Today’s customers are Brand oriented and therefore using any illusory name can have an effect on the market for original the brand. When the brand name is used without any approval from the owner, they look for any legal remedy to protect its brand name. Prevention of non-permitted use of the trademark is evenly significant as Trademark Registration in India. To protect the brand name as well as the value created, the brand name along with the logo is registered under the Trademark Act. In this Blog we are going to discuss the Trademark Infringement in India as well as how to file for complaint against Trademark Infringement.
Trademark Infringement in India
Section 29 of Trademark Act talks about the Trademark infringement in India. In layman language, when an exclusive right of the owner of the Trademark is violated, it constitutes to be a Trademark Infringement. A trademark registration offers the exclusive rights to the brand name of the owner of the registered trademark, who can be the applicant of the Trademark. In case, any third party uses the brand name in course of business without prior permission of the owner, it known to be the violation of owner’s right.
Section 30 of the Trademark Act talks about certain situations that are not considered as Trademark infringement. If any person has the license from the owner of the registered Trademark then it is not covered under infringement as the license is allowed by assignment agreement. Still, if the licensee uses the trademark for the goods & services that is not covered under the assignment agreement then the use can be asserted as unauthorized use.
Indian Law on Trademark Infringement in India
Legal protection for a registered trademark is managed by the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks, a government agency that gives its report to the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) that comes under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Types of Trademark Infringement in India
One must know that are two types of Trademark infringement-
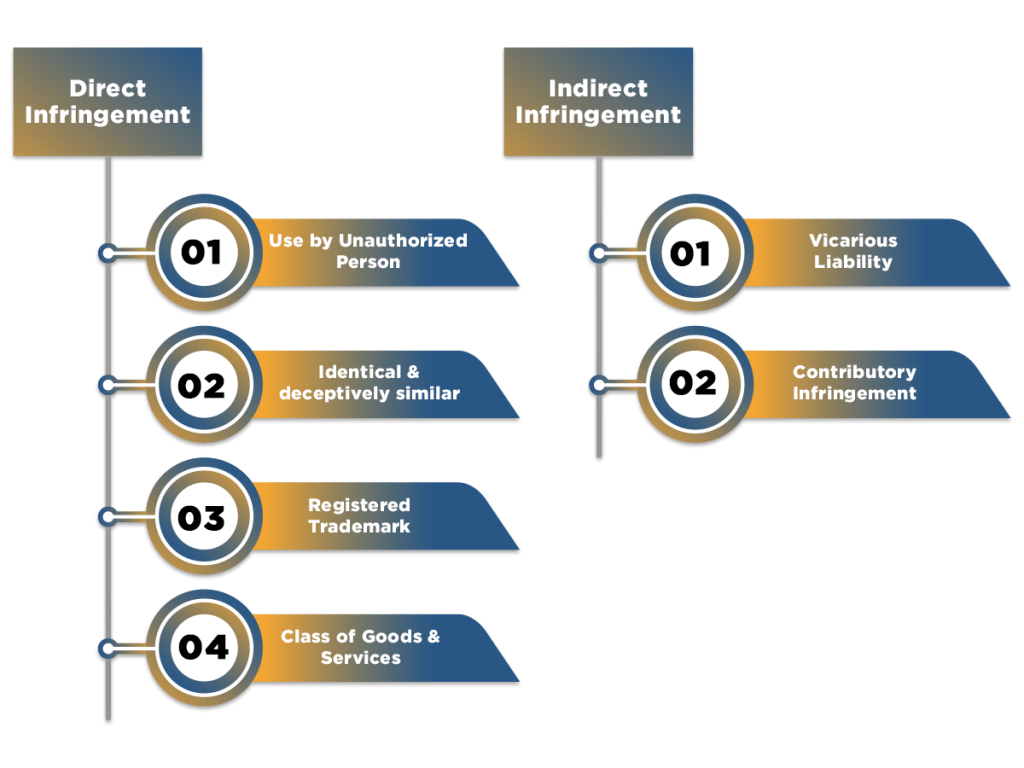

Direct Infringement
Direct infringement is defined by Section 29 of the Trademark Act. There a few basics
are to be met for a direct infringement of Trademark; those are as follows:-
Use by an Unauthorized Person
The violation of any trademark only occurs when the mark is used by a person who is not authorized or allowed by the owner of the registered trademark. If the mark is used with the permission of the owner of the registered trademark, it does not comprise to Trademark infringement.
