Double insurance refers to insurance where the same subject matter is insured twice or more than that. In such scenarios, the same subject is insured but with different insurance companies. The concept of Double insurance is not illegal at all. Double insurance come to light when a business avail insurance w.r.t the same risk and subject matter from two different insurers. This write-up will explore different instances where double insurance may occur and the real-life implications for businesses
Key takeaway
- Double insurance isn’t a critical problem; however, it can lead to insurance companies arguing about whether they have payout at all, causing an unexpected delay in the claim processing.
- Double insurance should not be perceived from a coverage layering viewpoint. Layering is where insurance policies are placed with distinct insurance companies to safeguard different exposure levels. The first losses are addressed by one insurance company to the prescribed limit; above that limit, another insurance company will pay out up to the limit cited in that policy & so on.
- The first layer is generally known as primary; meanwhile, another layer is being referred to as excess. In such circumstances, there is no duplication or overlap of insurance as the excess insurer does not have to dispense the cover until the limit on the underlying policy is paid completely by the primary insurer.
General principles of Double Insurance
- The first point on concurrent insurance is that, in principle, a business entity should not be left without an insurance payment. Where there is a presence of double insurance, & a business[1] entity intends to claim w.r.t a loss covered by more than one policy, it will be entitled to claim whichever insurance policy it prefers.
- The insurance company that does not dispense cover w.r.t the double insured risk can approach other insurers for the contribution which has rendered similar cover.
- Therefore, if a business does claim under one insurance policy & not the other, the insurance company that has not paid out probably has to pay a share to the insurer who has paid out.
Read our article:Factors that Influence Corporate Governance in India
So why this trigger issues for insureds?
First, various insurance policies entail clauses that deter an insured from claiming under the insurance policy if another policy covers the identical loss. If one insurance policy entails this term, there are no issues because the insured can claim on another policy (The right of contribution will cease to exist between insurers as there is no double insurance).
If either of the policies entails such a clause, then there is no issue for the insured, as the clauses cancel each other & the insured can claim in both insurance policies for its loss (with the paying insurance policy claiming a contribution right from another insurance company).
The issue is that the term of these ‘other insurance’ clauses is not standard & this can leads to disagreement between insurers as to which insurance policy should respond, leaving the business waiting for a claim.
When examining double insurance, it is critical to look at the interest being safeguarded and the property and the risk being insured against.
Clauses pertaining to Double Insurance
The legality of double insurance revolves around the following clauses:
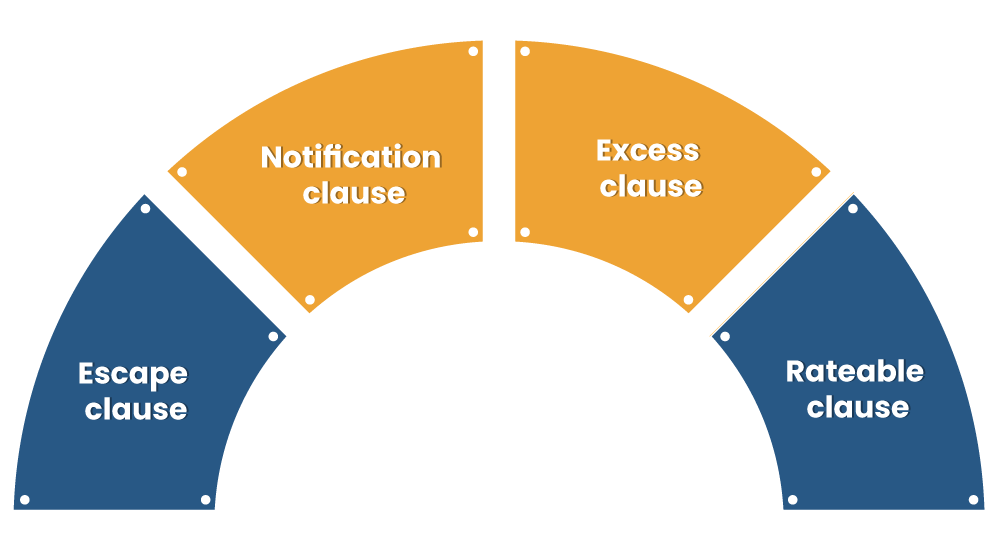

Escape clause: The escape clause allows the insurers to reject any claim request if they found that the insured is levering another policy that renders the same benefits.
Notification clause: The notification clause mandates the insurer to make prior intimation to the insurer regarding the existence of the alternative policy, failing to which policy will be cancelled.
Excess clause: Excess clause talks about the disbursement of the actual claim amount that comes out after subtracting the claim sum that already has been availed by the insured from another insurer.
Rateable clause: This clause prevents insurers from dispensing the entire claim amount to the insured in the case of Double insurance.
Double insurance = Indemnity + insurance?
It is important for the company to be cautious when contractual indemnities are given w.r.t the risk that the insurance company may also encompass.
In some scenarios, it is aimed that the indemnity is called on first with the insured then claiming on insurance. For instance, with directors & officers liability insurance, the entity is often needed to indemnify the directors & then seek reimbursement under the insurance policy.
But, in other scenarios, the indemnity may be aimed to be an alternative to the insurance. In these scenarios, make sure that the indemnity is not caught by ‘other insurance’ norms or that indemnity arrangement don’t render insurers with scope to argue that there ought to be a contribution right by the insurer against the indemnifier.
Difference between Reinsurance and Double insurance
| Basis of Difference | Double Insurance | Reinsurance |
| Meaning | In double insurance, the identical risk is protected with distinctive insurers or more than one insurance company | In the reinsurance, the risk is transferred to another insurer. The risk remains the identical. |
| Subject | This insurance is predominately secured for properties having a high worth. | This insurance encompasses the risk of the original insurance company. |
| Claim | You can make a claim to all insurers for compensation | In this insurance, claim is sought from the original insurer & it will claim from the reinsurer |
| Loss | The loss shall be shared by all the insurers | The reinsurer shall only be entitled to pay the proportion of the insurance. |
| Goal | The primary goal of double insurance is to render the benefit of insurance. | The primary goal of this insurance is to minimise insurer’s risk. |
| Interest of Insured | The insured possess an insurable interest in such kind of plan. | The insured lacks insurable interest in such kind of plan. |
| Insured Approval | The insured authentication is required in double insurance. | The insured’s approval is not required in Reinsurance since it is done from the end of the insurer. |
Bottom-line
From a practical viewpoint, if an insured have double insurance, it may be inviting some complications for its insurance. There can also be delays prior to the disbursement of the claim if there are arguments between the insurance companies as to which policy should respond. Apart from interest, the insured shall be compensated for any losses it encountered as a result of such delay. In most scenarios, businesses may not seek overlapping policies. This is so that the insurance coverage is clear and any claims made under the insurance policy can be settles as promptly as possible.
Read our article:Insurance Ombudsman: Resolve Insurance-Related Disputes with Ease











