Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points are defined as the systemic approach to prevent food from hazards due to chemical factors, biological factors, and physical factors during its production processes, leading to many risks. It is the international organization that focuses on finding potential hazards so that it can be identified and controlled at some point in an entire process starting from the raw materials until the final delivery of products. It is used at various stages of production as production, packaging, distribution, etc. HACCP Certification is essential for those companies which have been involved in the process of manufacturing.
As it applies to food safety management, the HACCP System uses an approach of controlling critical points in food handling in order to prevent food safety problems. Also, the HACCP system’s application can result in more focused risk management by food control regulatory authorities. It can promote international trade by increasing the confidence of buyers in food safety.
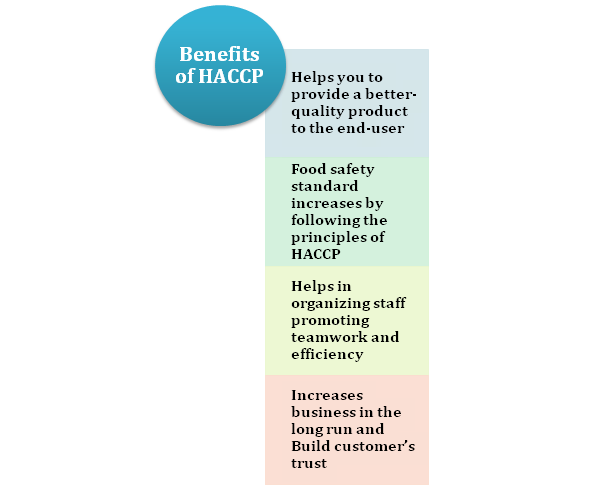
Advantages of HACCP Certification
- The system of HACCP applies to food safety management, which uses an approach in controlling critical points in food handling and prevent food safety problems.
- The system that is science-based and systematic identifies specific hazards and measures for their control to ensure food safety. HACCP is based on prevention and reduces reliance on end-product inspection and testing.
- The system of HACCP can be applied throughout the food chain from a primary producer to a consumer. Besides the enhancement of food safety, other benefits of applying HACCP include more effective use of resources, timely response to food safety problems, and savings to the food industry.
- HACCP enhances responsibility and degree of control at the level of the food industry. A correctly implemented HACCP system leads to greater involvement of food handlers in understanding and ensuring food safety.
- Implementing HACCP does not mean undoing the quality assurance procedures or good manufacturing practices already established by the company. However, it does require a revision of the procedures as part of the systematic approach and the appropriate integration into the HACCP plan.
- The HACCP application can aid inspection by food control regulatory authorities and promote international trade by increasing the buyer’s confidence.
- Any HACCP system must accommodate change, such as advances in equipment design, changes in processing procedures, or technological developments.

Application of HACCP Certification
While applying HACCP to all segments and sectors of the food chain is possible, it is assumed that all sectors must be operating according to good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and the Codex General Principles of Food Hygiene. The ability of the industry segment or implement or sector to support the HACCP system depends on the degree of its adherence to its practices.
A successful application of HACCP certification requires the full commitment and involvement of management and the workforce. It requires a multi-disciplinary approach that should include, as appropriate, expertise in agronomy, microbiology, veterinary health, public health, food technology, chemistry, environmental health, engineering, etc. according to the particular situation. The HACCP system’s application is compatible with an implementation of TQM systems, like the ISO 9000 series.
HACCP relation to Trade
Significant implications for Codex Alimentarius Commission arise from the Final Act of Uruguay Round, the Agreement on a Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT Agreement) and the Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS Agreement). The purpose of the SPS Agreement is to ensure that measures established by governments to protect the human, animal, and plant life and in the agricultural sector. It is consistent with obligations prohibiting arbitrary or unjustifiable discrimination on trade between countries where the same conditions prevail and not disguised restrictions on international trade.
The HACCP certification application, as a public policy, requires the definition of the government’s role in the utilization of the HACCP process. Food exporting countries can require additional resources to enhance their food industries to meet the requirements. Adequate steps must be taken to facilitate food trade, such as assessing food safety, training personnel, technology transfer, and strengthening the national food control system.
HACCP and Training
The Food industries and food control regulatory agencies worldwide have an interest in implementing the HACCP system. A common understanding of terminology and approaches for application will significantly enhance its adoption and lead to a harmonized approach to food safety among countries worldwide. Many countries are in the process of integrating the HACCP system into their regulatory mechanisms. In many countries, the application of the HACCP system to foods has become mandatory. As a result, there is the tremendous demand, especially in developing countries, for training in the HACCP system and also for the development and assembly of reference materials to support this training.
Read our article:A Complete Guide on How to obtain ISO Certificate? Benefits, Penalties and Fees
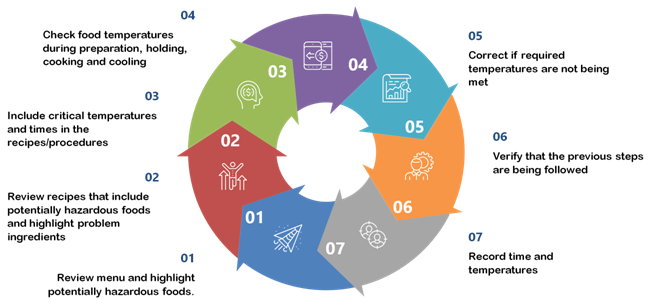
Practical HACCP seven steps

Where is HACCP applicable?
