The handicraft sector is one of the fastest-growing sectors in India. Over time, this sector has made some significant contributions to the nation’s economy. Also, it has played a vital role in creating massive employment in India. The Indian handicraft sector is bifurcated with more than 7 million regional artisans & over 65,000 exporters promoting craftsmanship in local as well as international markets. This blog addresses those individuals who are intending to export handicraft from India and are eager to use it as a legit business option. Apart from legalities, this blog will also unveil some information on the scope and benefits associated with this business model.
An Overview on Export Destinations and Key Markets
Exportation of the various segment during last year stood as follow:
- Woodwares = US$ 611.48 million
- Art metal wares = US$ 353.92 million
- Embroidered & crocheted goods = US$ 463.13 million
- Imitation jewellery = US$ 144.19 million
- Handprinted textiles & scarves = US$ 239.73 million
- Miscellaneous handicrafts = US$ 714.67 million
India handicrafts are shipped globally, with the top 5 destinations being the United States, United Kingdom[1], United Arab Emirates, France, and Germany.
Recent Developments in the Handicraft sector
Indian Government has escalated the incentive rate under the ambit of Merchandise Export from India Scheme (MEIS) to 7% for handicraft goods which will aid exporters to recoup the input costs and will lead to optimal pricing & boost export.
In Sep 2020, the Ministry of Textiles sanctioned Rs 2.8 crores for the Integrated project for growth and incentivization of handicrafts of Varanasi to compensate for the fiscal crisis triggered by the Covid 19 pandemic.
To aid local weavers and artisans before the advent of the festive season, the e-commerce giant Amazon launched the Handicrafts Mela from Sep 26, 2020, to Oct 10, 2020, which helped over 8 lakhs workers linked with this sector.
Read our article:Step by Step Guide to Raise IEC Certification for a Partnership Firm
How Export Promotion Council is helping businesses to export handicraft with peace of mind?
Exporting is a risky business especially when it comes to recovering payment from clients located abroad. EPCH has various insurance schemes at their disposal that enable exporters to avert such risk with ease. Exporters who aren’t in the condition to withstand losses incurred by such activities must enroll themselves under this scheme without thinking twice.
The Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH) is a government-backed entity administered by the Ministry of Textiles, Government of India. EPCH is also recognized as a ‘model council’, a self-sustaining entity that self-finances all its promotional activities.
Compulsory Licenses/Registration to export handicraft outside India
Following are the fundamental documents that one must arrange for venturing into the business of handicrafts export.
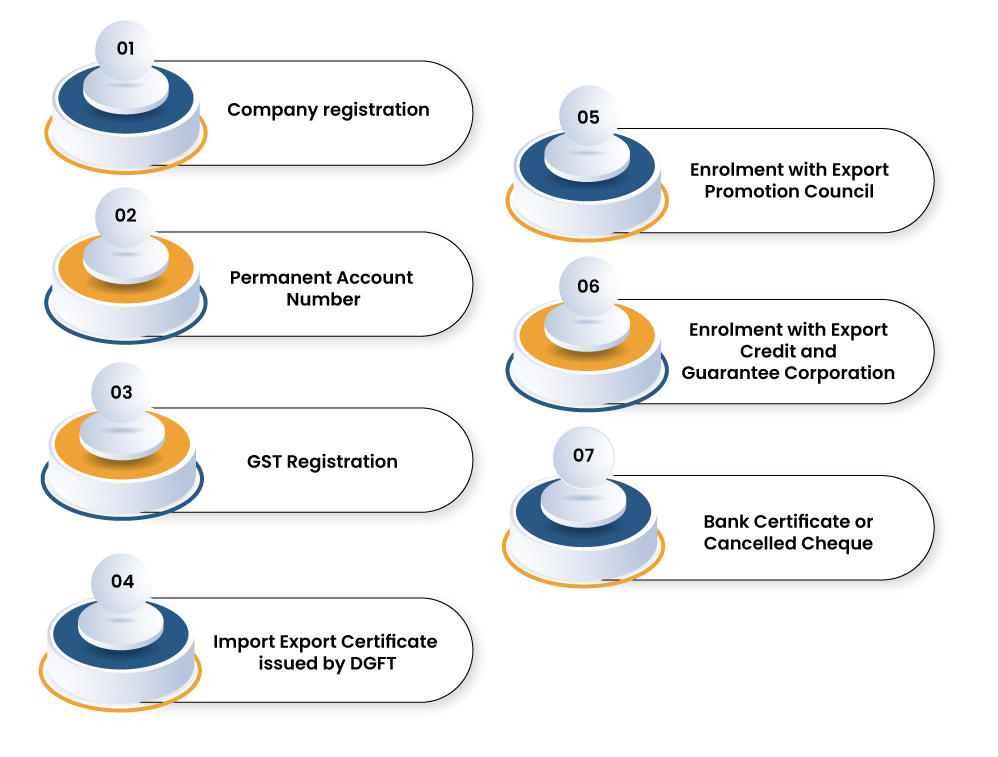

Company registration
Company registration creates a legal foundation for any entities that intend to engage with EXIM or any other business domains. Remember that company registration is a mandate and one should not overlook it at any cost. Our legal framework offers the following business structures to the business owners in India
- Private Limited company
- Public Limited Company
- One Person Company
- Partnership firm
- Limited Liability Partnership
- Section 8 (mainly for NGOs and trust)
- Nidhi Company
