Before filing a Patent Application, any applicant should be sure about the type of application that he/she wants to file with the Patent Office. There are majorly five different Types of Patent Applications in India. All different types of Patent Applications under the Patent Act serves a different purpose. Therefore, the applicant is required to choose the Type of Patent Applications that suits his/her requirements. In the article, we will discuss in detail the different Types of Patent Applications in India.
What is a Patent?
A Patent is a title that provides the owner of the Patent with a right to prevent another person from misusing the invention of the owner described in the Patent. A Patent to an invention gives the exclusive right to the owner of the Patent to exclude other people from making, using, selling, or importing the patented invention of the owner.
A Patent is granted to a person for a specific field in a defined country. The tenure of a Patent is only for a maximum of 20 years. The Patent Office will only grant a Patent if the owner of the invention fully discloses the invention and publishes the technical details related to the invention in his/her application of Registration of Patent. A Patent can protect an invention only for 20 years, and the Renewal of Patent is not allowed. There are several types of Patent Applications filed under the Patent Act, 1970. The basis of filing so many different types of Patent Application in India is ensuring security to the inventors of the invention that their work will be protected in India and outside India.
The primary criteria for a Patent to be granted as per the Patent Act, 1970, is as follows:
- Novelty
As per Section 2(1)(j) of the Indian Patent Act, 1970[1], an “invention” is a new product or process that involves an inventive step and is capable of industrial application. Further, Section 2(l) of the Patent Act, 1970, defines a ‘new invention’ as any invention or technology which has not been anticipated by publication in any document or used in the country or elsewhere in the world before the date of filing of patent application with complete specification, i.e., the subject matter has not fallen in the public domain or that it does not form part of any state of the art.
- Inventive Step
According to Section 2(1) (ja) of the Patent Act, 1970, an “inventive step” means a feature of any invention that involves technical advance as compared to the existing knowledge or having some economic significance or both and that makes the invention not obvious to a person skilled in the same art.
- Industrial Application
The third criterion of patentability in India is that the ‘invention’ should be capable of industrial application. As per Section 2 (1) (ac) of the Patents Act, 1970, “Capable of Industrial application” in relation to an invention means that the invention is “capable of being used or made in an industry.” Therefore, an invention must be useful to be patentable in India.
In India, the legislative frameworks which deal with the Registration and Protection of Patents are The Patent Act, 1970, and The Patent Rules, 2003. The Indian Patent Act, 1970, has undergone three amendments since it came into force in India. The amendments in the Patent Act, 1970, were made in the years 1999, 2002, and 2005. In the year 2005, an amendment related to Product Patent Protection for chemical, pharma and food inventions was introduced in the Patent Act, 1970.
What are the different Types of Patent Applications in India?
The different Types of Patent Applications in India are as follows:
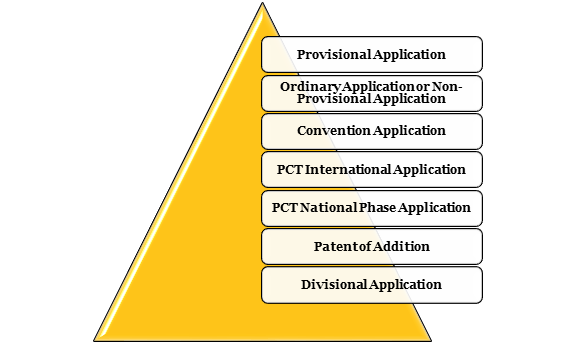

Provisional Application
A provisional application is a type of temporary application that is filed when the invention is not yet finalized and still is under experimentation.
The Advantages of Filing a Provisional Application are as follows:
- The applicant gets 12 months’ time period to develop the invention and determine its market potential fully;
- Helps to establish certain priority rights over the invention;
- The application enables the applicant to use the term ‘patent pending’ on their products;
- It is less expensive to prepare and file the Provisional Application;
- The applicant is enabled to file International applications and also claim priority within the time period of 12 months.
- However, for the grant of Patent, a provisional application should be followed by a complete specification within the time period of 12 months. Furthermore, the provisional application should be appropriately detailed and should be drafted very carefully to ensure that the priority rights for the invention are secured.
Ordinary Application or Non-Provisional Application
An application for the grant of Patent filed in the Patent Office without claiming any priority date of application made in a convention country or without any reference to any other under process application in the Patent Office is called an Ordinary Application. An ordinary application should be accompanied by a complete specification and claims associated with the invention.
Convention Application
An application for the grant of Patent filed in the Patent Office, claiming a priority date based on the substantially similar or same application filed in one or more of the convention countries, is called as Convention Application. To get a convention status, an applicant is required to apply to the Indian Patent Office within the time period of 12 months from the date of first filing a similar application or same in the convention country.
PCT International Application
A PCT application is an international application governed by the PCT (Patent Cooperation Treaty), and can be authorized in up to 142 countries worldwide.
An Indian applicant can file the PCT International Application in three ways. The three ways are as follows:
- Filing the application in the Indian Patent Office (IPO) acting as the receiving office;
- Filing the application directly in the International Bureau (IB) of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) after getting the foreign filing permit from the Indian Patent Office (IPO);
- The applicant can file the application in the International Bureau IB of World Intellectual Property Organization WIPO after 6 weeks and within 12 months’ time period of filing the application in India.
