Public Procurement is a process by which the Government obtains goods and services from the private companies and pays them in monetary conditions for the goods as well as services provided by them. India’s rigid and institutional frameworks look to make sure responsibility, answerability and effectiveness in the Public Procurement Policy. The fundamental principle is to acquire resources & services of specific pre-eminence at the most competitive cost in an apparent and non-arbitrary method.
Public Procurement Policy for MSME
The objective of Public Procurement Policy is promotion as well as development of MSME Sector by supporting them in advertising the goods produced and services provided by them. Yet, the policy relies upon the core principle of competitiveness, remaining to sound procurement performance and implementation of supplies according to the system that is fair, reasonable, transparent, competitive as well as cost effective.
How does the Government Carry out Public Procurement?
The government conducts the Public Procurement Policy by the following-
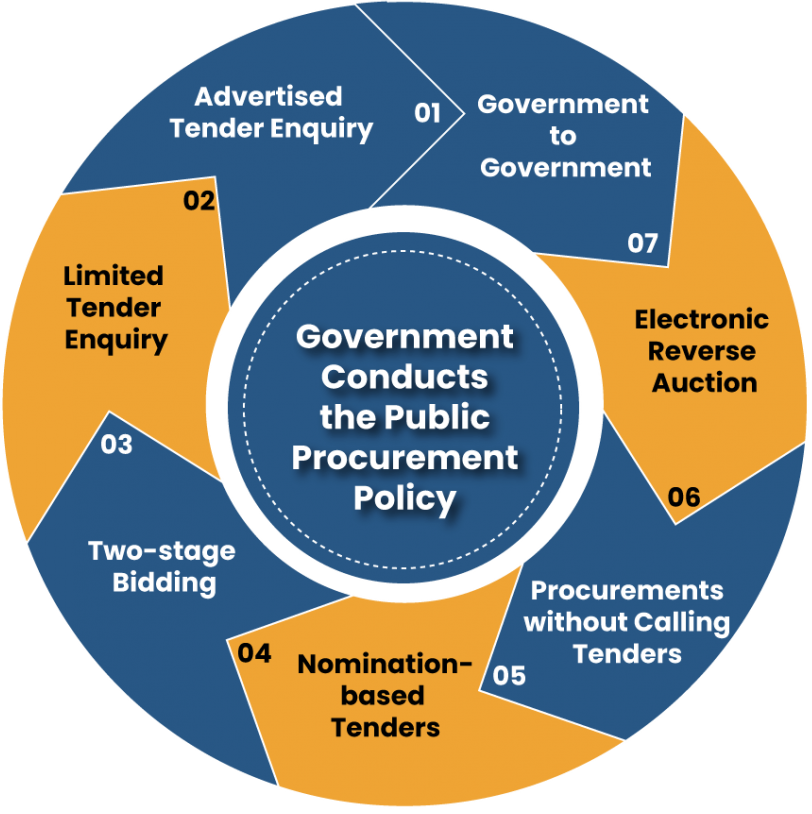

Advertised Tender Enquiry
Advertised Tender Enquiry is the default mode of procurement. The tender has to be advertised on Governmental Websites, National Newspapers, the Central Public Procurement Portal, Indian Trademark Journal, and Government E-Marketplace, and also circulated in Foreign Embassies.
Limited Tender Enquiry
Procurement is acquired through selected suppliers only. The selected lists of vendors are prepared through a screening process and are directly approached for bidding.
Two-stage Bidding
Two bids that are Technical and Financial are invited from the procurers.
Nomination-based Tenders
Some tenders are nomination based, that are called up by the government.
Procurements without Calling Tenders
This is classically assumed for small value purchases of standard qualifications.
Electronic Reverse Auction
Presentation by bidders of sequentially is more favorable bid during a scheduled stage of time and routine evaluations of bids are done.
Government to Government
Government to Government deals involve the transfer or sale of a country’s defense equipment, services, training, etc. to other foreign governments.
