MSME play a vital in the economic progress of the countries, so the implementation of GST under MSMEs has had an immense outcome on the continued existence in the market. Some enterprises found it helpful however majority visage problem in adopting it.
The MSME sector of market has been deliberated as a chief development driver of the Indian economy for many years now. SMEs have emerged as a principal employment-creating segment in India and have delivered stable growth through various sectors of our developing nation. The implementation of GST allows the government to have an improved hold on the taxpayers, which, in turn, improves the complete tax scheme and has several other benefits.
What are the Positive Impacts on Implication of GST under MSMEs?
The positive impacts of GST under MSMEs are as follows:
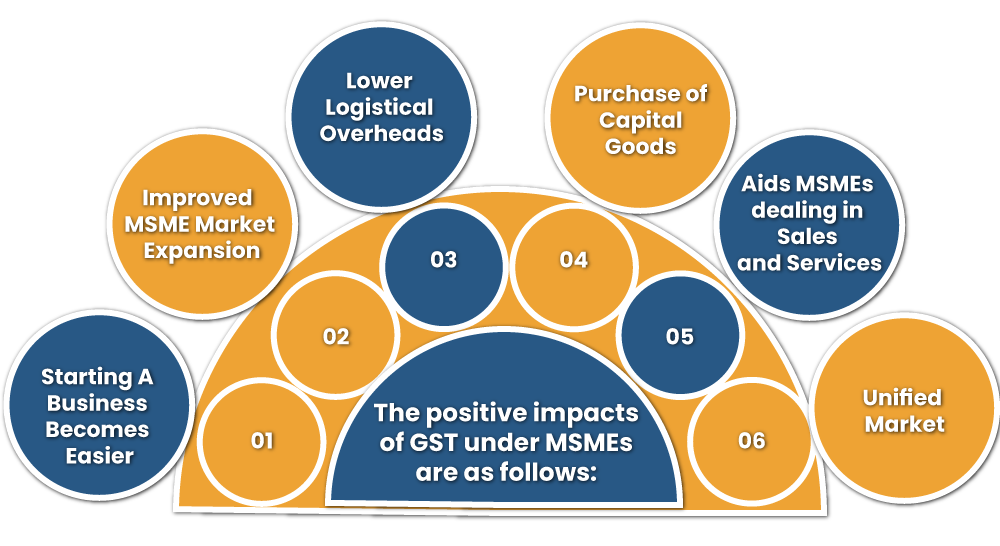

Starting a Business Becomes Easier
Presently, the Sales Tax department[1] has various turnover slabs which require VAT registration. The business with the multi-state operation, in this case, they have to follow various tax rules applicable in different states. It does not only create excess complication but also adds to procedural fees, due to which MSMEs were burdened. However, a uniform GST Registration will standardise the process.
Improved MSME Market Expansion
In the present system, big corporations procured goods based on MSME’s locality to reduce overheads. Thus MSMEs limit the customers within a state as they bear an ultimate burden of tax on interstate sales, reducing their customer base. With the implementation of GST under MSMEs, this will get nullified. The tax credit will transfer irrespective of the location of buyer and seller which will also allow MSME segment to expand and reach across borders.
Lower Logistical Overheads
The GST is tax neutral; it will eliminate time-consuming border tax procedures and toll check posts and encourages the supply of goods across borders. Accordingly, a logistical cost for companies manufacturing bulk goods will get reduced. Such costs may be crucial for the survival of MSMEs.
Purchase of Capital Goods
In the present system, only 50% of an input tax credit against the purchase of Capital Goods is available in a year of purchase and the balance amount in subsequent years. Under the GST regime, the entire amount of input tax credit can be availed in a year of purchase itself. It will automatically support “Make in India” campaign.
Aids MSMEs dealing in Sales & Services
The registered MSMEs will receive aids from both sales and services model of business and the GST can be calculated on the total amount itself as GST will levy same on sales and services.
Unified Market
The GST will provide flexibility in transferring the goods across states and reduce a cost of doing business, as the reform will now cut down the multiple taxes imposed by both state and central government.
What are the Negative Impacts on Implication of GST under MSMEs?