The advantages of filing a PCT Application are as follows:
- Filing of a PCT International Application gives the application around 30 or 31 months to enter into several countries from the priority date or international filing date. Hence, it provides the applicant with the application more time to assess the capability of the invention;
- Delays the expenses or expenditures related to applying for an application for Patent’s grant in various countries;
- Makes available an International Search Report citing prior art, which gives a suggestion to the applicant of the PCT application whether his/her invention is novel and innovative.
- A single PCT International Application can be filed to seek protection for an invention in up to 142 countries worldwide.
- The priority date is internationally recognized, which is obtained by filing a PCT application, and also has an effect in each of the designated countries.
- It provides an option for the applicant to make a request for an International Preliminary Examination Report. This report contains an opinion on the patentability of the invention of the applicant.
- The International Preliminary Examination Report and International Search Report, allows the applicant to make more elective and informed choices early in the process for grant of Patent, and to accordingly amend the Patent application to deal with any conflicting substance or material, before the beginning of the major expenses associated with the Patent Registration process in the national phase. The Reports also gives the applicant of the International application a fair idea on the patentability of the new invention before incurring any kind of charges for filing and prosecuting the application in each designated country.
PCT National Phase Application
When an international application is framed and made according to PCT designating India, an applicant is required to file the national phase application in India within the time period of 31 months from the priority date or the international filing date, whichever is earlier.
Patent of Addition
When any applicant of the application feels that he/she has come across an invention which is a slight modification or improvement in the earlier invention for which he/she has already applied for or has obtained Patent, in such a case the applicant can go for Patent of Addition, if the new Improved and modified invention does not include a substantial inventive step. There is no requirement to pay a separate renewal fee for the Patent of Addition during the tenure of the main Patent, and the Patent of Addition also expires along with the main Patent. The date of filing should be the date on which the application for Patent of Addition is filed with the Patent Office.
Divisional Application
When the applicant’s application claims for more than one invention, the applicant on his own desire or to meet the official objection can divide the Patent application and file two or more Patent Applications, as applicable for each of the different inventions. These types of applications, that divided out of the main or parent applications, are called as Divisional Applications. For all the divisional applications, the priority date will be the same as claimed by the Parent Application (Ante-dating).
Read our article:Procedure for Registration of Patent Agent in India
What are the essential mandatory requirements for filing different Types of Patent Applications in India?
The essential mandatory requirements for filing Different Types of Patent Applications in India are as follows:

Ordinary Application
The essential mandatory requirements for the filing of an Ordinary Application are as follows:
- Name of the applicants for the Patent;
- Address Proof of the applicants for the Patent;
- Nationality Proof of the applicants for the Patent;
- Name of the inventors of the Patent;
- Address Proof of the inventors of the Patent;
- Nationality Proof of the inventor of the Patent;
- The complete or provisional specifications of the Patent with description, abstracts, claims, drawings.
Convention Application
The essential mandatory requirements for filing of Convention Application are as follows:
- Name of the applicants for the Patent;
- Address Proof of the applicants for the Patent;
- Nationality Proof of the applicants for the Patent;
- Name of the inventors of the Patent;
- Address Proof of the inventors of the Patent;
- Nationality Proof of the inventor of the Patent;
- The complete or provisional specifications of the Patent with description, abstracts, claims, drawings.
PCT National Phase Application
The essential mandatory requirements for the filing of PCT National Phase Application are as follows:
- The earliest priority date of the application;
- The PCT Application number;
- The International filing date of the application;
- The title of the invention of the inventor;
- The English translations of the provisional or complete specifications of the invention. The specification should be accompanied with the claims, abstracts, and drawings related to the invention in English as well.
What are the types and requirements of complete specifications for different types of Patent Applications in India?
The complete specification for an application can be filed in 2 ways:
- Direct Filing
The complete specification of an application is filed directly with the Indian Patent Office first without filing any corresponding provisional or temporary specification for the same application.
- Subsequent Filing
The complete specification is filed subsequently after the filing of corresponding provisional or temporary specification, and the priority can be claimed from the provisional specification filed earlier.
The complete specification of an application should necessarily contain the following:
- Title
- Preamble to the new invention
- Technical field of the new invention
- Background of the new invention
- Objects related to the new invention
- Statement of the new invention
- Brief description of the invention’s drawings
- Detailed description of the new invention
- Claims associated with the new invention
- Abstract of the new invention
Conclusion
There are several ways to protect your new and originreal invention from any kind of Infringement from a third party in India. Not only this Patent protection is available in India but also in other countries all over the world. Hence, any person applying for the application of Patent in India is required to understand the basic mandatory requirements for filing different types of Patent Applications in India. The applicant of the application of Patent should always understand all the different types of Patent Applications in India and then accordingly file for the application with the Patent office of India.
The applicant should always consult an experienced professional for carrying out the process of filing for different types of Patent application for Registration in India. We at Corpbiz have trained professionals to help you with the process of filing for Registration of Patent in India. Our experts will assist and guide you throughout the process of Registration of Patent. Our skillful experts will ensure the timely and effective completion of your work.
Read our article:Provisional Patent in India: A Complete Overview