The government imposes taxes on both individuals and companies, which are a major source of income for the government. The amount collected from taxes helps the government to build an economy that helps the government meeting numerous public expenses. Taxation can be defined as pecuniary burden that is imposed on individuals and corporations to support government. Being a citizen of a country, it is the prime responsibility of the citizen to pay taxes to the government.
What are legal provisions w.r.t taxation in India?
The taxation structure in India is based on three (3) tier systems as it is to be regularized and imposed by the Central authority, the State Governments and the local authorities such as municipalities, councils, and panchayats. As per provisions of the Constitution of India, the right to levy taxes on individuals and corporations is given to the government of India through various statutory authorities. The right to impose tax by central and the state government has been defined under Article 246 read with Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution of India. As per that, No person other than center, state, and local authorities has the right to impose such taxes on any person or company. Further such imposition is to be backed by law as passed by a parliament or state legislatures. Schedule seventh (VII) have divided various subject matters in 3 lists such as:
List – I – under which only central government has authority to make and imposes taxes called as central list;
List – II – under which only state government has authority to make and imposes taxes called as state list;
List – III – under which both central government and the state government has authority to make and imposes taxes called as concurrent list
Types of taxation in India:
In order to fulfill this obligation, it is important to know different types of taxation in India. These taxes can be classified into two categories:

Direct taxation:
Direct tax is such tax that a citizen directly pays to the government or the authority that is imposing the tax. For instance, as in India, Income tax authority imposes a tax, so citizen shall pay the tax directly to the income tax authority. This tax cannot be transferred to some other entity or authority. Direct tax in India is regularized by several provisions of laws and authorities responsible for its administration. Such authority in India is the Department of Revenue through CBDT (Central Board of Direct Taxes), which looks after the administration and management of direct taxation. This department is also authorized with the power of planning and further to provide inputs to government authority in this respect.
Read our article:An Overall Assessment of Income Tax Notice
Various categories of Direct Taxation in India:
Some of the major types of direct taxation in India are as mentioned below:
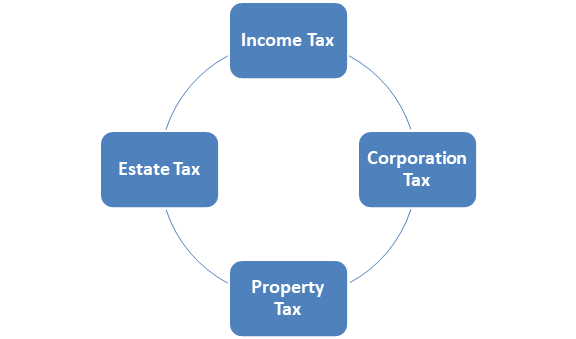

- Income tax:
This is one of the most common kinds of direct tax imposed in India. This tax is directly levied on income earned by an individual during a financial year as per income slabs provided by the income tax department. Provisions related to income tax are mentioned and regulated as per the provisions of the Income Tax Act of 1961. As per the said provisions, tax is to be imposed on earning or income of any individual or any undivided Hindu family or any trust or co-operative society, etc. This income is to be calculated on the basis of the residential status of a person for which points have to determine while calculating the same. All residents of India are liable to pay such tax for income generated in India as well as abroad. Whereas non-residents are taxable only for income generated or received in India only and not outside India.
- Corporation tax:
As per the provisions of the Income Tax Act of 1961, every India Company and any business organization are taxable in India for their transactions all over the world. Any company or corporation is deemed to be a resident of India if it was incorporated and registered in India, and its overall management and control are based in India only. For any non-resident companies, only such income is levied in India under this category if the business transaction was done in India.
- Property tax:
Property tax is imposed on owners of any residential land, building, etc. These taxes are delegated by local authorities after the proper valuation of the area.
- Estate tax:
This tax arises on the estate or total property of the person left behind after its death.
Indirect Taxation:
Some of the major types of indirect taxation in India are as mentioned below:
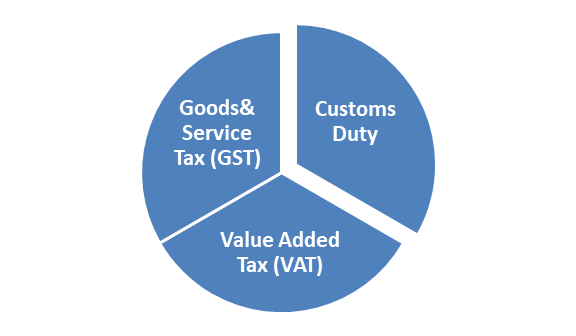

- Goods and Service Tax (GST):
The goods and services tax (GST) is one of the categories of the indirect tax which has connected or subsumes around 17 various types of indirect taxes as existed before, such as service tax, state AVT, central tax, and many others. This is a value-added tax (VAT) as levied on various goods and services as sold in India for its domestic consumption. This tax is indirect tax, which is endured by consumers only, but that is to be paid by sellers to the government. This is a major source of income for the government, which indirectly makes a burden on consumers only.
- Customs duty:
Custom duty is indirect tax to be levied on all goods that are imported and exported in and outside India. A tax that is levied while importing goods is called Import duty, and the other is Export duty. This type of indirect tax is regulated as per the provisions of the Customs Act of 1962[1], according to which government shall levy duty on both export and import. Any matters related to this are administered and regulated under the Department of Revenue of the Ministry of Finance by the CBEC (Central Board of Excise and Customs).
- Value Added Tax (VAT):
A VAT is another category of indirect taxation in India, which is particularly a consumption tax that is imposed on any products when its value is increased during the supply chain from the time of production till its sale. After the introduction of GST, VAT has been excluded from many items, but on certain items such as alcohol, it is still applicable.
Difference between Direct taxation and Indirect taxation:
| Direct Tax | Indirect Tax | |
| 1 | It is imposed on income and profits | It is imposed on all goods and services |
| 2 | It is to be paid by Individuals and businesses organizations | It is to be paid by End-consumers |
| 3. | Amount of taxation depends on income and profits generated by individual | Tax imposed is to be same for all category of people |
| 4. | This tax is of non-transferable nature | This tax is of transferable nature |
| 5. | Some individual do tax evasion by wrongly disclosing their incomes | Tax evasion is not possible |
| 6. | It is progressive in nature. | It is regressive in nature |
| 7. | Collection is of Complex nature. | Collection is not of very complex form and can be easily collected |
| 8. | Some examples are Income tax and securities transaction tax (SAT) | Some examples are GST, VAT and excise duty |
Conclusion:
While taxes generally impose a heavy burden on individuals and businesses, but play an abundant role in building the economy. Taxes are the main source of income for government that helps to build a nation, healthcare, infrastructure, defense, welfare initiatives, etc. So it is the responsibility of every citizen of India to pay taxation. But still many people are evading taxes, but the government is taking proper initiatives to avoid tax evasion.
Read our article:Income Tax Return Filing without Form 16