NBFCs make their way to the financial market about six decades back and since then they are playing a commendable role in serving the lower strata of society. Unlike banks, they are easier to access and facilitate lucrative financial services to the needy ones. Apart from providing easy finances, the NBFC also deals with numerous businesses such as hire/purchase, buying government securities, and insurance. In this article, we shall briefly describe the Operational manual of the NBFCs.
Overview of NBFCs
Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is basically an entity registered under the Companies Act, 2013, which offers financial services such as loans and advances. All NBFCs are registered under the Reserve Bank Act 1934 and are governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Area of Operations in NBFCs

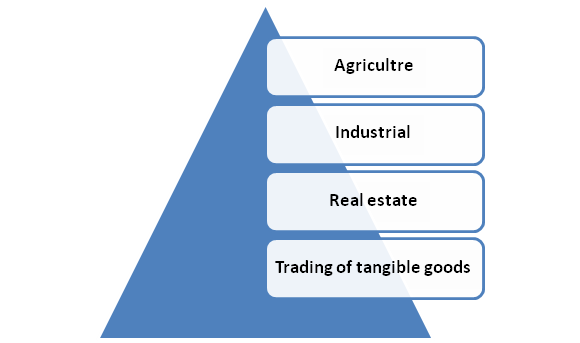
Areas that NBFCs don’t Serve
NBFCs don’t deal with the following areas:-

Read our article:Documents Required for NBFC Registration
Classification of NBFC
Depending on the type of business operation, Non-banking financial companies are classified into ten types.
ICC: Investment & Credit Company
Such category of NBFC carries out the given investment and lending activities:-
- Asset
- Providing Loan
- Financing
- Providing Investment solutions
IFC: Infrastructure Finance Company
This category of NBFC provides financing services to infrastructure companies such as construction companies and real estate.
NBFC-ND-SI (Non- Deposit taking Systemically Important Core Investment Company)
Such type of NBFC primarily deals in financial instruments such as debentures, Equity & Preference shares, and stocks. Also, these entities render credit to companies for different purposes. It should be noted that only those NBFCs come under the category of Systemically Important whose total assets are more than five hundred crores according to the last audited balance sheet.
IDF: Infrastructure Debt Fund NBFC
Such NBFCs are mainly concerned with facilitating long- term debt to the infrastructural projects.
Microfinance NBFCs
As the name suggests Microfinance institutions are involved in providing small financial loans to individuals from lower strata of the society.
NBFC- Factor
These categories of financial lenders are primarily engaged in acquiring accounts of receivables of an assignor. They conduct such activities with an objective to render discounted loans against the security interest over the receivables.
Non-Operative Financial Holding Companies (NOFHC)
These forms of NBFCs provide financial credit to those entities looking to establish new bank or financial institutions.
Mortgage Guarantee Company
Such companies mainly serve those individuals who are confronting repayment issues against the home loan. The mortgage guarantee helps them to address the risk of default on a home loan.
Account Aggregators
Account aggregators essentially retrieve or accumulate information of its client in relation to financial assets under a contract.
Peer to Peer Platform
Peer to peer platform is an online platform registered by the Reserve bank. It essentially conducts the activities regarding Peer to Peer Lending through an online platform. Such a form of NBFC allows the borrowers to interact with exhaustive list of lenders registered on the platform.
Operational and Credit policy (operational manual of the NBFCs)
As mentioned above, all NBFCs are regulated by the Reserve bank. Henceforth, for hassle-free operations, these entities are needed to comply with certain credit and operational policy as mentioned by the central bank i.e. Reserve Bank of India.
The following section exhibits the crucial elements of the operational and credit policy provided by the Reserve Bank of India[1].
Customer KYC Policy
Reserve Bank of India directs all the financial lenders to operate pursuant to the prescribed ‘Know your Customer’ procedure (KYC). KYC is imperative to scrutinize the flimsy or vague transaction and report it to the relevant authority.
The primary objective behind the KYC guideline is to protect the financial institutions from being tricked by fraudulent borrowers engaged in money laundering activities. Besides, the motive of KYC is to empower financial institutions to get familiar with their borrowers’ needs in a better way. Consequently, this will allow them to address the disparities in an authentic way.
