This blog discusses the various types of shares/securities available to Private Limited Companies. Shares, also known as securities under the Companies Act of 2013, are amongst the financial tools used to obtain revenue for a corporation. Shares are ownership interests in a business entity or financial assets that provide an equitable distribution of profits in the form of dividends, if any are declared.
A private limited company is described as one with a minimum paid-up share capital of Rs. 1 lakh, as specified under section 2(68). Except in the context of a one-person company, where the number of members is limited to 200, the company’s AOA prohibit the transfer of shares to the public.
Private limited companies are created with the intention of forming a people’s organisation that is not open to the public. They are allowed to hold securities or shares, but they cannot be distributed to the general public. The only persons who can buy and sell stocks are the members itself.
Types of Shares
There are two types of shares:-

Equity share
All equity is considered equally in this form of share, which is the most prevalent amongst all the types of shares. The terms “equal” and “quality” can be used to describe equity shares. These shares have the same value and are so considered the same. Equity shares are the ones that do not have any preferential privileges when it comes to capital repayment or dividends. Equity shares are described as shares other than preference shares, according to the Companies Act. If someone holds stock in a business entity, their shares come with all of the voting and other rights that come with it. It’s known as common stock in the United States. Equity shares are riskier as compares to preference shares.
Equity shares with differential voting rights
Equity shares are one of the specific types of shares of private limited company shares. Ordinary shares with differential voting rights are similar to equity shares with differential dividend or voting rights, if any. These stakeholders have a high level of control over the company’s day-to-day operations.
Only a few businesses in India have issued shares with distinct voting rights, like Tata Motors and Future Retail. These shares are typically offered to founders or CEOs in order for them to have greater influence over the company’s day-to-day operations.
In simple terms, one may only issue equity shares with unequal voting rights if your private limited company generates sufficient revenues to pay the dividends (part of profits) to shareholders for 3 years in a row. For issuing equity shares with differential voting rights, the business must meet specific requirements outlined in Rule 4 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debenture) Rules, 2014.
Sweat Equity – Issued exclusively to employees who deserves
Sweat equity are the types of shares is given to qualified employees who have worked with the firm for at least a year. It is given to hardworking employees at free cost, which means that the employees do not have to pay anything in exchange for such shares. The shares are simply assigned. These shares could not be allocated to those who already hold them. Before they are allotted, an appraisal of the organization must be performed.
ESOPs – Shares that encourage employees to perform well for the organization
Most entrepreneurs battle with how to encourage their employees in a mutually beneficial way. The Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP), which is utilised by both small and big firms, is the most practical solution to this problem. It deserves personnel engaged to help the organisation develop. It also guarantees that you don’t lose them for a long time. In an ESOP, companies give their employees equity ownership. It is frequently done at no upfront expense, but in lieu of the job they accomplish. Employees are given shares, but they are only granted after a set duration of time. It is not available to freelancers, promoters, consultants, and the like.
Preference Shares
As previously indicated, these are preferred. Preference Shares are those types of shares that have priority rights to dividend payments and preferential rights to capital return upon the company’s liquidation. The majority of preference shares have a set or absolute dividend rate, whereas common shares do not have such preferential rights. A preferential right does not have right to vote and are less risky than equity shares. The benefit of owning a preferential share is that if the business entity is liquidated, the preferential shareholders will be compensated out first, after all of the firm’s obligations have been fulfilled.