HACCP certification applies to industries like food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. HACCP is based on seven principles. The seven principles are mentioned in ISO Certification 22000 FSMS 2011. HACCP and quality management together form the Total Quality Management System. The seven principles are as follows: –
Conduct a Hazardous Analysis
- It is a process where industries find potential hazards and what kind of hazards is introduced in a whole manufacturing process. Hazard analysis may be done in two steps that are identification of hazards and evaluation of hazards. A hazardous analysis is for developing a list of hazards that are likely to cause injury or illness if they are not controlled.
- Points will be considered in this analysis that includes skill level of employees, transport of food, serving elderly, sick, very young children, immune-compromised, thawing of potentially hazardous foods, volume cooling, a high degree of food handling, contact, adequacy of preparation, storage, holding equipment available and method of preparation.
- The next step is for determining if the factors may influence the likely occurrence and severity of the hazard being controlled. Finally, the hazards associated with each step in the flow of food must be listed along with the measures necessary to control a hazard.
Establish Critical Control Points
The critical control point is defined as the point in the entire process where measures can be taken to prevent the hazards. A critical control point is the step in which hazards can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to acceptable levels. CCP’s are usually practices that, if not done correctly, are the leading causes of foodborne illness outbreaks. Examples of critical control points include cooking, re-heating, cooling, holding.
Establish Critical Limits
There are certain parameters in manufacturing or production like temperature, pressure, salt level, chlorine level, etc. Therefore, there must be certain minimum and maximum critical limits for the critical control points. A critical limit ensures that a CCP controls a biological, chemical, or physical hazard. Each CCP must have at least one critical limit. Critical limits must have something that can be monitored by measurement or observation. They must be scientifically and regulatory based. Examples include temperature, time, pH, water activity, or available chlorine.
Establish Monitoring Procedures
It is necessary to monitor the activities that check the critical points that are controlled. Monitoring is the plan that includes observations or measurements to assess whether a CCP is being implemented or not. It also provides a record of the “flow of food” through the establishment. If monitoring indicates that the critical limits are not being met, an action must be taken to bring the process back into control. This monitoring system must be easy to use and meet the food establishment’s needs, as well as the regulatory authority. The job of monitoring must be assigned to a specific individual, and they are trained in the monitoring technique.
Establish Corrective Actions
In case the critical points have not achieved, the organizations must establish the correct approaches to meet them. If the criteria for CCP are not being fufilled, then some corrective action must be taken. They must be based on facts for reasonable working conditions and measurable. Corrective actions may range, for example, from “continue cooking until the established temperature is reached” to “throw out the product,” depending upon a severity of the situation. HACCP plans must include the following: who is responsible for implementing the corrective action and what corrective action was taken. They must be established in advance as part of the HACCP plan.
Establish verification procedures
This principle helps test the effectiveness of the measures and check whether the equipment is under control. The procedures are activities, other than monitoring, that determine the validity of the HACCP plan and that the system operates according to the plan. An important aspect of the verification is to determine if the plan is scientifically and technically sound. Also, all the hazards have been identified and that, if the HACCP plan is implemented correctly, these hazards can be effectively controlled. This verification can be accomplished by expert advice and scientific studies and observations of the flow of food, evaluations, and measurements. Another way of verification is an on-site review of the established critical limits. Each CCP shall have independent authority. This verification step gives an opportunity to make modifications to the plan if required.
Establish record-keeping and documentation procedures
It is essential to find the vital records which are necessary to meet the critical point. Record-keeping and documentation procedures must be simple to complete and include information that illustrates that the established standards are being met. Employees need to be trained for the record-keeping procedures and why it is a critical part of their job. Examples of records include time/temperature logs, checklists, flowcharts, forms, employee training records, and SOP[1].
Objectives of the FAO approach to HACCP
- Promote the implementation of the HACCP system based on the harmonized Codex General Principles of Food Hygiene and GMPs
- Develop a program to train trainers in a position to train others who can apply the knowledge gained
- Identify the appropriate reference and training materials on the application of HACCP to support the training
- Provided training to individuals involved to varying degrees with the preparation, administration, monitoring, and verification of HACCP plans
- Enhance the role of science and risk assessment in the development of HACCP systems.
- Create the framework for determining the equivalence of food safety control programs through the harmonized approach to HACCP application.
Conclusion
The HACCP identifies specific hazards and control measures, ensuring the safety of food. The HACCP plan is specific to the particular food and processing application. The HACCP system is also capable of acquiring changes like advances in equipment design, new processing procedures, new information concerning health hazards or risks, or other technological developments. CorpBiz shall be happy to serve you and assist you in any manner needed.
Read our article:Extended Producer Responsibility for the E-Waste and Plastic Waste Management










