The Factoring Regulations (Amendment) Bill, 2020 was introduced in the lower house of the parliament on September 14. The bill aims to make significant changes in the Factoring Regulation Act, 2011. It focuses on widening access to credit for businesses seeking funds to ensure uninterrupted growth. In this article we described about Factoring Regulations (Amendment) Bill, 2020 Introduced in Lok Sabha.
As per the said Act, the factoring business is referred to as a business where an entity (regarded as a factor) obtains the receivables of another entity (recognized as assignor) for a specific amount. Receivable is referred to as a total amount that is owed by the customers.

The factor can either referred to as a bank, company registered under company bank, or non-banking financial company. Keep in mind that facilities rendered by the financial institutions against the receivables are not regarded as factoring business.
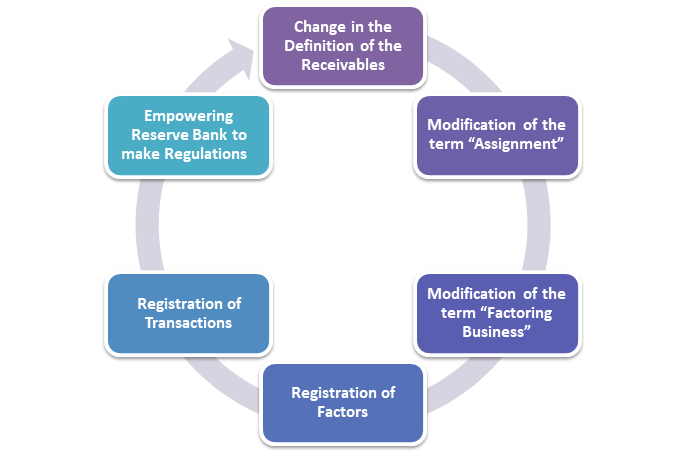
Change in the Definition of the Receivables
As per the act, the receivable is defined as the monetary amount, which is a legal right of an individual under an agreement. This right may be accruing, existing, or conditional from the use of the services. The bill amends this definition to mean any amount of money owed by the customers (regarded as debtor) to the client (assignor) for the use of services or facilities.
Modification of the term “Assignment”
The Act expresses “assignment” as transfers of an interest (undivided) related to the assignor in any the bill amends this definition and states that receivables are regarded as the amount owed by the customers (the debtor) to the client (assignor) for the use of the facilities and services.
Modification of the term “Factoring Business”
“Factoring business” implies the business related to the acquisition of receivables of assignor by taking an assignment of such financing, whether through credit or advances or otherwise related to a security interest over any receivables but does not enclose credit facilities rendered by a financial institute in the course of business against receivable’s security.
Registration of Factors
Legal approval of the Reserve bank is compulsory to conduct a factoring business in the country. With that said, no company is liable to pursue such a business until and unless they obtain the registration for the same from the Reserve bank. For NBFC to get into factoring business, its: (i) financial assets must exist in factoring business, and (ii) income generated from such a business ought to more than fifty percent of net income or more than the limit as notified by the Reserve Bank. The bill discards this limit of a non-banking financial company.
Registration of Transactions
As per Factoring Regulations (Amendment) Bill, factors are liable to register all the transaction details related to receivable’s assignment in their favour. These details need to be spared in Central Registry Setup under SARFAESI Act, 2002, within thirty days. Any failure in this regard would attract a penalty up to Rs 5000/day till the default continues to remain in existence. The bill removes this time frame. The bill states that the regulations related to the period, payment fees, registration procedure, and late fee may be specified later.
Bill also adds that if the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS[1]) is used for financing the trade receivable, then the transaction-related details ought to be filed with the Central registry by the relevant TReDS, on behalf of the factor.
Empowering Reserve Bank to make Regulations
The Bill grant the right to Reserve Bank to prepares the regulations for:
- The procedure for granting registration certificate to a factor
- The procedure of submitting transaction details with the Central Registry related to transaction done via TReDS
- Other related concerns.
Conclusion
The Factoring Regulations (Amendment) Bill aims to support micro, small, and medium companies by rendering avenues for the credit facility, especially via Trade Receivables Discounting System. The increment in the resources of working capital may attract the growth for small scale entities and also ramp up employment in the country.
Read our article:Farmer Bill, 2020 – Highlights, Benefits, and Limitations
Factoring-Regulation-Bill-2020