The introduction of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) in the Indian market is a hope for people to make money for the long term. These Depository Receipts are like equity shares but with subtle differences. The Indian Government initiated the IDR to globalize the Indian capital market and to allow entry of local investors in foreign companies. The foreign companies can now access the Indian Securities market and raise funds through Issue of IDR. In this article, we will discuss the procedure followed for the issue of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs).
What are Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
The depository receipts with denominations in Indian Rupee, and which are issued by the Domestic Depository in India are known as Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs). IDRs are like an ownership pie of Company, much like the equity shares. The foreign companies are not allowed to be listed on Indian Equity markets. So, to create a way to invest in foreign companies, IDRs were introduced. The IDRs are listed on the Indian Stock Exchanges, and now anybody can invest Indian Rupees in the international companies which are now available at the doorstep of each investor.
In IDRs the shares will be issued by foreign companies to Indian Depository. Hence, foreign companies are able to mobilize funds from India by selling shares. IDRs are opposite to GDR (Global Depository Receipts) or ADR (American Depository Receipt).
The IDRs holders are entitled to the same rights as that of equity shareholders of the Company. The IDRs holders have rights such as voting rights, bonus and right issues, dividends, and all other rights which an equity shareholder possesses.
What laws are related to Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
The primary laws related to Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) are as follows:

- Section 390 of Companies Act, 2013[1];
- The SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018;
- Guidelines of Reserve Bank of India (RBI);
- Guidelines of FDI;
- The Companies (Issue of Indian Depository Receipt) Rules, 2004.
- Companies (Registration of Foreign Companies) Rules, 2014.
Who are eligible to Issue Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
Rule 13 of Companies (Registration of Foreign Companies) Rules, 2014, provides for the guidelines the issuing Company should follow for the issue of IDRs. The guidelines the Issuing Company should follow are as follows:
- The track record of Issuing Company of the distributable profits for 3 years at least out of immediately preceding 5 years.
- The eligibility criteria laid down by the SEBI from time to time should be fulfilled by the Issuing Company.
- The Issuing Company should be continuously trading on the stock exchange in its home or parent country (in which country the incorporation of Company took place) at least for last 3 years preceding the issuance of IDRs.
- The paid-up capital and free reserves for the Issuing Company before the issue of IDRs should be US$ 50 million.
- The minimum average market capitalization of the Issuing Company before the issue of IDRs should be US$ 100 million in its parent country for 3 financial years preceding the issue of IDRs.
Which intermediaries are involved in the Issue of Indian Depository Receipts?
The issue of IDRs involves foreign collaboration. The process of Issue of IDRs includes a large-scale load of intermediaries and different market players in the market. The intermediaries are essential for completing the process of issue of IDRs and are recognized by participating countries in the process of issuance. The intermediaries involved in the issue of Indian Depository Receipts are as follows:
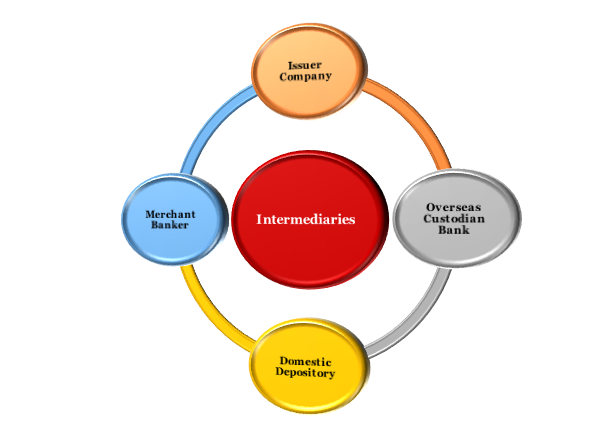

Issuer Company
- The foreign Company which is intending to raise money by issuing IDRs is Issuer Company.
- Companies like Google, Starbuck, Facebook, etc., are the main hub to raise money in the Indian market.
- Companies like Google, Facebook, Starbuck, etc., are playing the role of Issuer Company for raising capital in the market.
- The Foreign Company acting as an Issuer Company should be listed in their countries incorporation or where the registered office is located.
Overseas Custodian Bank
- It is a type of banking company which is established at a place outside India and has a place of business in India.
- The banking company acts a custodian of issuing company equity shares, against which Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) are proposed to be issued. The banking company act as a custodian by establishing a place of business in India or by entering into a custodial agreement or arrangement with Domestic Depository.
- These banking companies act as a safety valve for the foreign investors of countries.
- This banking company holds equity shares on behalf of the Domestic Depository.
Domestic Depository
- The Issuer Company appoints Domestic Depository.
- The Domestic Depository is the custodian of securities which are registered under the SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- The Issuer Company authorizes the Domestic Depository to issue IDRs.
- The Domestic Depository acts as trustee of the IDR holders.
- The legal rights and obligations of Domestic Depository are specified in depository agreement signed between Domestic Depository and Issuer Company.
- The depository agreement is the one of the primary documents while issuing the IDRs.
- The Domestic Depository bears all the obligations and rights related to the IDRs holder.
Merchant Banker
- The Merchant Banker is a person engaged in the business of issue management.
- The Merchant Banker can do issue management by making arrangement regarding buying, selling or subscribing to the securities or by acting as a manager, advisor, consultant, or providing corporate advisory service.
