Information Technology has gained some special significance in the past 2 decades and developed as a vital tool for scientific advancement. Information Technology includes the entire possibility of entering, storing, loading, recovering, communicating, and management of data through the usage of computers and various other networks, hardware, software, electronics, and telecommunication equipments. Computer Related Inventions or CRIs are those that include the use of computers, networks of computers, and another programmable device. Additionally, the Computer Related Inventions in India also includes such inventions that are having one or more features of which are comprehended wholly or partly by means of a programme of computer or programmes of the computer.
Inventors of knowledge in the area of Computer Related Inventions or CRIs have constantly endeavored for suitable protection of their Intellectual Property Rights. The regime of Patent has to deal with the challenges of processing the applications of Patents related to inventions related to computer and other technologies related to it. The majority of Offices of Patent all over the world have to confront the issue related to the patentability of Computer Related Inventions or CIRs. They have developed certain examination guidelines or manuals for the purpose of examining the applications of Patent from the areas of technology so that the countries can achieve uniform examination practices. In this article, we will discuss in detail the complete overview of Computer Related Inventions in India.
What is a Computer Related Invention?
The Office of the Controller General of Trademarks, Patent and Design in the recent years has issued several sets of guidelines or guiding principles for interpreting and understanding the scope of Computer Related Inventions and the protection of them in India. In India, the examination guidelines for Computer Related Inventions or CRIs were issued by the Office of Patents on 30th June in the year 2017. The guidelines issued by the Patents Office in India were first published in the month of August in the year 2015, but due to very strong resistance from investors, the guidelines were put in abeyance. After this, the guidelines were again issued in February 2016. But the resistance of investors continued, and ultimately the matter was handed over to an expert committee in India by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry for proving expert recommendations for the same.
As per the guidelines provided by the Office of Controller of Designs, Patents and Trademarks for the examination of Computer Related Inventions in India, the inventions related to computer should involve the following things:
- The usage/use of computers;
- The networks of computer;
- Other programmable devices or apparatus; or
- The inventions with one or more features that are comprehended exclusively or partly by means of a programme of computer.
What are the Basic Requirements to determine the Patentability of Computer Related Inventions in India?
For an invention to get patented in India, a Computer Related Invention should fulfill the following four criteria’s:
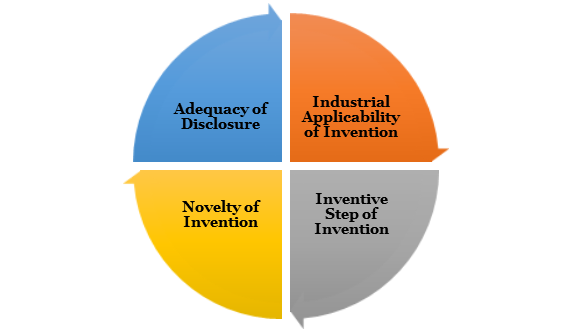

Industrial Applicability of Invention
An invention related to should be capable of industrial application. The industrial application, in relation to a Computer Related Invention, means that the computer related invention must be capable of being used or made in an industry. The invention should have usefulness and workability in industrial applications to become eligible for the grant of Patent.
Inventive Step of Invention
An Inventive step of a Computer Related Invention or CRIs means a feature of an invention that contains a technical development as compared to the prevailing knowledge or having some economic significance or both, and, hence this does not make the invention related to the computer not obvious to any person skilled or expert in the art.
Supreme Court of India in the case of Biswanath Prasad Radhey Shyam vs. Hindustan Metal Industries Ltd., [AIR 1982 SC 1444], which is related to inventive step, stated the following steps to objectively judge to determine by looking at the whole invention, that whether an inventive step is there in the invention or not:
- The identification of the “person skilled or expert in the art,” i.e., the craftsman or engineer is competent and is distinguishable from being a mere artisan.
- The identification of the significant common general knowledge of the person at the priority date.
- The identification of the inventive concept of the claim, which is in question or if that cannot be done readily, interpret it.
- The identification of what variations exist between the matter referred to as forming part of the “state of the art” and the inventive idea of the claim or the claim as interpreted.
