A business in India can be conducted under different forms of entities. Among them, you can consider these most popular types: limited liability partnership, sole proprietorship, co-operative societies and partnership, companies, in which each of the kinds of business has its benefits and drawbacks.
Overview of Forms of Companies
The sole proprietorship and partnership companies have significant advantages over the outstanding structures in the well-being of establishment as well as the closure of the company. Moreover, the Limited liability partnership, companies, and co-operative societies need to comply with various regulations during its existence and known to be the entities created under a statute. Furthermore, closure of these forms of entities can be done only by following the specified procedure under the statutes under which they were established. In this article, we shall concentrate on the closure of entities that were registered under the Companies Act, 2013[1] .
What is a company under Companies Act, 2013?
A company registered under section 3(20) of the Companies Act, 2013(“The Act”) may be defined as an association of persons. It has the characteristics of a separate legal entity, perpetual succession, limited liability, share capital, common seal, transferability of shares, and any other previous act consider a distinction between ownership and management if it.
It can be established to carry on business to make profits or be performed even for non-business objectives. Therefore, irrespective of the object or business, every company shall come into existence only after incorporation under the Act. The Registrar must issue the Certificate of Incorporation on completion of registration. Moreover, the Companies name must enter into the Register of Companies.
After its continual existence, until it is wound up or declared defunct by the Registrar according to the provisions of the Act, it shall operate on-going concerns.
Methods in which a company can cease to be in presence are as follows:-


Brief: Winding up and Striking off
The process of winding up and striking off may be initiated under the operation of law without any company’s application or be done voluntarily by the company. The provisions concerning striking off (Section 248 to Section 252 of Companies Act, 2013), and winding up (Section 270 to Section 365 of Companies Act, 2013) prescribes the same rules and procedures.
Winding-up
Winding up is a procedure by which the dissolution of a company gets conducted. Moreover, its assets are collected and realized and applied in payment of its debts over time. After that, the remaining amount gets returned to members who have contributed to the company. It was prominently pronounced in the articles of Halsbury’s Laws of England.
Winding Up: Voluntary by Members or Creditors
In a Voluntary Wind Up, few requirements need to be adhered to.
Those are as follows:-
- A resolution must be passed in the General Meeting where all the Appointments & remuneration should get fixed.
- A notice has to be issued by the company to Registrar concerning the Appointment of the Liquidator for winding-up.
- Afterward, a declaration of financial stability/solvency has to be filed. Moreover, if it is a Member Wind Up or a Creditor Wind Up, it must be specified in the same declaration.
- The liquidator’s report concerning all states of affairs must be placed at the General Meeting.
- Within a week of General Meeting, the liquidator must send a report to the Registrar as per prescribed format.
- The company considered to be dissolved from the report’s date if the Official Liquidator possesses no opposition.
Winding Up: Compulsory or by Tribunal
- All the circumstances/Grounds should exist, as mentioned in Section 433.
- The petition is to be filed by an appropriate person before the Tribunal.
- The petition should be admitted by the National Company Law Tribunal for future commences.
- Intimation has to be given by the Tribunal to the Official Liquidator.
- The Statement of Affairs has to be filed with the Official Liquidator by the company.
- The preliminary report has to be given within six months by the Official Liquidator to the Tribunal.
- After the fulfillment of the report of the Official Liquidator, Tribunal must initiate dissolution of the company.
Incidents available for Compulsory Winding Up
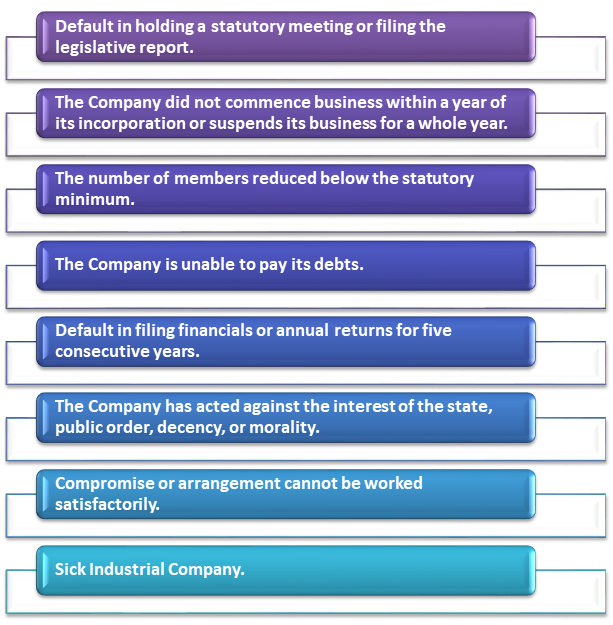

What are the Benefits of Winding up of a Company?
Discharged from duties/debts later liquidation
The administrators and all company leaders are free from all lender accounts and pressure after the liquidation method is over.
Withdrawing legal action upon the company
If the recommendation is passed deliberately by directors, they will ignore legal action brought by the court or the Tribunal, and provide a program to company directors to focus on other business possibilities.
Inexpensive cost for liquidation
As rates will apply to the sale of assets, the price or duties expected in the liquidation method will get relatively smaller.
Contract agreements will get terminated.
During the liquidation process, if any company or entity has entered into a lease for a prescribed time, it will terminate all the terms and conditions of the agreement.
Security for creditors
After all the followed processes, creditors will benefit from the liquidation method as they will be ready for a failed payment, concerning the statement of credits provided by all creditors.
Read our article:New Winding Up Companies Rules (2020) under Companies Act 2013
Winding Up Registration Procedure: Recent 2020
Winding-Up) Rules 2020 for companies came into effect from the 1st April 2020. Complying with the new rules will reduce the burden of the National Company Law Tribunals (NCLTs) by enabling a summary of liquidation plans/procedures. Appeals or Petitions for winding up company is subjected to various conditions, which include thresholds on turnover and paid-up capital.
According to the latest winding-up Registration Procedure, a company attempting to wind up Section 361 must adhere to the below-mentioned requirements.
Those are as follows:-