What is the Legal Framework Adopted in India for Public Procurement Policy?
The Legal Framework adopted in India for Public Procurement Policy are as follows-
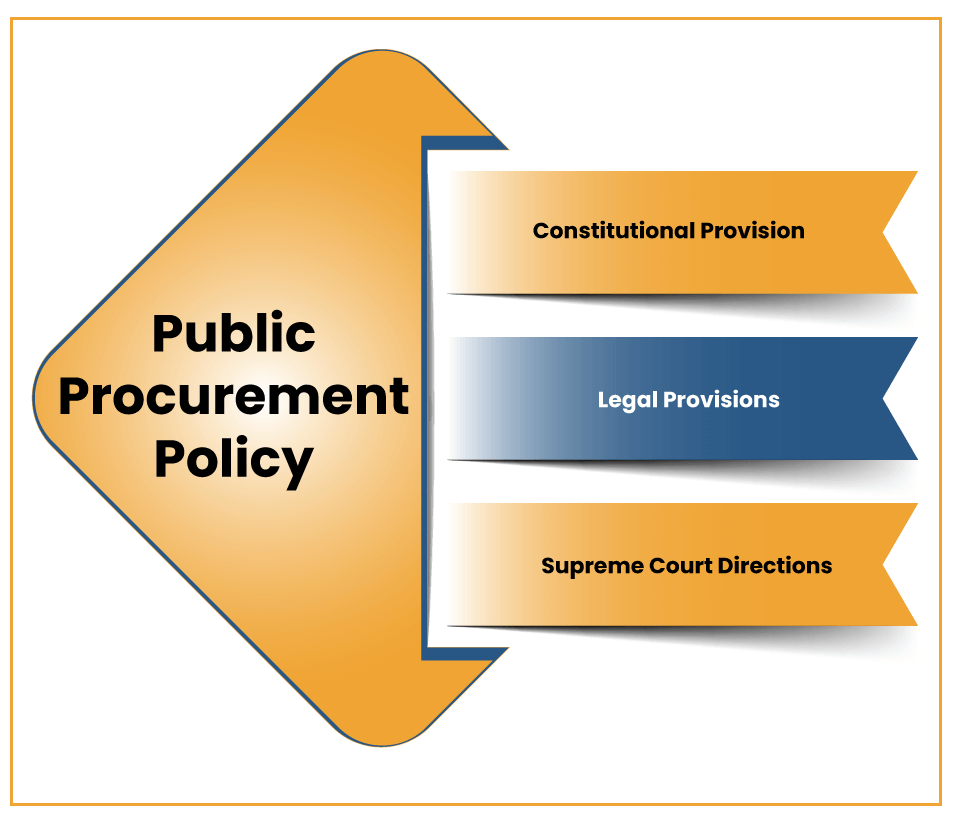

Constitutional Provision
The Constitution of India authorizes the Central and the State Governments to deal for goods and services in the name of the President of India or the Governor of the State respectively, and it directs self-sufficiency in public spending. Though, it does not stipulate any procurement policies or procedures.
Article 282 provides for financial autonomy in public spending, however there are no provisions to address any grievance.
Legal Provisions
A Public Procurement Bill was proposed in Lok Sabha in 2012, which could not be passed, where this bill was revamped in 2015 and introduced in 2015. But it suffered the same fate as that of earlier bill. So, as of now, there is No Central Legislation in India that administers public procurement of goods and services. Only 5 states in India, i.e. Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh and Assam have state public procurement legislation.
Competition Act, 2002
The Competition Act, 2002[1] penalizes anti-competitive activities such as bid rigging, collusive bidding, cartelization, and abuse of dominance.
Right to Information Act, 2005
It promotes transparency in government dealings by enabling Indian citizens to efficiently procure information from the government through “Right to Information” application.
Integrity pact under the General Financial Rules (GFR) & CVC guidelines
The pact addresses integrity in procurement of activities including the appointment of any external monitor to alleviate corruption as well as ethical risks.
Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 & Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
This Act penalize bribery and money-laundering and provide for confiscation of property derived from money-laundering and other illicit activities.
Supreme Court Directions
The directions by the Supreme Court are as follows-
- All contracts by the State should be granted by public auction or tenders to guarantee complete transparency and provide the eligible persons with the opportunity to participate in the auction;
- All official acts should be set in motion by public interest and should encourage public confidence;
- The State should not grant contracts by any private negotiation subject to specific exceptions based on the nature of the trade, and emergency circumstances;
- Government actions should be fair and nothing should be done which gives an impression of biasness, favoritism or nepotism. Emergence of public justice is as important as doing justice itself.
What are the Issues in the Public Procurement System in India?
The issues in the Public Procurement Policy in India are as follows-
The Absence of a Comprehensive Procurement Act
It has resulted in diverse procedures and multiplicity of rules across the procuring companies. Many times undertaking any comprehensive actions against the stakeholders involved in unfair practices become challenging in the absence of a strong legislation
Lack of standard bid documents
Instead of the initiatives taken for regulation of the bid documents and code of contract following the international organizations such as IMF or the World Bank, there continues to be a diversity of bid documents across the businesses in terms of addition, rephrase or repetition of clauses and provisions. Such uncertainty and disagreements in the bid documents stand against the philosophy of standardization, transparency as well as accountability.
Delays in Activities in Procurement Series
The procurement process is more often delayed in the stage of assessment need, budget preparation as well as approval. Likewise, unavailability of adequate procurement professionals and non-realization of the necessary information regularly appears to be responsible for the delay in preparing the technical qualifications.
Unfair Practices and Corruption
Despite the procedural protection, corruption level in India is supposed to be high in recent years that lead to low quality of public services which eventually hampers the development.
Presence of Anti-competitive Elements
The survival of anti-competitive practices by the bidders’ community tends to obstruct the procurement process by opposing the best value of money. Competition issues in India mostly concern with collusive bidding, bid rigging, cartelization and Abuse of Dominance.
Low Participation of the Domestic MSMEs
Despite the MSMEs provisions, the participation of domestic MSMEs in the public procurement policy remains low in India. Apart from the resource related entry barriers including anti-competitive fundamentals, many MSMEs do not take part in public procurement due to an insight that government obtained companies often delay in releasing the contract payment.
Competency and Skill of the Procurement Officials
India doesn’t have an Independent Grievance Redressal Mechanism in the procurement Policy. At the first level, an aggrieved bidder files for complaint on the misdeed or irregularities of the concerned officials of the procuring company. The judgement lacks reliability as the authority is from the procuring company itself that is responsible for causing grievances.
The Government of India imposed restrictions on Public Procurement Policy from bidders of the countries that share a border with India, citing the grounds of defense as well as national security. It was done by amending the General Financial Rules 2017.
Earlier the Central government made mandatory for sellers on the Government E-Marketplace Portal to explain the country of goods when registering for new products.
FDI
The government amended Foreign Direct Investment Rules authorizing prior approval for investment by companies in countries that share land borders with India.
Reason for Recent Changes in Public Procurement Policy
According to authority, the decision for amending Public Procurement Policy was taken to prevent the invasion of Chinese products and investments into India, to push India towards Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Conclusion
The present study reviews that the Public Procurement Policy and recent reform initiatives taken in India, outlines the requirement for changes in the institutional structure. The current system appears to be complex due to heterogeneity in the requirements in the federal structure of the government functioning and absence of a comprehensive procurement Act.
The system suffers from some serious drawbacks such as fragmented procedures and rules, lack of standard bid documents, unavailability of sufficient procurement professionals, and lack of transparency, widespread corruption, and lack of independent grievance redressal mechanism. Therefore, these need to be backed up by legislative power and Draft Bill 2015 & enacted with revisions in certain areas. Contact Corpbiz for more information related to MSME Registration.
Read our article: An Overview of New Debt Facilities for Distressed MSME













