It is always believed that share capital is the most convenient way to increase one’s money. But let’s just understand what the meaning of share capital is. Share Capital is the possession of the company or any organization by two or more than two individuals. In this article we shall go through the details about the concept of Share Capital, it’s Importance for issuing share capital in a company and the types of share capital.
Meaning of Share Capital and its Characteristics
Share capital refers to the portion of a company’s equity that has been raised through the sale of shares to investors or shareholders. This is the amount of money that a company has received from issuing its shares to the public or private investors.
The following are some of the characteristics of share capital:
- Ownership: Share capital represents the ownership interest of shareholders in a company. Shareholders own a proportional part of the company in accordance with the number of shares they hold.
- Fixed Amount: The share capital of a company is a fixed amount that is specified in the company’s Articles of Association. This amount does not change unless the company goes through a process of issuing additional shares or repurchasing existing shares.
- Perpetual Existence: The share capital of a company is perpetual in nature. It remains as a permanent source of funds for the company unless the company chooses to return the funds to the shareholders through dividends or buybacks.
- Limited Liability: Shareholders have limited liability for the debts and obligations of the company. This means that their liability is limited to the amount of share capital they have invested in the company.
- Dividend Payments: Shareholders are entitled to receive dividend payments from the company. Dividends are payments made out of the profits of the company to its shareholders, and the amount of dividend paid is usually proportional to the number of shares held by each shareholder.
- Transferability: Shareholders have the right to transfer their shares to others subject to certain restrictions as mentioned in the company’s Articles of Association. The transfer of shares involves a change in ownership of a portion of the company.
What Is The Importance Of Issuance Of The Share Capital In A Company?
Issuing share capital is one of the primary ways for a company to raise funds from investors. Share capital refers to the money that a company raises by issuing shares to the public or private investors. These shares represent ownership in the company and give the shareholders the right to vote on important decisions such as the election of the board of directors or any major changes in the company’s operations.
There Are Several Reasons Why A Company May Choose To Issue Share Capital:
- Fundraising: Issuing share capital is a way for a company to raise funds for its business operations. By selling shares to investors, the company can generate significant capital without incurring debt.
- Expansion: Share capital can be used to fund the expansion of a company’s operations. This may include opening new locations, developing new products or services, or acquiring other companies.
- Reduce Debt: By issuing share capital, a company can use the funds to pay off existing debt, thereby reducing its interest payments and improving its financial position.
- Enhance Company Valuation: The value of a company is determined by the market value of its shares. By issuing shares and increasing the number of shareholders, a company can increase its market value and enhance its attractiveness to potential investors.
- Incentivize Employees: Companies can issue shares to their employees as a form of compensation or incentive. This can align the interests of the employees with those of the company and motivate them to work towards the company’s success.
What Are The Types Of Share Capital?
Share capital refers to the total amount of money raised by a company through the issuance of shares to investors. Shares represent ownership in a company and entitle shareholders to a portion of the company’s profits and assets. Following are the different types of share capital:
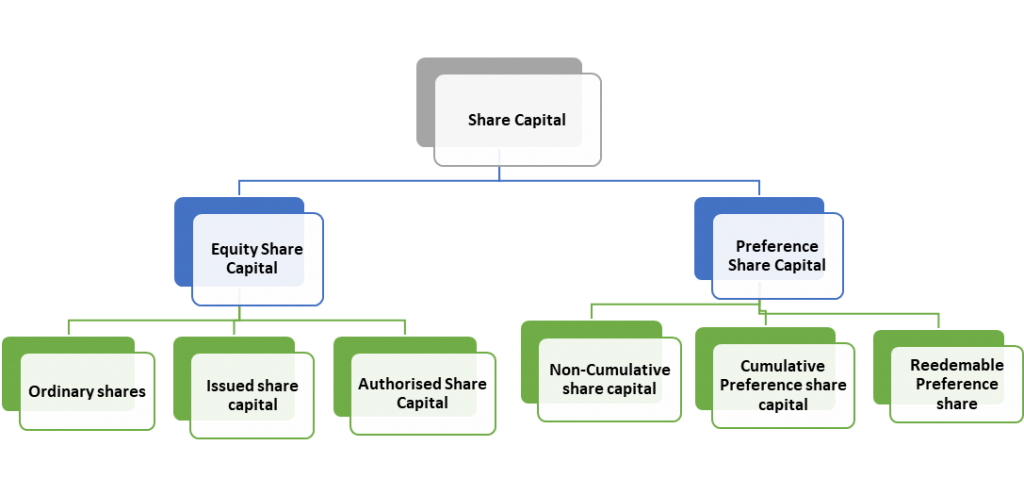

Share Capital is classified into two broad main divisions, which is mentioned below:
- Equity Share Capital
- Preference Share Capital
Let’s take a closer look at the different types of share capital:
- Equity Share Capital
Also known as ordinary shares, equity share capital represents the ownership stake of shareholders in a company. Equity shareholders are entitled to participate in the company’s profits through dividends and have the right to vote on company matters such as the election of the board of directors. However, equity shareholders have the lowest priority when it comes to repayment in the event of company liquidation or bankruptcy.