While MSMEs enjoys the tax neutrality, however, there are some negative impacts, which are as follows:-
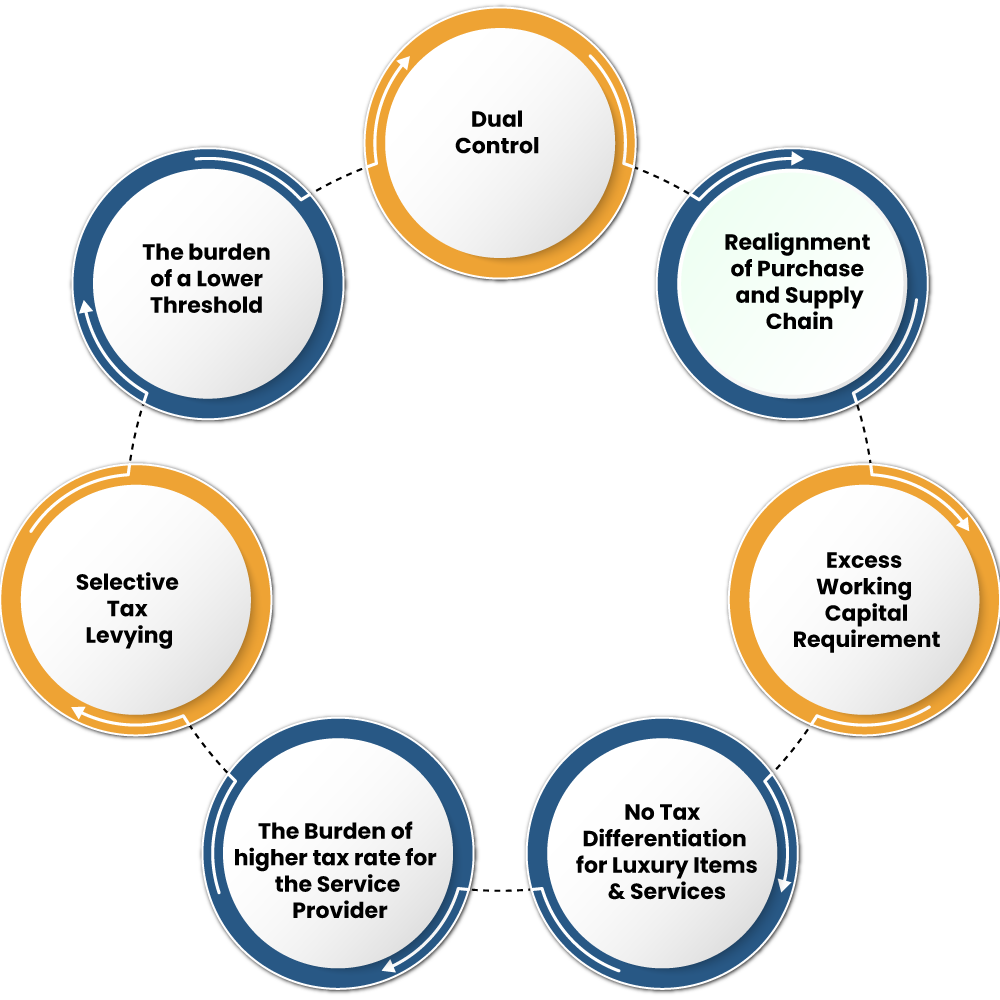

The Burden of a Lower Threshold
The GST bill proposes the reduction in threshold to be Rs. 9 lakh to increase the tax net, Rs. 4 Lakh for North-Eastern states. (However, GST council has increased threshold limit from 10 lakh to 20 lakh and from 4 lakh to 10 lakh for North-eastern states) Under this reform, any service provider or retailer subject to the tax levy. In the present central excise law threshold is Rs.1.5 crore. The reduction will significantly impact the MSME’s working capital.
For example, the manufacturer who trades today at Rs. 25 lakhs without any tax levy will be expected to pay GST post-implementation only. As threshold is low, most MSMEs are now exempted and have to pay a chunk of their capital towards tax in future.
Selective Tax Levying
GST cannot be applicable to Alcoholic liquor for human consumption and Petroleum-based businesses, which creates a further gap and does not support unified market ideology of GST.
The Burden of Higher Tax Rate for the Service Provider
The scenario in the service sector will impact as the concept of Centralised Registration and each unit in various states will have to take the separate registration. Therefore even if services are supplied by the company’s one Unit in State A to another Unit in State B, then also taxes are payable.
No tax Differentiation for Luxury Items & Services
The tax neutrality will not differentiate any luxury goods and normal good. The central and state government levy higher taxes on the luxury goods and services. Under GST implementation, all goods and services have to pay same tax, which will lead to rich becoming more richer and poor becoming poorer. This situation is not good for the MSMEs competing against large businesses.
Excess Working Capital Requirement
Taxation of stock transfer can primarily impact on working capital requirements. The quantum of impact varies depending on stock turnaround time at warehouse, credit cycle to a customer, quantum of stock transfer, etc. The higher amount of Capital Requirement will increases interest cost, which ultimately increases the price of Finished Goods.
Realignment of Purchase & Supply Chain
The GST credit will not be available to a compliant company if the vendor from whom MSME is purchasing goods does not show a same in his return. Hence, sourcing strategies will change on account of GST credit mechanism. Also, there will be reconsideration of Supply Chain on account of taxation of Stock Transfers.
Dual Control
In the GST Council Meeting, it was decided by the Ministry that those assesses having turnover of less than of 1.5 Crores will be assessed by State Government, and existing Service Tax assesses, irrespective of turnover. It will be assessed by the Central Government as there is lack of expertise with State Government in relation to Service Tax matters. As a result of this, small traders dealing in both goods and services will have dual administrative control both by Centre and State.
Conclusion
It was concluded that the impact of GST under MSMEs sector could go both positive and negative ways. For existing enterprises, GST simplified the tax structure, unified the market thus improved among all operational efficiencies of MSME, to this point the unorganised MSMEs were growing quicker than the organised ones as a result of the minimisation. With GST in effect, it has made the taxation system transparent, thus making the entities liable for tax payment.
Read our article:MSMEs under Gujarat Industrial Policy 2020 : Strengthening the Pillars for Atmanirbhar Gujarat