Preference shares are further categorised as follows
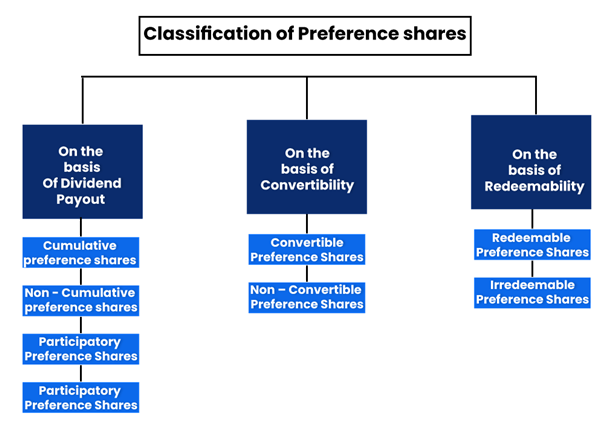

Types of Shares on the basis Of Dividend Payout
Cumulative Preference Shares
Cumulative Preference Shares are the types of shares in which dividend arrears are cumulative in nature and are paid before any dividend is paid to equity shareholders. Cumulative preferred shares continue to provide priority shareholders the opportunity to demand an unpaid dividend in any future year or years when profits are available for distribution. In this situation, when revenues are available, uncompensated dividends are collected and handed out each year.
Non-Cumulative Preference Shares
Non-Cumulative Preference Shares are those types of shares in which the dividend is paid exclusively from the previous year’s net earnings. If no profits are made in any of the years, the arrears of dividends from those years could not be claimed in the later years. If the corporation does not pay the dividend on the preference shares within the fiscal year, the dividend will expire. Unless otherwise indicated to be non-cumulative, preference shares are assumed to be cumulative.
Participating Preference Shares
In addition to the fixed or absolute rate of preference dividend, Participating Preference Shares are allowed to take part in the balance of profits with equity shareholders. Following the company’s liquidation, participating preference shares will be entitled to a portion of the company’s surplus assets. Such a privilege must be clearly specified in the company’s MoA and AoA.
Non-Participating Preference Shares
Non-Participating Preference Shares are the types of shares that are solely subject to a predetermined or fixed rate of dividend and have no option to participate in surplus earnings. Unless otherwise indicated in the company’s MoA or AoA of the company, or in the conditions of issuance, preference shares are considered to be non-participating.
Read our article:What are the Types of Share Capital? – Detailed Overview
Types of Shares on the basis of Convertibility
Convertible Preference Shares
Convertible Preference Shares are shares which can be converted into equity shares within a specific time frame.
Non-Convertible Preference Shares
Non-convertible preference shares are shares that have no right to be converted into equity shares.
Types of Shares on the basis of Redeemability
Redeemable Preference Shares
Redeemable Preference Shares are those types of shares that can be redeemed within or after a specific time frame. Redeemable preference shares are preferential shares that must be repaid by the corporation. This occurs after the time for which the preference shares are issued has expired.
Irredeemable Preference Shares
Irredeemable Preference Shares are the ones that do not have a redeeming right. Irredeemable preferences imply that the corporation is not required to pay back preference shares unless the company is liquidated. In India, the Companies Act, 2013[1] prohibits a company from issuing irredeemable preference shares.
If a company is not able to redeem any preferential shares within a specified time frame, the corporation may issue redeemable preferential shares, with the approval of the company’s Law board, equivalent to the redemption of those old preferential shares that could be redeemed on a fixed date or within a specified time period of 10 years from the beginning, provided that the below mentioned terms and conditions are met:-
- The share may only be redeemed if it has been paid in full.
- In order to make such an issue, the AOA must be certified.
- If a redemption premium is payable, it should have made proceeds, profit, or premium accounts accessible before the shares are repaid.
- The share can be redeemed with profits from the organization. It can also be redeemed from dividends or earnings, as well as fresh shares created, in order to resale shares.
- Whenever the shares are redeemed from profits, earnings from the capital reserve account must be remitted in an amount equivalent to the nominal amount of the shares being redeemed. This amount must be used to repay redeemable preference shares. This reserve could be utilised to provide fully paid bonus shares to the company’s members.
Conclusion
You now understand everything there is to know about the types of shares in a private limited ltd company. Feel free to reach out in case you have further queries or would want to take the next step and establish your own business. We are always available to listen to and suit your requirements.
Read our article:Right Issue of Shares: Step by Step Procedure