Equity shares may be further classified into two categories:
i) Authorized Share Capital: This is the maximum amount of share capital that a company is authorized to issue as per its memorandum of association.
Issued Share Capital + Unissued Share Capital = Authorized Share Capital
ii) Issued Share Capital: This is the portion of the authorized share capital that has actually been issued to shareholders.
Subscribed Share Capital + Unsubscribed Share Capital = Issued Share Capital
- Preference Share Capital:
Preference shares, also known as preferred shares, represent a class of shares that have certain preferences over equity shares in terms of dividend payments and repayment of capital in case of liquidation or bankruptcy. Unlike equity shareholders, preference shareholders do not have voting rights in the company.
Preference shares can be further classified into two categories:
i) Cumulative Preference Shares: These shares have the right to receive arrears of dividend in case the company is unable to pay dividends in any year.
ii) Non-Cumulative Preference Shares: These shares do not have the right to receive arrears of dividend in case the company is unable to pay dividends in any year.
In addition to these two main types of share capital, some companies may also issue other types of shares, such as redeemable shares or convertible shares. Redeemable shares can be redeemed by the company at a fixed date or at the option of the shareholder, while convertible shares can be converted into another class of shares or into debt instruments.
There Are Different Types Of Share Capital That A Company Can Issue. Here Are Some Of The Common Types Of Share Capital:
- Preference Shares: These shares give their holders a preferential right to receive a fixed dividend before any dividends are paid to ordinary shareholders. They may also have priority over ordinary shares in the event of a company liquidation.
- Redeemable Shares: These are shares that the company can buy back from the shareholder at a predetermined price and date.
- Cumulative Preference Shares: These shares give the shareholder the right to accumulate any unpaid dividends from previous years and receive them before any dividends are paid to ordinary shareholders.
- Non-Voting Shares: These shares do not give the shareholder any voting rights, but they may still be entitled to receive dividends.
- Deferred Shares: These shares may have limited or no voting rights, and they are usually issued to founders or management as a form of incentive.
- Bonus Shares: These are shares that are issued to shareholders free of charge, based on the number of shares they already own.
Additionally, there are other types of share capital that a company issues can vary depending on the company’s goals, financial position, and legal requirements.
- Subscribed Capital
This refers to the total amount of capital that shareholders have agreed to subscribe to a company’s shares. This can be seen as the maximum amount of capital that a company can raise through the issuance of shares.
- Reserve Capital
This capital is the part of subscribed capital that a company chooses to keep as a reserve for future use or to provide additional security for creditors.
- Called-Up Share Capital
This refers to the portion of subscribed capital that the company has called upon shareholders to pay for their shares.
- Paid-Up Capital
It is the portion of called-up share capital that has been paid by shareholders[1]. In other words, it is the amount of money that shareholders have actually contributed to the company in exchange for their shares. This amount cannot be called upon again by the company.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Share Capital
Share capital is a type of financing that allows companies to raise capital by selling ownership shares to investors. The advantages and disadvantages of having share capital are:
Advantages of Share Capital:
- Access to Capital: One of the biggest advantages of share capital is that it provides companies with access to a large pool of capital that can be used to fund growth, expansion, and other business activities.
- Limited Liability: Shareholders of a company have limited liability, which means that they are not personally liable for the debts or obligations of the company beyond the amount of their investment.
- Easy Transfer of Ownership: Shares can be easily transferred between investors, making it easier for investors to buy or sell their ownership in the company.
- Increased Credibility: Having share capital can increase a company’s credibility, as it shows that there are investors who believe in the company’s potential and are willing to invest in it.
- Diversification: By issuing shares, a company can diversify its investor base and reduce its reliance on any one source of funding.
Disadvantages of Share Capital:
- Loss of Control: When a company issues shares, it dilutes the ownership of existing shareholders, which may result in a loss of control for these shareholders.
- Cost: Issuing shares can be costly, as it involves legal and administrative fees, as well as the cost of listing on a stock exchange.
- Disclosure Requirements: Companies that issue shares are required to disclose a significant amount of information to the public, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Dividend Payments: Companies that issue shares may be required to pay dividends to shareholders, which can be a significant cost for the company.
- Volatility: Share prices can be volatile, which may make it difficult for companies to plan and budget for the future.
Overall, share capital can be a useful financing tool for companies looking to raise capital, but it also comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that companies should carefully consider before deciding to issue shares.
Conclusion
In summary, share capital represents the permanent and fixed amount of funds that a company has raised through the sale of shares to its shareholders. The characteristics of share capital include ownership, fixed amount, perpetual existence, limited liability, dividend payments, and transferability. Overall, issuing share capital provides a company with a flexible and cost-effective way to raise funds, expand its operations, reduce debt, enhance its valuation, and incentivize its employees.
Read Our Article: What Are The Types Of Share Capital? – Detailed Overview