Identical or Deceptively Similar
The trademark used by the unauthorized person needs to be either identical or deceptively similar to that of the registered trademark. The term ‘deceptively similar’ means that the common buyer may be confused between the marks and think them of being of the same brand. As long as there is a chance of misrepresentation of the trademark, it is sufficient for proving trademark infringement.
Registered trademark
The Trademark Act only provides protection to trademark that has been registered with the Trademark Registry of India. In the case of infringement of any unregistered mark, the common law of passing off can be used to settle the disputes. Passing off is a Law of Tort that can be used when the injury or damage is caused to the goodwill linked with the activities of any other person.
Class of Goods & Services
For Trademark infringement, the illegal use of the trademark has to be used for the dissemination of Goods & Services that falls under the same class of any registered trademark.
Indirect Infringement
Different from direct infringement, there is no proviso in the Trademark Act that deals with indirect infringement exclusively. This does not state that there is no legal responsibility for indirect infringement of trademark. There are two types of indirect infringement, they are as follows-
Vicarious liability
As per Section 114 of the Trademark Act[1], if any business owner commits any offence under this provision, then the entire company will be liable for Indirect Infringement. Those people who acted in good faith and without knowledge of the infringement they won’t be liable for Trademark infringement.
The essentials for vicarious liability are as follows-
- The person can control the activities of the principal infringer;
- The person knows about the infringement and also contributes to the infringement of trademark;
- The person obtains any financial gains from the infringement of trademark.
The exception to vicarious liability of any company for infringement of trademark is when the company acted in good faith and had no idea about the trademark infringement.
Contributory Infringement
There are three basic essentials to contributory infringement; those are as follows-
- The person knows about the infringement of trademark;
- The person considerably contributes to the direct infringement;
- The person provokes the principal infringer to commit infringement of trademark.
There is no exception in case of indirect infringement as there is no chance of the contributory infringer to act in good faith.
Penalties for Trademark Infringement
Trademark infringement in India is a cognizable offence that means that the infringer can face civil charges along with criminal charges. It is not mandatory as per Indian law that trademark should be registered for the institution of civil as well as criminal proceedings.
Cost of Legal Proceedings
In case of criminal proceeding, the court orders the following punishment-
- Imprisonment for a period not less than 6 months that may extend to 3 years;
- A fine that is not less than INR 50,000 that may extend to INR two lakh.
Remedies for Trademark Infringement in India
The Registered Trademark owner can initiate legal proceedings against the infringer declaring the unfair business practices that he carried on.
There are two types of remedies available to the trademark owner against any unauthorized use of trademark by any third party. The Trademark Act defends the trademark with criminal & civil remedies. Civil dealings can be initiated by the trademark owner before the District Court as per the jurisdiction.
Civil Remedies for Trademark Infringement
The civil remedies for Trademark infringement in India are as follows-


Injunction
Injunction can be referred as prohibition of one person from doing specific activity or task through the judicial proceedings. With respect to trademark infringement in India, it is preventing a person from unauthorized use of trademark. By a temporary or permanent stay order, the Court can grants protection to the trademark owner.
Damages
Damage refers to the recovery of any loss faced by the trademark owner by trademark infringement. The fiscal value of loss or brand injury is recovered under Damages. The amount of damages will be decided by the court after considering the actual and predictable loss of owner due to Trademark infringement.
Conclusion
In India, the knowledge to protect the brand name through trademark registration is increasing. Though, the owners are still inert about the unauthorized usage of their registered trademark. Violation of the right over trademark can happen internally in an organization that affects the brand name as well as the market share in the business of the owner. With the help of Corpbiz, one may recover and compensate all the damages occurred due to Trademark infringement in India.
Read our article: How to win a Trademark Infringement Case?











