Dyes are organic compounds that are used to impart colour to substrates such as cloth, paper, leather, and plastics in a permanent manner. They are applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve their fastness on the fibre. On the other hand, pigments are insoluble and are essential inputs to products such as paints. Dye intermediates are the raw materials used in the manufacturing of dyestuff. The production of dyes involves several stages, starting with petroleum-based products such as naphtha and natural gas, which produce benzene and toluene. Nitro-aromatics are manufactured from benzene and toluene, which are further used to make dye intermediates. The State Environmental Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MOEF)[1] govern the EC process for dyes & dye intermediates in India.
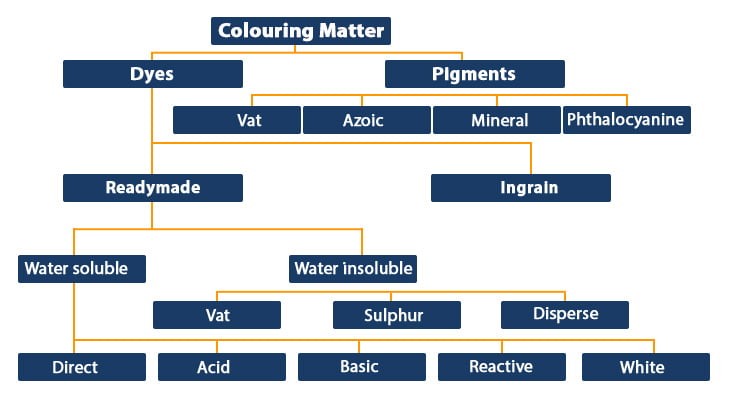

Diagrammatic representation of types of Dyes & Dye Intermediates
EC Process for Dyes & Dye Intermediates Manufacturing Industry
Environmental compliance is a critical aspect of the dyes and dye intermediates industry. In India, the environmental compliance process for dyes and dye intermediates is governed by the State Environmental Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MOEF).
The SEIAA evaluates and approves new projects related to the state’s dyes and dye intermediates industry. The SEIAA evaluates the project’s potential environmental impact and determines whether it meets the environmental standards and regulations. The MOEF is responsible for formulating and enforcing environmental regulations and policies related to the dyes and dye intermediates industry at the national level. The MOEF ensures that the EC process for dyes & dye intermediate includes all applicable environmental standards and regulations prescribed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
The process for obtaining environmental clearance (EC) for dyes and dye intermediates projects typically involves the following steps:
Submission of Application: The first step is to apply EC to the SEIAA. The application must include a detailed project report (DPR) that outlines the project’s scope, potential environmental impact, and mitigation measures.
Screening and Scoping: The SEIAA review the DPR and conducts a preliminary screening to determine the scope and extent of the environmental impact assessment (EIA). The SEIAA may also conduct public consultations and stakeholder meetings to gather feedback on the project.
Conducting the EIA: The EIA is a comprehensive study that evaluates the project’s potential environmental impact. The EIA includes a baseline study, impact assessment, and mitigation plan.
Submission of EIA Report: Once the EIA report is complete, it is submitted to the SEIAA for review and approval.
Public Hearing: The SEIAA conducts a public hearing to gather feedback on the EIA report from local stakeholders, experts, and the general public.
Granting of EC: Based on the EIA report and public hearing findings, the SEIAA grants or rejects the EC for the project.
Monitoring and Compliance: Once the project is operational, the SEIAA and MOEF monitor the project’s compliance with environmental standards and regulations. The project must also submit regular reports on its environmental performance to the SEIAA and MOEF.
Factors Affecting the EC Process for Dyes & Dye Intermediates
The EC process for dyes & dye intermediate is affected by factors which are as follows:
- Poor Economies of Scale: Many small and medium-sized firms operate in India’s Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector, resulting in a need for economies of scale. As a result, the cost of production is high, making it difficult for the industry to compete globally.
- Issues Related To Environmental Pollution: The Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector is one of the significant contributors to environmental pollution. The industry is under constant scrutiny from environmental authorities and must adhere to strict pollution control norms. Compliance with these norms increases the cost of production and reduces profitability.
- Ban on Certain Dyes in the Export Market: Certain dyes have been banned in some countries due to their harmful effects on human health and the environment. Such bans reduce the need for Indian manufacturers and lead to a decline in demand for specific products.
