to $108.4 billion in the financial year 2017-18. Given the current growth and expansion of the software industry, the government has amended the IP laws on a couple of occasions. However, the IP laws still lack provisions related to the software & computer program.
As of now, the software is being protected under trade secrets and copyright. Furthermore, the Information Technology Act of 2008 doesn’t include any provision pertaining to computer software and programs.
Essential Points Regarding Software Patenting That worth Remembering
- As per Sec. 2 (o) of the Copyright Act, 1957, the software comes under the regime of literary works. However, the Act does not render enough clarification between the object code and the source code of the computer program; henceforth, both are considered as the literary works of the software.
- Merely having an algorithm cannot ensure that the given software can be patented. For patent, the computer program must have an element of uniqueness and inventiveness.
- Idea, algorithm, and the design element of a computer program might be cover under the ambit of a trade secret. The applicability of the trade secret protection is entirely based on the nature of the computer programs and their distribution channel. A computer program sold out as an object code could be partially protected if the source code is kept isolated from the general public.
- If a computer program satisfies the definition of “Goods’ as per the Sale of Good Act, it will be regulated by the provisions of the Sale of Goods Act[1].
- One has to adopt a proactive and holistic approach to prepare the Software patent applicant. An experienced patent agent can help you draft patent claims that might have diverse scope of the invention. But, the aim of the article is to impart inventors with a common idea how to outline a patent application for computer program invention.
- The software patent specification should be customized for a specific invention addressing one issue in the prior art domain. There is no thump rule for drafting a well-balanced software patent application. The most imperative trait of software patent writing is to define the legal right of the patentee.
Conclusion
It is always recommended to avail expert assistance for drafting the software invention & prosecuting the application before the patent office. The inventor must provide flowcharts or illustrations of the program’s algorithms to the patent attorney.
Software is meant to transact for the purpose of sale or licenses. Their transaction is carrying out via licenses that favour the licensor for the most part. The ownership of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) in the computer program vests by the licensor. Furthermore, there may be the provision of fair use by the licensee and the utilization of encrypted technology, which may reflect the conflict of laws.
When it comes to the transaction in the form of sale, it becomes a subject of normal warranties and conditions, tax & regulations related to the product liability. Henceforth, the law scatters on these fronts, which requires rendering more clarification.
Read our article: Is it Possible to Increase the Timeline of Patent Validity? Let’s find out.