Novelty of Invention
A novelty or new invention means any invention or technology which has not been predicted by any publication in any document or is being already used in the country or elsewhere in the whole world before the date of filing of application of Patent with complete specification. Hence, it can be said that the subject matter of the invention related to computers has not yet fallen in any public domain or does not form a part of the state of the art.
Adequacy of Disclosure
The prerequisite of “What” the invention is all about and “How” to perform the invention should always be satisfied in the invention specifications. To meet the essential requirements of the Patent Act, 1970[1], the complete disclosure of the specifications of the invention should be done. The description of the invention made in the specifications must be unmistakable, clear, correct, and precise.
Read our article: Provisional Patent in India: A Complete Overview
What is all not Patentable under Computer Related Inventions in India?
As per the guidelines issued by the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks in India, the below stated things are excluded from Patentability under Computer Related Inventions or CRIs:
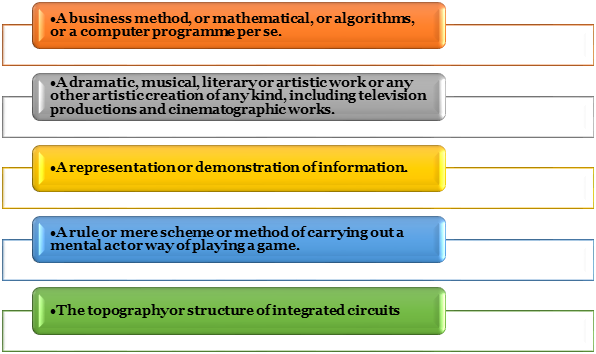

Claims directed as Mathematical Method
The claims which are not patented under the following head are:
- Certain mathematical methods, like a method of formulation of equations, calculation, finding roots of different numbers and all other alike acts of mental or intellectual skills;
- Simple manipulations of an intellectual idea or solving a purely mathematical equation or problem without stipulating a practical application of it.
- The below-mentioned methods does not come under elimination:
- The Encoding;
- The reduction of noise in electronic, electrical, communication systems;
- The Encrypting or Decrypting electronics.
Claims directed as Business Method
The claims which are not patented under the following head are:
- Any claims directly not drafted as “business methods” but deceptively with some indefinite means;
- When any claim is “business methods” in its substance;
- Merely the presence of words like enterprise, transactions, commerce, payment, business, business rules, order, sales, supply chain, etc. in the claims will not lead to the assumption of an invention or creation for being just a “Business Method.”
- The subject matter of the invention is basically about carrying out business, trade, financial activity, transaction, or a method of buying and selling of goods through the web should be treated as a method of business and should not be patentable.
Claims directed as Algorithm
The claims which are not patented under the following head are:
- A set of procedures, rules or any other sequence/order of steps;
- Any technique stated by way of a fixed list of definite instructions, whether for solving any problem, and
- Whether employing an arithmetical, logical or computational method, recursive or otherwise.
Claims directed as Computer Programme per se
The claims which are not patented under the following head are:
- Programmes of computer
- Certain Set of instructions
- The Routines and subroutines.
- The Computer programme products
- Certain storage Medium having instructions
- The Database
- The memory of computers with some instructions stored in a computer-readable medium.
Claim directed as a dramatic, musical, literary or artistic work or any other artistic creation of any kind, including television productions and cinematographic works
As per the procedures of chapter 08.03.05.11 in the Patent Manual, the claims under this chapter includes:
- Writings, music, paintings, works of fine arts, sculptures,
- electronic databases, computer programmes
- books, pamphlets, sermons, lithography, lectures, addresses, photographic works, applied art,
- maps, plans, illustrations, sketches,
- 3-D works relating to geography, topography
- choreographic works, engravings cinematographic works, dramatic-musical works, drawings, architecture
- translations, arrangements of music, adaptations, multimedia productions, etc.
Claim directed as a representation or demonstration of Information
As per the procedures of chapter 08.03.05.13 in the Patent Manual, the claims under this chapter includes:
- Any manner, means, or method of expressing or stating information, whether audible, visual, or tangible by words, signals, codes, symbols, diagrams, or any other mode of representation available.
For example, a speech instruction means in the form of printed text where vertical separating lines divided the works into rhythmic groups and where horizontal underlining indicated stress, 100 years calendar, railway time table, etc.