- Prices of Raw Materials: The costs of raw materials used in producing dyes and dye intermediates, such as benzene and toluene, fluctuate frequently. The volatility in raw material prices makes it difficult for manufacturers to plan and maintain stable product pricing.
- Competition from Other Developing Countries: India faces stiff competition from other developing countries like China, Taiwan, and Korea, which have lower labour and production costs. Indian manufacturers struggle to compete with their foreign counterparts, which affects their profitability.
- Low Expenditure on Research and Development: Research and development are crucial for the growth of any industry. However, the Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector in India spends very little on research and development, which results in a lack of innovation and new product development.
Sustainable Strategies in EC Process for Dyes & Dye Intermediates Manufacturing
Cleaner Production is an approach that aims to reduce the environmental impact of industrial processes while improving the efficiency and productivity of the industry. The benefits of Cleaner Production in the Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector are numerous and include the following:
- Conservation of Raw Material and Energy: Cleaner Production helps to reduce the consumption of raw materials and energy by optimising production processes, reducing waste, and increasing resource efficiency. This leads to cost savings and sustainability in the long run.
- Lower Costs: Cleaner Production practices can reduce production costs through the efficient use of resources, such as water, energy, and chemicals. This helps improve the industry’s competitiveness and reduces the financial burden on businesses.
- Improved Environment: Cleaner Production practices help reduce the industry’s environmental impact by reducing waste, emissions, and pollution. This results in a cleaner and healthier environment for workers and the community.
- Better Compliance with Environmental Regulations: Cleaner Production helps businesses to comply with environmental laws and avoid penalties for non-compliance. This helps to improve the reputation and image of the industry.
- Enhanced Working Environment: Cleaner Production practices help to improve the working environment by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals, dust, and noise. This leads to better health and safety for workers and enhanced productivity and conducts a successful EC process for dyes & dye intermediates.
- Improved Quality: Cleaner Production practices can improve the quality of products by reducing defects and improving consistency. This helps to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Efficiency: Cleaner Production practices help to optimise production processes and reduce waste, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Market Requirements: Consumers increasingly demand environmentally friendly products, and Cleaner Production helps meet these market requirements and enhance the industry’s competitiveness.
- Public Image: Cleaner Production practices help improve the industry’s public image by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. This helps the industry build trust and confidence among its stakeholders.
Cleaner Production Assessment (CPA) Approach in EC Process for Dyes & Dye Intermediates
The Cleaner Production Assessment (CPA) approach is a systematic method used to identify and evaluate pollution prevention and resource conservation opportunities in industrial processes. The CPA approach involves identifying the sources of waste and inefficiencies, evaluating the potential for improvement, and implementing cost-effective solutions to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimise environmental impacts. The CPA approach can be applied in the Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector to identify opportunities for improving production processes and reducing the industry’s environmental impact. The CPA approach in the Dyes and Dyes Intermediates sector involves the following steps:
- Identification of Inputs and Outputs: The first step in the CPA approach is to identify the inputs and outputs of the production process. This includes the raw materials, energy, and water used in the process and the waste generated and the emissions released.
- Analysis of The Process: The next step is to analyse the production process to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. This includes evaluating the use of raw materials, energy consumption, and waste generation.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: The third step is to evaluate alternatives to the current production process. This includes evaluating new technologies, process modifications, and changes in raw materials and inputs to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Implementation of Solutions: The fourth step is implementing cost-effective solutions to reduce waste and improve efficiency. This includes process modifications, equipment upgrades, and changes in operational procedures.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: The final step is to monitor and evaluate the results of implementing the solutions. This includes tracking the reduction in waste and emissions, evaluating the impact on production costs, and assessing the environmental benefits.
Conclusion
The EC process for the dyes & dye intermediates industry in India is a critical aspect that ensures the dye industry operates in an environmentally sustainable manner. Environmental clearance involves a detailed project report, screening and scoping, environmental impact assessment, public hearing, and monitoring and compliance. Compliance with environmental regulations and policies benefits the environment and enhances the industry’s reputation and competitiveness in the global market. Therefore, the dyes and dye intermediate industry needs to prioritise environmental compliance to ensure a sustainable future. The assistance of certified EIA experts can help identify the need for EIA and the extent of study required and make the process streamlined.
Also Read:
Hazardous Waste Management Authorization Norms: An Overview











