India is one of the prominent destinations where exquisite qualities of spices are being cultivated on a grand scale. For this reason, our nation is also widely acknowledged as the spice bowl of the world. Owing to the favourable climate & massive cultivating land, India has a long history of exporting spices all across the globe. The global demand for Indian spices has hardly encountered any negative dip in the past year. That is why new businesses prefer to venture into this domain as an exporter. To be an exporter in India, one has to address plenty of legal formalities. This blog addresses those who wish to conduct Spice Export from India in a legalized way.
Spice Export from India: Is it Profitable?
Indian Spices are praised all across the globe owing to their distinctive flavour and quality. India has the largest consumer of spices in the world. Spice cultivation is rapidly gaining popularity among the small landowners because it lures fewer expenses and ensures a high return. At present, our country is exporting more than 75 varieties of spices all across the globe. Tropical and subtropical weather patterns of our nation play a vital role in the massive production of various spices.
Read our article:A brief Outlook on FSSAI license for Spices in India
Have a look at the list below that depicts the potential of this venture:
- In FY20, India exported more than US$ 3.62 billion of spices worldwide.
- In FY 2019, the worldwide exportation of spices stood at US$ 2.80 billion, marginally better than the preceding year figure.
- The potential importers of Indian spices in FY 19 include China, the USA, Vietnam, Thailand, Hong Kong, UK, Sri Lanka, and Malaysia[1].
- During FY19, the top 10 exported spices in terms of value were mint products, chilli, cumin, cardamom seeds, turmeric, Asafoetida, Garlic, Cassia, pepper, and curry powder/paste.
During FY19, the overall export of spices in terms of quantity stood as follow:
- Chilli= 468,500 tonnes
- Turmeric = 133,600 tonnes
- Cumin = 180,300 tonnes
- Cardamom large = 860 tonnes.
The overall valuation of spice’s export during Apr 2021-Feb 2021 was stood at US$ 3.55 billion, and for the month of Feb, it was US$ 348.32 million. In FY 20, ginger export achieved promising growth of 47% with 19,410 tonnes. Moreover, cardamom export was witnessed a sharp increase of 31% in the same year.
How is Spice Board of India boosting spice export from India?
Spices Board, established by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, contributes significantly in the direction of rising global demand for Indian spices. Apart from promoting exporting activities, it also regulates the quality of spices being shipped to overseas nations.
Here are the activities performed by this government-backed organization that help boost spice export from India
- Development & deployment of improved production of methods via technological, scientific, and economic research
- Training farmers, agriculturalists with the latest technologies to increase the production yield
- Facilitating material & fiscal support to the growers
- Providing registration to legalize the business of spice exportation
- Rendering education and promotional materials to importers and exporters
How to get involved with the business of Spice Exportation?
The most common way to get started with the spice export from India
- Spices Manufacturer
- Wholesale Trader
- Spices Trader
- Third-party Manufacturer
- Exporter
The following sections will discuss the documentation and basic procedure to get started with spice export from India.
Basic Certifications required for Spice Exportation
- Registrations for setting up Spice Export Business in India
- Incorporation Certificate
- Certificate of Registration as Exporter of Spices from the Spice Board
- Import Export Code
- Food Safety and Standard Authority of India (FSSAI) registration
- GST registration
- Phytosanitary Certificate
- Company PAN card
- Bank certificate
You may also need to secure the following certificates from the Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS) in case of the exportation of the given spices
- Chili powder ISI number: 2445-1963
- Curry powder ISI number: 1909-1961
- Coriander powder ISI number: 2444-1963
- Sampling & testing of Spices ISI number: 1997-1961
- Turmeric powder ISI number: 2446-1963
Arrange the following documents to obtain the Certificate of Registration as an Exporter of Spices from the Spices Board of India:
- Import Export Certificate
- Demand Draft worth INR 5,000 in favour of the Spices Board
- GST tax registration certification
- Confidential Bank Certificate.
- PAN card
Some Additional Licenses
Both these registrations don’t have any connection with the export business, but they could stimulate the company’s growth. While MSME registration helps small businesses and manufacturers to grow, trademark registration provides a much-needed shield to your IPR assets.
Prerequisites for conducting spice export from India
- First, choose how you wish to venture into this business model. You can enter into the export of spices as a wholesaler, retailer, supplier, retailer, or exporter, based on the interest and operating capital at hand.
All these individuals mentioned in this list would need to get registered under the apt Act and bylaws.
