The motive behind an introduction of the RERA Act, 2016, was to ensure greater transparency, speedy dispute redressal, and ensure capital into the real estate sector. Therefore, RERA Authority playing a role in this matter, is given some responsibilities to fulfill the ultimate objective. Every State Government must, within one year from the date of coming in force of the Act. The Authority must be Body Corporate having a name as aforesaid, having perpetual succession and a common seal with power subject to provisions of the Act.
Functions of the RERA Authority
Section 34 of the RERA Act, 2016 defines functions of a RERA Authority which it needs to follow:
- Firstly an authority must obtain RERA registeration for a project and for real estate agents with it. Consequently, it must also regulate the registered projects with it.
- For public viewing, the Authority has to publish and maintain a website of records of all real estate projects with relevant details which required to be furnished.
- For public viewing, an authority must maintain a database on its website with names and photographs of the promoters as defaulters, including all details of a project or any imposed penalty.
- For public viewing, an authority must maintain a database on its website with the names and photographs of the real estate agents who have applied and registered under the Act.
- The fixation of a standard fee to be paid by a promoter, agent, or allottee through regulations according to the jurisdiction.
- It must ensure that an obligation of the promoters, agents, or allottees is duly complied with according to the RERA Act.
- The Authority must look that the orders, directions, or regulations issued by it are duly complied too by relevant parties.
- It must ensure that all other functions given to it by an appropriate Government to carry out necessary provisions of this Act are duly performed by it.
Read our article:Guide on RERA Registration for Real Estate Agents
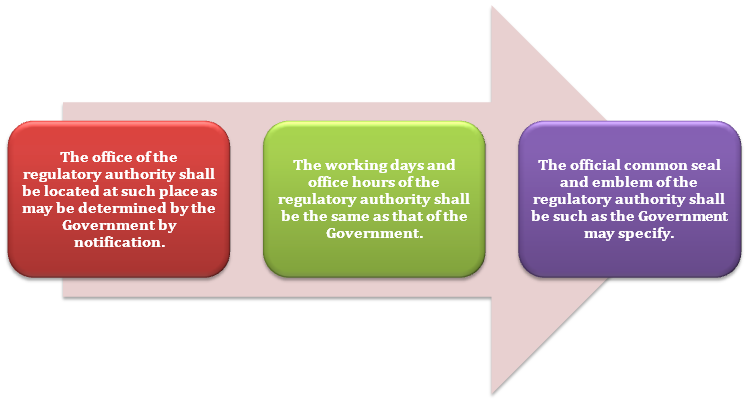
The functioning of the Authority

Powers of the Authority
- In addition to powers specified in sub-section (2) of section 35, the Regulatory Authority must have the following additional powers:
- to require the promoter, allottee or a real estate agent to furnish in writing such information or explanation or to produce such documents within such reasonable time, as deemed necessary;
- to requisition, subject to the provisions of section 123 and section 124 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 (Central Act of 1872), any public record or document or copy of such record or document from any office.
- The regulatory Authority can call upon such experts or consultants from the fields of an urban planning, urban land administration, disaster management, accountancy, fire services, construction, architecture, structural engineering or engineering or from any other discipline as it may be necessary, to assist the regulatory authority in the conduct of any inquiry or proceedings before this.
- On the receipt of an application in the prescribed form and complete in all respects under section 4, read with rule 3 to register a project. The Authority can review the documents submitted along with the application under the rule 3 and enquire, inter-alia, into the following matters and other matters, as may be necessary, before the grant of registration within a time prescribed under sub-section (1) of section 5, namely:-
- The nature of rights and interest of a promoter to the land which is proposed to be developed;
- extent and location of the area of the land proposed to be developed;
- layout plan of a project;
- The technical, financial, & managerial capacity of a promoter to develop a project
- Plan regarding development works to be executed in a project
- Conformity of development of the project with neighboring areas.
- The Authority may in the interest of the allottees, enquire into the payment of amounts imposed as a penalty, interest or compensation, paid or payable by a promoter, to ensure that the promoter has not:
- withdrawn the amounts from the account maintained as provided under sub-clause (D) of clause (l) of sub-section (2) of section 4; or
- Used any amounts paid to the promoter by the allottees for a real estate project for which a penalty, interest or compensation is payable, or any other real estate project;
- Recover the amounts paid as a penalty, fine, or compensation from the allottees of a real estate project or any other project.
Conclusion
The applicant can be either appear in person or authorize one or more practicing CA or Advocate or any of his officers to present a case before an Adjudicating Officer. No civil court must have jurisdiction to entertain any suit or proceedings in respect of any of the matter over which an Adjudicating officer, RERA Authority[1], or RERA Appellate Tribunal is empowered by under the Act to decide the matter.
No injunction or stay must be granted by any court or any other authority in the pursuance of the power conferred by under the Act. CorpBiz shall be at your disposal if you require any assistance on this behalf. We shall be happy to help you.
Read our article:All You Need To Know About RERA Registration Process