- The Merchant Banker is responsible for the Due Diligence in Company.
- The Issuer Company filed the draft prospectus for Issuance of IDRs through the Merchant Banker.
What are the requirements for Issue of Indian Depository Receipts?
The requirements for Issue of IDRs are as follows:
- The applicant of IDRs should follow the procedure as prescribed in the prospectus for applying for issue of IDRs;
- The minimum amount of application for IDRs should be 20,000 Rupees;
- The size which is issued should not exceed 50 crore Rupees;
- The institutional buyers should be allotted based on proportion a minimum of 50% of issue IDRs;
- At the time of issuance of IDRs, the denomination of IDRs should be one for all the Issuing Company;
- The Indian Companies investment in IDRs should not exceed the prescribed limit of investment under any applicable laws;
- As per FEMA, the IDRs can only be purchased by any person who is a resident of India.
What is the procedure for Issue of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
The procedure followed for the Issuance of IDRs is as follows:
- The Issuer Company will obtain all the approvals or exemptions under the relevant laws relating to the issuance of IDRs from the concerned authorities from the country of incorporation of Issuer Company.
- An application should be filed with the SEBI for obtaining approval for the Issue of IDRs. The application for approval should be made at least 90 days prior from the date of opening of Issue of IDRs. The application should be submitted along with a due diligence report through the Merchant Banker. The application along with the due diligence report should be filed in the form prescribed by the SEBI.
- The SEBI within 30 days of the filing of the application can ask the Issuer Company to furnish additional information as needed. After the additional information and explanations are received, the application should be disposed of by SEBI within 30 days.
- The Issuer Company have to make changes in the prospectus as directed by SEBI. The changes in the prospectus should be made within 60 days from the date of submission of application or prospectus. The prospectus cannot be submitted to SEBI if the changes are not made in the prospectus as directed by SEBI.
- After being satisfied, the SEBI will grant approval to the application. After the approval, the Issuer Company has to submit the issue fee as prescribed from time to time by SEBI.
- The Issuer Company should file the prospectus to SEBI and the Registrar of Companies (RoC). The prospectus should be certified by at least two authorized signatories of Issuer Company. The two authorized signatories can be the whole-time Director and the Chief Financial officer of Issuer Company. The signatories should state the particulars of the Board Resolution passed approving the Issue of IDRs.
- While filing the prospectus to the Registrar of Companies, the Issuer Company should also attach a copy of approval granted by SEBI and the statement of fees paid to SEBI by the Issuer Company.
- The Issuer Company should appoint a Merchant Banker, a Domestic Depository and an Overseas Custodian Bank for Issuing IDRs.
- To underwrite the issue of IDRs, the Issuer Company should appoint underwriters who are registered with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- The underlying equity shares should be delivered to the Overseas Custodian Bank.
- The Overseas custodian Bank should authorize the Domestic Depository for the issuance of IDRs.
- The Issuer Company should obtain in-principle listing permission from one or more stock exchanges in India.
What are the documents required for Issuance of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
The documents required for Issuance of Indian Depository Receipts are as follows:
- The agreement entered between the issuing Company and the Merchant Banker.
- The Merchant Banker should submit a due diligence certificate to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- Merchant Banker should issue the certificate stating the authenticity of the prospectus.
- The certificate of due diligence with the prospectus is to be submitted to the Registrar of Companies (RoC) by the Merchant Banker.
- The Merchant Banker should forward the draft prospectus of the issuing Company to Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- The instrument defining or constituting the constitution of the Issuer Company
- The address of principal office of Issuer Company, if the Issuer Company has established a place of business in India.
- In case no principal place of business in India, the address of any place where the enactments, instruments or copies related to Issue Company are available for public inspection.
- A true certified copy of incorporation certificate of the Issuer Company.
- A copy of the agreement between Issuer Company and Overseas Custodian Bank specifying the rights of IDR holders.
- A copy of the agreement between Issuer Company and Domestic Depository specifying the rights of IDR holders.
- The copy of translations of documents in English which were not in English originally. The copy of translations should be certified to be correct by key managerial personnel of Issuer Company. The copy of translations should be attested by authorized officer of Embassy of Issuer company country in India.
What are the merits of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)?
The merits of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) are as follows:
- Reduction in the possibility of the hostile takeover
- Funds provided are low in cost and terms
- More access to the liquid market
- Expansion of the investor base of issuing Company
- Improved brand image increases the availability of more marketing advantages
- Protection of investor against any decline in its local economy
- Provides means for wealth protection
- Provides means for diversification in investment
- The exploitation of international demand for shares.
- Elimination of risks associated with foreign exchange
Conclusion
The introduction of IDRs in the global arena is the very first step towards the beginning of a new era of capital market in India. The foreign companies visualize the Indian markets as an unexplored region with a hidden treasure inside. Quite naturally, the foreign companies are attracted to the Indian market. The IDRs are the primary source which gives them the means to access the vast Indian capital market pool easily and creates a large number of opportunities for future fundraising. The IDRs are issued to increase the overall productivity of the capital market of India. The process of Issue of IDRs is time-consuming and lengthy. We at Corpbiz have experienced professionals who can help you with the process. Our professional will assist you in the process of Issue of IDRs. The professional will ensure the timely and successful completion of your work.
Read our article:What is GDR (Global Depository Receipt): An Overview