- Conduct in-depth marketing research to know every possible detail of the spice market. This will let you outline an efficient supply chain for the spice.
- Next, you will need to create a pool of trustworthy suppliers and vendors for the bulk purchase of quality spices. To accommodate this, you must locate an apt storage location & either buy or rent it. In case you wish to venture into the retail business, then you need to install suitable equipment and machinery for the seamless production of spices.
Manufacturer cum exporter needs to arrange the following machinery used in the processing and packaging of spices:
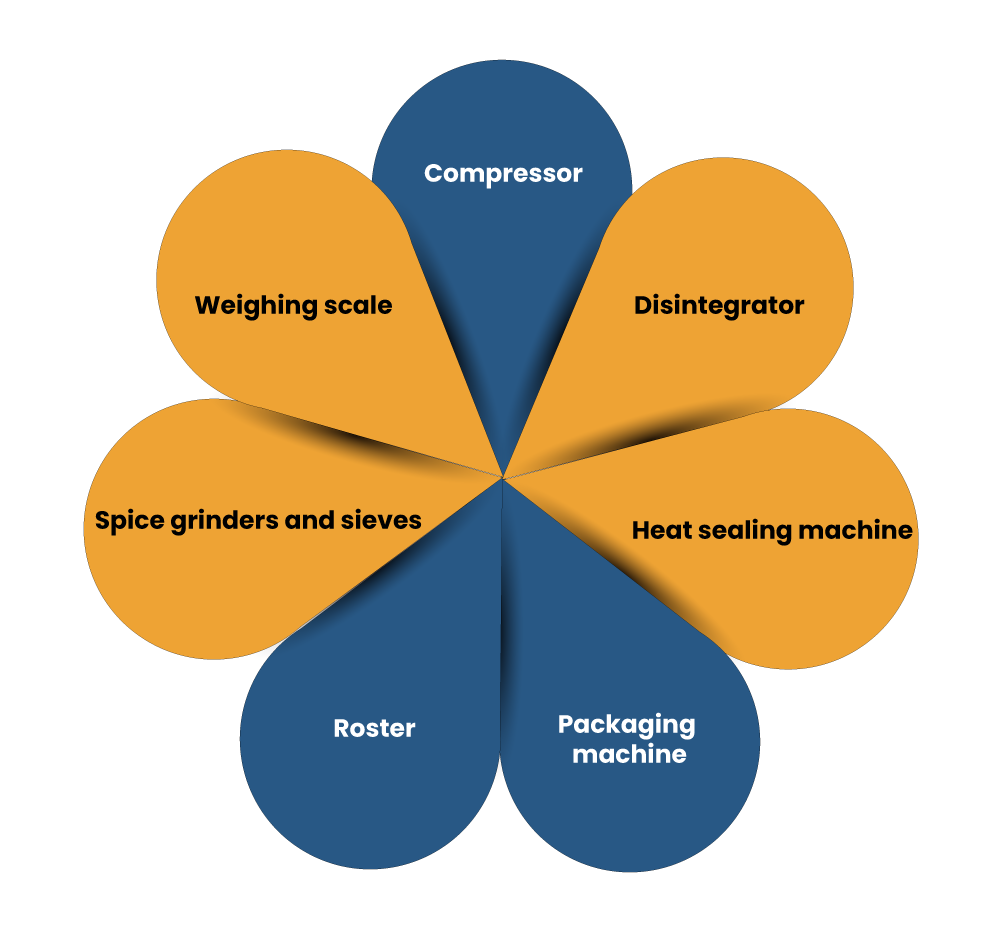

- Next, approach the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) to avail the Import Export Code. First of all, you need to create an account on the DGFT portal and then fill the relevant e-form. While entering the details, you will be prompted to upload some essential documents such as business registration, Aadhaar card, rent agreement, etc. After paying the requested fees against the e-form, the application process will reach its completion.
- Next, head over to the Spice board to avail of mandatory certification. This certificate serves as the fundamental legal document to conduct spice export from India.
- Lastly, exporters who deal with the processing and packaging of spices need to obtain an FSSAI license. It is a mandate, and there is no way you can overlook it.
- Draw a contract with an experienced and reputable company that will handle your shipping formalities in a legalized way.
Conclusion
This is how one can set up a legit business of spice exportation in India. Make sure to get in touch with a customs agent before starting your business journey. This is important because most start-ups aren’t familiar with the legal formalities and strict compliances incurred during the supply chain of the cargo.
Read our article:How to obtain IEC Code in India













