The issue of raising funds for a company is the most challenging thing that the company faces during its initial stage. Though there are several options available to choose from such as personal investment, Angel investors, Venture Capitals, Bank loans etc, it is always a wise option to research on all the available options first. Issue of Debentures to the public is one of the methods by which companies raise the fund and in return the companies offer interest to the public which is termed as Debenture Interest. They are the medium to long-term debt instrument used by companies to borrow money at fixed rate of interest. Here in this article, we will see in detail the procedure for the issue of Debentures.
What are Debentures according the Companies Act?
According to the Companies Act 2013[1], Debentures are the debt instrument that indicates the debt, whether secured by the asset of the company or unsecured. They represent the debt of the company which contains the details such as Loan amount, maturity date, and rate of interest. Also, it can be transferred as per the Article of Association (AOA) of the Company.
Features of the Debentures
Some of the features are listed below:
- Debentures represent the debt of a company which makes debenture holders the creditors for the company.
- There is a certificate of debt called Debenture deed issued under the Company seal in which the date of redemption and amount of repayment is mentioned.
- They have fixed rate of interest which is payable either half yearly or yearly.
- Unlike shareholders, debenture holders do not get any voting rights because they are the creditors of the company.
- Debenture holders have advantage over the shareholders because interest is paid even if there is no profit.
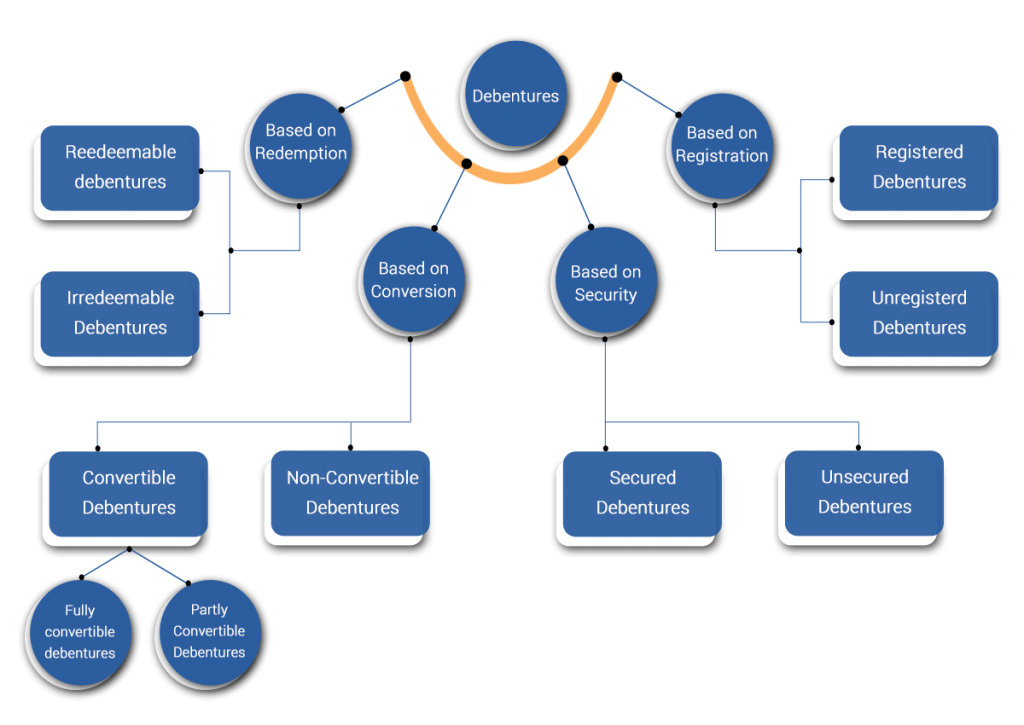
What are the types of Debentures?
Debentures in a company are classified based on different categories which totally rely on the agreement agreed between the corporation and debenture holders. These are mentioned below:
Based on Redemption
- Redeemable
Redeemable debentures carry a specific date of redemption which is mentioned in the Debenture Certificate. The company is liable to repay the principal amount to the debenture holders on the maturity date. They can be re-issued only if they have been canceled before.
- Irredeemable
Irredeemable Debentures do not have the date of redemption mentioned in the debenture certificate. These are redeemed either on the liquidation of the company or when the Company chooses to pay them off.
Based on Conversion
- Convertible
Here, the debenture holders can opt for either converting the debentures fully into equity or partially into equity. These terms and condition are mentioned in the agreement which is prepared according to the norms of company.
- Fully Convertible
These debentures are fully convertible into shares and these shares are subject to issuer’s notice on the ration of conversion determined by the company.
- Partially Convertible
Here the debentures holders have the option to convert their shares partially into shares, through which they will act both as Debenture holder and shareholder.
- Non-Convertible
These debentures are not convertible into the equity of the issuing company. Instead the Debenture holders are compensated with a higher rate of interest.
Based on Security
- Secured
Secured Debentures are secured by creating the charge on assets or property of the company. Here the debenture holders have the right to recover the principal amount in case the company fails or defaults in repaying the amount.
