Every person who earns has to contribute to this tax of the state, irrespective of his/her income share of monthly or annually. The employer will deduct this tax from the salaries of employees, and the same amount has to be paid to the respective department of Government.
The self-employed people require to obtain a ‘Certificate of Enrolment’ from a prescribed authority of the state he/she is living in, to pay this tax.
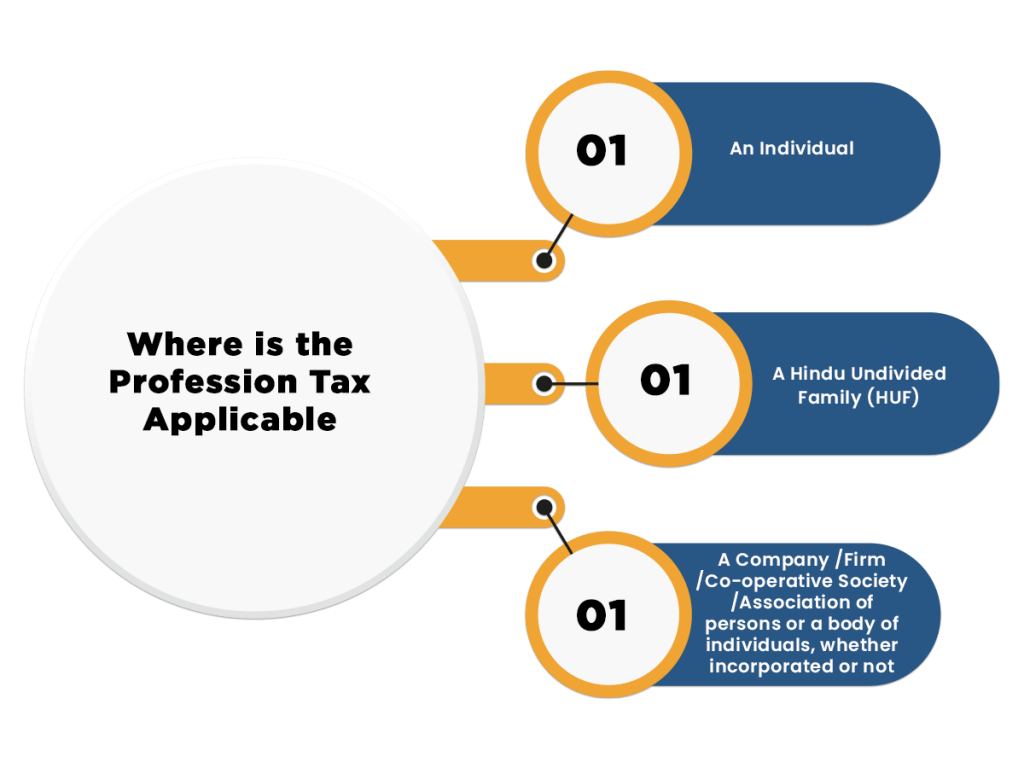
Where is the Profession Tax Applicable?
Profession tax is applicable upon the following classes of persons:-

Importance of Profession Tax
Self-employed persons who carry their profession or trade on their own and fall in the ambit of profession tax are liable to pay tax themselves to the state government. The Commercial Taxes Department of a state and union territory is the nodal agency which collects professional tax on basis of predetermined tax slabs which vary for each state and union territory.
The tax is calculated on an annual taxable income of an individual. However, it must be paid either annually or monthly. The Self-employed taxpayers require to obtain a Certificate of Enrolment from prescribed authority (of a concerned state) in a prescribed manner.
In case of the salaried individuals and wage earners, an employer is liable to deduct the profession tax from employee’s salary on a monthly basis (as per applicable professional tax slab) and deposit the same with state government. An employer needs to get a Certificate of Professional Tax Registration from concerned authority.
Profession Tax under Income Tax Act
- A maximum of Rs. 2,500 may be levied as professional tax on any person per financial year.
- According to Section 16 (iii) of Income Tax Act 1961[1], the profession tax paid by an employee who is allowed to deduct from his/her gross salary income.
People who are Exempted from the Professional Tax
The certain exemptions in professional tax for those people who are:
- Parents or guardian of the physically or mentally challenged child.
- People who are handicapped more than 40% physically or visually.
- Senior citizens above age of 65 years and in Karnataka above the age of 60 years.
Professional Tax Rates that are Applicable in India
The chart is given below for all the States and Union Territories with their imposable professional tax rates for FY 2019-20. However, there are few states, for instance, Delhi and Haryana which do not make this tax applicable.
|
State |
Per month income |
Tax rate /amount(per month) |
|
Andhra Pradesh |
|
|
|
Assam |
|
|
|
Bihar |
|
|
|
Goa |
|
|
|
Gujarat |
|
|
|
Jharkhand |
|
|
|
Karnataka |
|
|
|
Kerala |
|
|
|
Madhya Pradesh |
|
|
|
Maharashtra |
|
|
|
Manipur |
|
|
|
Meghalaya |
|
|
|
Nagaland |
|
|
|
Odisha |
|
|
|
Puducherry |
|
|
|
Punjab |
|
|
|
Sikkim |
|
|
|
Tamil Nadu |
|
|
|
Telangana |
|
|
|
Tripura |
|
|
|
West Bengal |
|
|
Penalties for Non-Payment
For any delay in the payment of professional tax, a government has set up a penalty of 2% per month till the time the payment is made. In case if there is a delay in obtaining the ‘Certificate of Enrolment’, then there is a penalty at the rate of Rs. 2 per day, and if any information gave is found to be inaccurate, then the penalty increases to three times the tax to be paid.
Conclusion
The professional tax rates vary from state to state, and the salaried individual must be aware of the prevailing rates. Consulting a Chartered Accountant is always better as it would help in the prevention of loss. Some states also provide the tax rebate if a tax is paid as a lump sum. So, prepare yourself in advance and gather all the facts before submitting the professional tax by contacting at Corpbiz.
Read our article:Let’s Understand the Concept of Professional Tax in Tamil Nadu











