Evolving customer’s taste, increasing competition, limited funds often make life difficult for the companies. Series of unprofitable years could drive the companies to opt for voluntary winding up.
Closure of a registered establishment in India has to be done through a legal procedure. This write-up consolidates four ways through which a private limited Company can be closed.
Sell Out of an Entity – A Way of Voluntary Winding Up
Transferring the ownership of the Private Limited Company to another entity is also a form of voluntary winding up. It can be accomplished by selling shares against the predetermined price. Practically, selling off a company through share transactions cannot be deemed as a winding-up method by the virtue of the prevailing bylaws.
What is Mandatory Winding up of an Entity?
Any registered organization in India under the purview of the Companies Act, which is found to be guilty of breaking laws, has to face the compulsory winding up as ordered by the Tribunal.
Procedure Relating to Mandatory Winding Up
Following instructions can be followed for the Mandatory Winding Up of a Private Limited Company:-
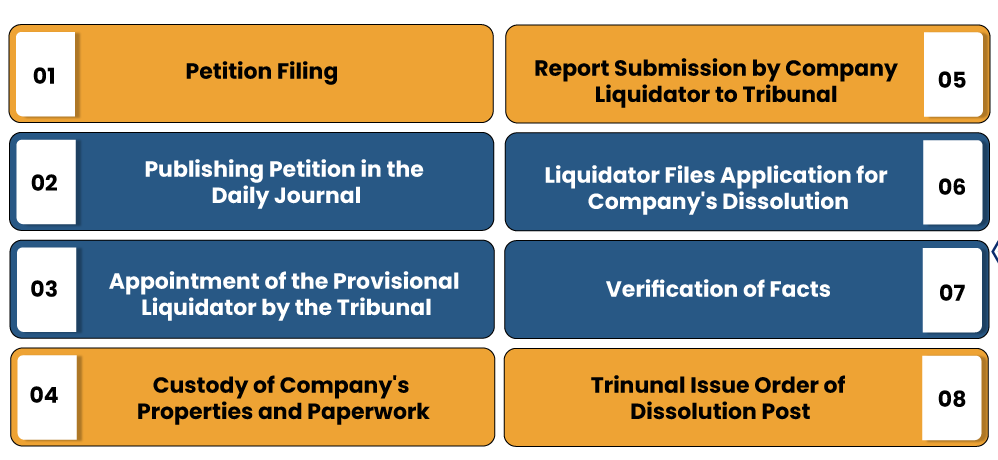

Filing of Petition
The petition filing will be done by the following:-
- The Company or Trade Creditors
- Contributors to the Company or
- Any or all of the above mentioned categories or
- The Central or State Government or
- By ROC i.e., Registrar of the Companies
Form WIN 1 or WIN 2 is generally used for the petition filing. The applicants are required to submit the said Form in triplicate. Before petition filing, the applicant must arrange an affidavit in Form WIN 3 which will go along with the same.
Attach the Petition with Statement of Affairs of Company
All the documents annexed with the petition should be audited and verified by a practicing CA. Form WIN 4 in duplicate must be filed for providing a statement of affairs. The same must be verified by an affidavit in Form WIN 5.
Advertising the Petition for 14 days
The Company must publicly share the petition in a preferred language via a daily journal for 14 days. To serve this purpose, the Company has to leverage the Form 6.
Proceedings of the Tribunal
The Tribunal will hear the petition on the hearing date; accept replies & objections from the petitioner as well as respondent. The Tribunal may appoint a provisional liquidator during the legal proceeding.
The appointment order of the provisional Liquidator shall be made in Form WIN 8. Meanwhile, the winding-up order shall be made in Form WIN 11. The winding-up order must entail:-
- The duty of such individuals to submit the audited books of accounts up to the order’s date.
- Provide the date, time & location for the Liquidator.
- Surrender the assets & documents related to assets to the Company liquidator. Post-winding-up order, the Liquidator shall take the custody of Company’s properties and paperwork. The Company liquidator will then forward a report to the Tribunal within 60 days of the winding-up order’s date.
- After the complete winding up of Company’s affairs, the Liquidator shall file an application to the Tribunal for the Company’s dissolution. After being satisfied by the grounds supporting Company’s dissolution, the Tribunal will issue a dissolution order for the Company, which shall become effective from the order’s date. The Company Liquidator shall forward the order copy to the registrar within the 30 days of the date of the order,
If the Tribunal fails to spot an error in account or compliance requirement, the Tribunal will issue the Company’s dissolution order within 60 days of receiving the application. After this, the registrar will issue a notification in the Official Gazette specifying that such a Company is dissolved.
What is the Voluntary Winding Up?
A company seeking voluntarily winding up has to follow a long list of legal prerequisites. Following are the scenarios under which voluntarily winding up is feasible:-
The Company passes a resolution after the expiration of the timeline for which it is formed, or upon the occurrence of an event that supports winding up as per the article or- The Company passes a special resolution for the same with the approval of at least 3/4th of the shareholders.
The winding-up in such cases starts Form the date of passing of resolutions cited above. The Company is also required to appoint a liquidator in the same meeting. The appointment of Liquidator seeks the approval of all the creditors of the Company.
Procedure Concerning Voluntary Winding Up
- The Company passes a resolution as mentioned above in their general meeting. However, most directors must give their consent for the same.
- The Winding-up of Company is impossible without the Trade Creditors’ permission.
- The Company must make a Declaration of Solvency after taking approval from the trade creditors. Declaration of Solvency must reflect the Company’s credibility.
- The Liquidator is the one who would carry out the winding-up proceedings and draft a report on Company’s assets, debt, and so on. The report has to be presented before general meeting for approval and passing the resolution for Company’s dissolution. The Company’s Liquidator will forward a copy of final account & resolutions to the ROC.
- The company liquidator shall file a petition before the Tribunal to avail an order to dissolution of the Company. Upon examining all the facts about winding up, the Tribunal shall issue a dissolution judgment within 60 days of the application. A final order copy must be filed with the Registrar of Companies.
The aforesaid procedures shall be filed in a standard form & even after the firm gets wind up; its name cannot be taken by other applicants for 2 years. The format regarding various forms and winding-up procedures is mentioned under the Companies (Winding-up) Rules, 2020.
Winding Up of a Defunct Company as per Company Act, 2013
In light of the Companies Act, 2013, a Defunct Company refers to an entity that has gained the Dormant Company’s status. Since these institutions lack fiscal accessibility of any kind, the Indian Government renders certain relaxation in this regard.
The Companies Act, 2013[1] provides Defunct Company with the legal procedure of Winding up. For that, such entities are supposed to file an application in the Form known as STK-2 Form with the Registrar of Companies. The winding-up cannot be possible without the consent of the Companies’ directors and board members.
For the purpose of the said scheme, a defunct company is known as an entity that has:
- Nil asset and Nil liability
- No activities have been undertaken post incorporation
- Has not been executing business functions since last one year before filing an application under FTE (Fast Track Exit Scheme).
Conclusion
A company may wind up its affairs if it is finding it hard to carry on its business, or if it was established only for a specific purpose, or if it fails to meet its financial obligation. It is evident from the above that a private limited company’s winding up is not a straightforward process. There is a lot of legal complicacies involve in the winding-up process.
Read our article:Difference between Winding up & Striking off a Company in India