In case you opt for a business structure other than LLP and partnership, then you need to apply for the SPICe+ form available on the MCA’s website. The top three companies mentioned in the aforesaid list revolve around plenty of legal formalities and seeks tedious post-registration compliances. Thus; if your scope of operation and number of members are on the lower side, then you can also opt for options like LLP and partnership firm and still functions as a legalized firm.
Permanent Account Number
Income generated via exporting activities attracts several deductions and exemptions under various sections of the Income Tax Act. To avail of these exemptions and deductions, exporters are mandated to register their export house with the IT department and obtain PAN. Remember PAN act as a mandatory document for availing IEC, Import Export Code.
Import Export Certificate
The import-export code (IEC) is a basic legal document for any importers and exporters in India. Thus; ruling out this certificate is not prudent from the legal standpoint. One can hop onto the DGFT website to get this certificate against a properly filled e-form and registration fees. Do not forget to open the current bank account in the name of your company before opting for this certificate.
GST registration
The exportable goods do not attract Value Added Tax and Central Sales Tax provided the export house has VAT registration in place and obtains exemption as per norms cited under the concerned Acts. GST registration is mandatory for every exporter with effect from the date fixed by GOI by 2017.
Registration with Export Promotion Council (EPC)
It is important that every exporter enrolls with EPC and avail of the Registration-cum-Membership Certificate’ (RCMC). Presently, 21 EPCs are dealing with an array of commodities. The benefits extended to exporters are only accessible to the registered exporters having valid RCMC.
Registration with Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC)
Exporters often encountered political and commercial risks in the global market. Thus, to avert such risks, it is pertinent for exporters to get enroll with the ECGC. This government-backed institution also aids exporters in accessing fiscal support from commercial banks and other related avenues.
Mandatory Documents for Exporting Handicraft Goods beyond Indian Territory
- Pro Forma Invoice – Needed During Quality Check
- Customs Packing List- Needed During Quality Check
- Country of Origin or COO Certificate –
- Shipping Bill
- Commercial Invoice
- Bill of Sight
- Bill of Lading or Airway Bill
- Bill of Exchange
- Letter of Credit
- Import Export License ( for Shipping Purpose)
- Warehouse Receipt ( If Inland Cargo Deport (ICD) is involved)
It is evident from above that one has to encounter myriad of legal implications and documentations to export handicraft from India. The Customs department, in particular, pays extra attention to shipping documents owing to the tightened law and prevailing Acts. Since these documents are highly susceptible to errors, it is pertinent to prepare the same under the guidance of a certified custom agent.
Conclusion
Handicraft export has witnessed sharp growth in the past few years due to ever-increasing global demand. To crank up this demand further, the Indian Government has introduced various schemes to boost local production and incentivize craftsmanship. Since the Indian economy is recouping swiftly after being dented by the Covid-19 Pandemic, it is certainly a good time for start-ups to engage with this sector in the form of an exporter.
Read our article:How to obtain IEC Code in India