All the Non-banking financial companies are needed to lay out their KYC policy pursuant to the given essential elements. Those are as follows:-
- Financial Risk Management
- Customer Acceptance Policy
- Monitoring of transactions
- Customer Identification process
Anti-Money Transaction
It does make sense that transparent transactions are imperative not only for brisker growth of the industry but also for the sovereignty of the country. In the purview of the above, the Department of Banking Operations and Development, aka DBOD and Reserve bank had laid down elaborate directions to all NBFCs and Banks, under the supervision of the Financial Action Task Force.
The recommendation of the Financial Action Task Force, (FATF) on terror financing standards and Anti-money laundering have now becomes a benchmark for the regulatory authorities for framing out the policies for terror funding and Anti Money Laundering (AML).
Compliance with these benchmarks by these financial institutions is therefore essential for global financial relationships. Here are some crucial directions by the Reserve Bank for the NBFCs for laying out operational guidelines of anti-money laundering and KYC measures. Those are as follows:-
- The customer’s information must not be accessible to anyone other than NBFCs.
- Client information must be pertinent to the perceived risk, and not interfering by nature.
- Banks cannot get their hand on the client’s information without their permission. Such activities are required to perform after the opening of a bank account.
- The operational directions for Non-Banking Financial Companies are issued under section 45K and 45L of the Reserve Bank Act 1934. In case of any violation, the defaulter has to confront prescribed penal actions drafted under this Act.
Customer Acceptance Policy
Customer’s acceptance policy is an imperative part of the operational manual of the NBFCs. NBFCs must layout detailed and clears guidelines regarding the acceptance of customers. The policy should enclose the clear-cut direction regarding the given aspects.
- Banks must avoid opening an account on somebody’s name that is not legitimate or doesn’t even exist.
- Classification of the customer on the basis of risks and other aspects such as business activity, mode of payment, location, and turnover, etc.
- Documentation and other information in accordance with the Reserve bank guideline and PML Act 2002 should be issued from time to time.
- Bank cannot open or close the account in the event of the non-cooperation of the customers.
- Preliminary validation checklist for opening a new account.
- If in case any customer is permitted to act on behalf of any another entity/individual, should be visibly spelt out.
Customer Identification Procedure – Operational manual of the NBFCs
Customer identification indicates probing a customer and its credibility depending on the documents and information. Henceforth, Non-banking financial companies are needed to accumulate adequate and legitimate information for every new customer. Consider the following points during the validation process of new customers.
- Verify the relevant documents to determine the legal status of the entity/individual
- Check that the person if approved by the relevant source to act on the behalf of another company/person.
- Get familiar with the entitlement structure and ownership of a new customer.
- Ascertain the ownership and entitlement structure of a new customer.
- NBFC must examine the person who is in authority or acting as a legitimate individual on the behalf of another person.
Probing of Financial Transaction- KYC Framework
Probing the transactions is indeed an imperative part of an effective KYC framework. In reality, the NBFCs can efficiently control and overcome their risk factor by ascertaining the financial activity of new customers. In view of this, the given pointers could prove to be effective:
- NBFCs should lay out a system for probing the risk categorization of the account.
- In the view of the same, NBFCs must take appropriate measures to mitigate suspicion.
- NBFCs must take good care of transaction records with utmost diligence and care in the view of u/s 12 of the PML Act, 2002.
- Additionally, it’s essential for making sure that flimsy or vague records are reported promptly to the relevant authority.
Risk Management
Companies deploy Risk management with an aim to mitigate the immediate and complex threat. The same is also true with NBFCs. Nonetheless, in order to overcome intricacies, NBFC must implement an effective KYC program that consolidates effective measures for risk elimination. Here are some crucial elements of the KYC program, which must encompass proper management flaws, assignment of taks, training, etc.
- The NBFCs should prepare risk profiles of their existing and new customers by taking Anti Money Laundering measures into account to mitigate transaction risks.
- An efficient training program should be there in place to train the employee about KYC procedures.
- Distinctive training modules for the front-end and back-end compliance employees.
The business members should enact a sound risk management policy as soon as they availed the NBFC registration.