Claim directed as a rule or mere scheme or method of carrying out a mental act or way of playing a game
As per the procedures of chapter 08.03.05.12 in the Patent Manual, the claims under this chapter includes:
- A rule or scheme of performing mental act;
- A rule or method of playing game.
For example: Method of playing chess or Method of learning or Method of teaching.
Claim directed as the topography or structure of integrated circuits
As per the procedures of chapter 08.03.05.14 in the Patent Manual, the claims under this chapter includes:
- 3-Dimensional configuration of the electronic circuits used in semi-conductor chips and microchips.
What are cases in which Computer Related Inventions Patent was granted in India?
The following are few examples where Computer Related Inventions Patents were granted in India:
- A Patent protection was granted to the company Facebook on 25th April in the year 2017 “for a method of providing access to third party application of the user profile data preserved by the company Facebook.” The company Facebook submitted that “the present invention includes certain hardware limitation and provides some technical developments and aids like examination of privacy setting linked with the user profile and grounded on the privacy settings the access is provided to the third-party application, and the third-party application personalizes the content data of the user.” The Office of Patent concluded that such invention related to computer doesn’t fall under the horizon of Section 3(k) of the Patent Act, 1970, and the Patent was duly granted.
- In February 2005, the company Google required a protection of Patent for an invention titled, ‘phrase identification in a system of information retrieval.’ The company Google disclosed its one of the claims to be a basic simple mathematical algorithm with some logical steps, thus falling under the purview of Section 3(k) of the Patents Act, 1970, and consequently is not patentable. However, the company Google gives the reason that the invention is not a mathematical algorithm or a programme of the computer per se, “but offers a technical solution to a technical problem of how to recognize phrases in a collection of several documents automatically”. The company also claimed that the technical solution i.e., the end product of the invention, is an index, which is stored in a memory comprising of certain related lawful or valid phrases, and hence the step is inventive. On hearing the submissions of the company Google, the Office of Patent decided that the invention related to computers is “a technical advancement over the art which is prior.” Hence, Patent was granted to Google in May 2017.
- In the year 2009, the company Apple applied for a protection of Patent on a ‘technique or method for browsing of data items with respect to a display screen associated or linked with an electronic device and computing device.’ The objections against the invention related to the computer was that the invention was simply a software program and hence is falling within the scope of computer programs per se, i.e., under the provision provided in Section 3(k) of the Patent Act, 1970. The company Apple submitted that the technique or method “even though the steps of the technique or method can be performed by means of computer software, the technique or method establishes a practical application of the computer software to yield a valuable result conveying an enhanced technical effect. The company Apple also said the computer software would present the advantages and other overcoming drawbacks of any previously known techniques.” Accepting the submission of the company Apple, the Office of Patent at Kolkata granted the Patent.
What are the benefits of the protection of Patent in India?
As a general rule, all new inventions in any field of technology can qualify for Patent protection in India if these new inventions are useful, non-obvious and novel. The benefits of Patent protection to innovators are as follows:
- The protection of Patent will ensure the inventors to get a reasonable return on the commercially effective innovations made or invented by them;
- To make it easier for innovation-based small businesses and start-ups to establish productive business associations;
- By disclosing of Patent, the innovators will promote the systematic sharing of knowledge, which is in itself an essential driver of innovation; and
- Help to attract good investment partners and support the expansion of business.
Conclusion
The protection of Patent is a recognized means of supporting inventions, improving the living standards, and boost the employment of a country. As the economy is becoming digitized globally at a very high speed and also increasing competition in the market, there is a need to introduce Patent protection in the case of Computer Related invention in a country. The primary aim of giving Patent protection is to allow the creators and innovators to have dedicated resources for the development of software. The development of software will help do a good business and connect with people globally. Hence, to increase overall growth, the guidelines related to the Patentability of Computer Related Inventions were introduced in India. The process of patentability of Computer Related inventions is lengthy and time-taking. We at Corpbiz have skillful professionals to help you with the process of obtaining Patent protection of inventions related to computers. Our professional will guide and assist you throughout the process of invention protection. Our professionals will ensure the timely and successful completion of your work.
Read our article: Procedure for Registration of Patent Agent in India