Striking off
Striking off a name is one of the methods of the company from the ROC of executing an end to the existence of the company.
Striking off: Initiated by the Registrar of his motion
If a company is not carrying on business or is not in operation, then the Registrar should send a letter to the company inquiring about the same. A second letter should be sent if no response is received for the second letter if there is no reply within one month. A notice shall be issued in the Official Gazette stating the (or “intending to”) striking off the name of the company. He can proceed with striking off only if there is no response to the second letter or confirmation that the company is not optimizing on business or is not in operation.
It can be done in two steps:-
- If there is no cause proofed against it, the company would be dissolved at the end of 3 months. In this case, kindly send a notice to be published in the Official Gazette. The notice, as mentioned above, will be shipped by registered post to the Company and Income Tax Authorities.
- If he is contended/satisfied that liquidator is not acting, or the affairs of the company are entirely wound up, you can issue a notice to a company under liquidation. It would be best if you also took care of the returns required to be filed by the liquidator is not performed for six months. The Registrar can go for striking off the name of the register and issue a notice in the Official Gazette to that effect on the expiry of 3 months.
Striking off: Application by the Company
- Along with necessary attachments, as prescribed, the company should make an application with the assistance of e-form 61.
- Registrar may go for striking off the name and publish a notice in the Official Gazette if he is satisfied with the correctness of the application.
Striking off: Fast Track Exit Mode
The Fast Track Exit mode for Striking off is available only for few conditions. Those conditions are as follows:-
- No assets and liability.
- Not starting any business activity or service since incorporation or is not carrying any business activity or sustenance for the last one year.
- Not Applicable for listed companies, delisted companies for non-compliance, Section 25 companies, etc.
- Fast Track Exit Mode-form should be presented along with necessary attachments as directed.
- Registrar shall issue an email to the address mentioned in the form, giving 30 days to show cause why the name must not be struck off the register only if he is satisfied with the correctness of the application.
- The Registrar shall provide the information of companies opting for and give 30 days for objecting to this method in the MCA Portal.
- The Registrar may proceed for striking off the name and publish the notice in the Official Gazette after the prescribed limited time.
Requirements to proceed to make an application for Striking off are as follows:-
- No pending statutory dues.
- No pending litigation/proceedings against the company.
- No assets and liabilities.
- Not in working mode for at least a year.
What are the Advantages of Striking Off?
Striking Off can be performed speedily.
Striking Off is an instant method to close it if a company is dormant and has no creditors. The company will be taken off the register at Companies House after a period of three months. Nevertheless, three months’ notice must be given to them before the application can be submitted if the company has any outstanding creditors.
Striking Off is economical to execute
The charges to submit a Striking Off application form at Companies Registrar is insignificant. Even if you decide to pay for professional help, the dissolution process will be far less costly than the cost of converting the Company status.
No examination of director’s charges and authority
There is no formal investigation of the conduct of the directors after a company got Struck Off. There is no risk for treating accused of wrongful trading until and unless the company converted by a creditor and a winding-up petition announced.
No obligation to fulfill annual returns and accounts
There are no longer required file on-going annual returns and accounts with Companies House if a company got struck off. The appropriate accounts and returns must be filed even if the company got left dormant rather than struck off. If the substantial part has not been done, the financial penalties will be levied on the directors.
Comparing Striking Off & Winding-Up
General Assumption
One might tend to conclude that there is not much difference between the two processes in achieving closure of the company based on a simple review of the above procedures. Equally, both have a set of formalities to be met by following the statute.
Reality
On the other hand, based on real regimes, there is a vast difference between striking off and winding up procedures. The process of winding up takes over a couple of years on an average to complete the process, which is relatively slower. Comparing to the other, the striking off procedure is a lot simpler and quicker. However, it is potentially permitted to monitor this route only in case of ‘defunct companies.’
Liabilities
Striking off is the preferred option with nil or minimal obligations for defunct companies or companies. Companies that no longer need to exist need to wind up their affairs and require them when companies have assets and liabilities. On the other hand, the striking off procedure is not as expensive as compared to winding up. In the case of winding up, there are fees sustained concerning the court/tribunal, charges of the liquidator, etc.
Conclusion
Striking off is a suitable option to achieve closure given the simplicity of the procedure, then the limited time occupied and being less expensive when a company has stopped operating. Nevertheless, the company needs to pay off all its liabilities and statutory dues and not have any pending litigation/proceedings for this process. Companies mostly stop operations because their net worth is eroded entirely or significantly, and they are not profitable.
The Ministry delivered a vide circular in July 2011 to accelerate winding up proceedings. The procedure under the latest Companies act should be completed more straightforward and effectively, taking into deliberation the scope and nature of the company.
Our CorpBiz group will be at your disposal if you need expert advice on any aspect of Winding-up or Striking off a company. We will help you to ensure complete compliances concerning all the issues related based on your desired activities, ensuring the fruitful and well-timed completion of your work.
Read our article: Commencement of Winding Up of a Company by Tribunal under Companies Act 2013