Pre-settlement policy
As the name suggests Pre-settlement policy is referred to as early payment of the loan. Under this policy, borrowers can clear all its dues related to the loan before the completion of the loan tenure. The banks and financial institutions are liable to lay out policy regarding the same so that customers can pre-settle their loans without any hassle. There must be proper terms and conditions in place for the pre-settlement policy. The T&C of pre-settlement policy must the following conditions:-
- Clarify whether part prepayment is permitted or not.
- Mention about penalties provision regarding prepayment, if any.
- Mention rebate/reward for pre-settlement policy, if any.
- Mention whether pre-settlement of loan permits next loan cycle or not
Asset Classification – Operational manual of the NBFCs
It should be noted that loans are valuable asset for financial institutions. Thus; it’s imperative for the banks to classify the borrowers into standards and non-performing assets.
Flowchart of Complete Asset classification
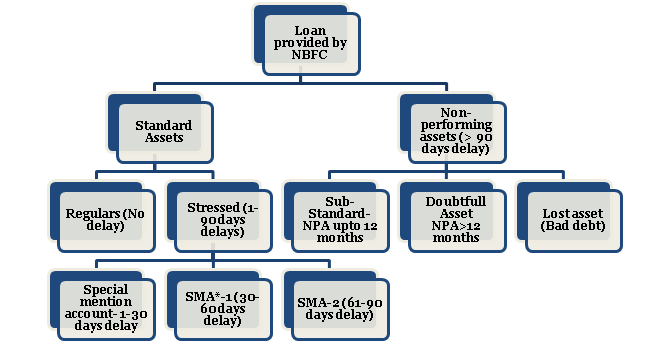

“SMA* stands for Special mention accounts. It is referred to as the loan asset on which the principal and interest are overdue for ninety days.”
Income recognition by the Non-banking financial companies shall be done on the basis of the accounting standards drafted by ICAI. In view of the above:-
- Income that consolidates interest plus any other charges in pursuant to non-performing assets shall be recognized only when realized.
- Income generated from non-performing assets shall be recognized on a Cash basis.
Loan Write off Policy
When the non-performing assets loan manages to spend some time in arrears, then it can be written off. RBI has drafted some guidelines in the view of the above. The following tabular representation exhibits the same. Loan Write-Off Policy Drafted by Reserve Bank
| Types of loan assets | Reserve Bank Guidelines |
| Standard Assets | One percent of outstanding |
| Sub-Standard Assets | Fifty percent of outstanding |
| Loan asset | Hundred percent of outstanding |
It is evident, that financial houses including NBFCs must draft an effective accounting policy with respect to loan write-off. A policy that is capable of removing NPA loans from the account book can however devalue the credibility portfolio; while unnecessarily exaggerate the portfolio’s quality. Thus; while examining the quality of the portfolio, the analyst must probe the level of bad debts.
Loans Restructuring
NBFCs reserve the right to alter the terms of the ongoing loan agreement as the policy drafted by the board of Directors. The following events entice such a situation:-
- Prior commencement of the business
- In case the asset is classified as sub-standard.
- Post commencement of the business after the asset has been classified as sub-standard.
- In each said cases, the restructuring of interest or principal can be done, with/without sacrifice.
Restricted Loan
In the purview of the bylaws and RBI’s regulation, all financial institution including NBFCs and MFIs cannot approve loan to the following candidates.
- Loans to bailout/replace the lenders who wish to withdraw. Loans to political candidates, parties, or other political organizations.
- Loans to gambling enterprises.
- Loans for drugs and alcohol-related activities. Loans for weapon/ armament activities
Conclusion
Well, that’s all about the operational manual of the NBFCs. NBFCs and MFIs playing a pivotal role in stabilizing the turbulence exists in the economic infrastructure of the country. With that being said, NBFCs are still evolving and seeking soft regulations from the governing authorities to carry out their operations more proactively. Hope this presentation has strengthened your understanding regarding the operational manual of the NBFCs. Please do connect with us or communicate with CorpBiz’s experts if you need help regarding NBFC registration or other matters.
Read our article:NBFC Registration: Step by Step Procedure