- Unsecured
These are the non-secured debentures in which there is no charge on the assets of the company.
Based on Registration
- Registered
In Registered Debentures, the name, address and other holding details are registered with the issuing company. This is done for the purpose in case the debenture is transferred to other shareholder, the interest and principal will be transferred to the previous holder. So to avoid this, the debentures are being registered.
- Unregistered (Bearer Debentures)
Unregistered Debentures are not recorded in the company’s record book and are easily transferable without any need for registration.

What are the Obligations a Company shall take while issuing Debentures?
The Company while issuing the Debentures to the Public gives an option to the public to convert them into shares, either wholly or partly at the time of redemption.
There are certain limitations which need to be followed. These are listed below:
- A company can issue Debentures to the Public with an option to convert such debentures into shares, either wholly or partly at the time of redemption which must be approved by conducting a general meeting.
- A Company cannot issue debentures carrying any voting rights.
- A Company may issue Secured Debentures according to the terms and conditions agreed during the agreement.
- According to the agreement, the company shall create a Debenture Redemption Reserve account from the profits of the company available for payment of dividend. Also, the amount credited to such account should be utilized only for the redemption of Debentures.
- The company cannot issue prospectus to the public or its members exceeding Rs 500 for the subscription of its debentures.
- The Certificate of Debentures must be issued within 6 months of allotment of debentures.
- The company is obliged to take the necessary steps to protect interest of debenture holders.
- As per the Debenture agreement, interest rate, payment mode of interest, redemption of debentures is fixed.
- In case, the company fails to redeem or pay the interest of the debentures on the date of maturity, the Tribunal shall pass the order directing the company to repay the amount of principal and interest.
- Any default in complying with the orders of the Tribunal, the officer involved is punishable with a imprisonment of maximum 3 years or a fine of 2 lac rupees which may extend to Rs 5 lac.
Read our article: Issue of Sweat Equity Shares
How do Companies issue Debentures to the Public?
There are certain procedures that need to be followed which are listed below:
- Call Board Meeting
A Board meeting is called to decide which kind of debenture is to be issued.
- The date, time and venue is fixed for the Extra-Ordinary general meeting.
- For the private placement, an offer letter is approved in form PAS-4.
- Approval of form PAS-5.
- Terms and Conditions approval for the appointment of debenture trustee and the agreement signed with it.
- Appoint an expert for approval of increase in borrowing powers.
- Authorization for creation of charge on the assets of the company.
- Requires approval of Debentures subscription agreement.
- Consent of a debenture trustee should be taken to be appointed.
- Within 60 days of allotment, Debenture trust deed shall be executed in form SH-12.
- Following documents need to be prepared after board meeting
- Debenture Subscription Agreement
- Offer letter for private placement in the PAS-4 and application forms.
- Record of the private placement officer in Form No.- PAS-5.
- Debenture trustee Agreement.
- Mortgage Agreement.
- A notice period of 21 days is issued for the EGM before the date of meeting and a special resolution is passed for issuing the secured debentures.
- Form PAS-4 and PAS-5 is submitted by attaching in form GNL-2 to ROC.
- A special resolution is filed by attaching the same in form MGT-14 with ROC.
- Form PAS-3 is filed for return of allotment to ROC (Registrar of Companies) after allotment.
- Form CHG-9 is filed for creating charge on the assets of the company.
Conditions for issuing of secured debentures
- Secured debentures can be issued by the company for a time period not beyond 10 years from the date of issue. In case the company is involved in arrangement of infrastructure projects then it can issue debentures for a time period beyond 10 years but not more than 30 years.
- By way of creation of a charge, the company has to secure the debentures on the company’s assets that are of the sufficient value for repayment of interest and principal.
- Before the issue of letter of offer or of prospectus, a debenture trustee shall be appointed for the subscription of debentures and a debenture trust deed is prepared to protect the interest and rights of debenture holders within a period of 60 days from the allotment date.
- The security for the debentures by way of mortgage or charge shall be formed in favour of the debenture trustee on-
- Any particular movable property of the company except being any kind of pledge or
- Any particular immovable property situated anywhere or any interest there.
Drawbacks of issuing Debentures
Issuance of Debentures has its other cons apart from the advantages. These are listed below:
- The company needs to pay interest to its debenture holders even if there is a loss to the company.
- Issuance of these types of debt instruments leads to the loss of credit in the stock market by creating several charges on the assets of the company.
- The Company can liquidate if the company fails to pay the interest on time.
Conclusion
Borrowing money from the bank is the last resort of funding that companies prefer for raising funds. But there are certain drawbacks of taking loan from the banks as they charge higher interest rate. General public by investing in the Debentures of the company get a good return in comparison to the government deposit schemes or Bank deposits. These advantages compel the companies to issue debentures while the public also shows interest in buying.
Read our article:Operating Nidhi Company; Know about the Restrictions on Nidhi Company











